Chemistry:N-Methyliminodiacetic acid
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
N-(Carboxymethyl)-N-methyl-glycine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H9NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 147.130 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 223–225 °C (433–437 °F; 496–498 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P332+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P337+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
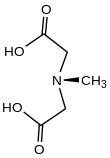
N-Methyliminodiacetic acid is an organic compound with the formula CH
3N(CH
2CO
2H)
2. It is a white solid, which as its conjugate base CH
3N(CH
2CO−
2)
2 is used as a chelating agent for iron.[2] It is a component of organoboron reagents as well.[3]
Synthesis and reaction
It is prepared from imidodiacetic acid by N-methylation using the Eschweiler–Clarke reaction:[4]
MIDA boronates are derivatives with the formula CH
3N(CH
2CO
2)
2BR, where R is a cross-coupling partner.[5]
Related compounds
- Imidodiacetic acid (IDA)
- N-(2-Carboxyethyl)iminodiacetic acid
- Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA)
- N-Hydroxyiminodiacetic acid (HIDA), HON(CH
2CO
2H)
2 (registry number = 87339–38–6).[6] See HIDA scan.
References
- ↑ "N-Methyliminodiacetic acid" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/20441#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Lovley, D. R.; Woodward, J. C.; Chapelle, F. H. (1996). "Rapid Anaerobic Benzene Oxidation with a Variety of Chelated Fe(III) Forms". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 62 (1): 288–291. doi:10.1128/aem.62.1.288-291.1996. PMID 16535218. Bibcode: 1996ApEnM..62..288L.
- ↑ Dailey, Ian; Burke, Martin D. (2010). "N -(Carboxymethyl)- N -methyl-glycine". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01228.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ↑ Ballmer, Steven G.; Gillis, Eric P.; Burke, Martin D. (2009). "B-Protected Haloboronic Acids for Iterative Cross-Coupling". Organic Syntheses 86: 344. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.086.0344.
- ↑ "MIDA Boronates". https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/technical-documents/technical-article/chemistry-and-synthesis/cross-coupling/mida-boronates.
- ↑ Hubregtse, Ton; Hanefeld, Ulf; Arends, Isabel W. C. E. (2007). "Stabilizing Factors for Vanadium(IV) in Amavadin". European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2007 (15): 2413–2422. doi:10.1002/ejoc.200601053.
 |

