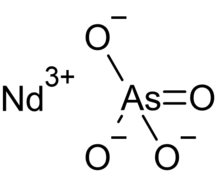
Chemistry:Neodymium arsenate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Neodymium(III) arsenate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NdAsO4 | |
| Molar mass | 313.89 |
| Appearance | faint pink powder |
| Density | 5.3-5.9 g/cm3[1] |
| insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H350, H300, H314, H410 | |
| P201, P264, P273, P280, P305+351+338, P310 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Neodymium(III) nitrate Neodymium(III) phosphate Neodymium(III) antimonate Neodymium(III) bismuthate Neodymium(III) carbonate |
Other cations
|
PrAsO4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Neodymium arsenate, also known as neodymium(III) arsenate, is the arsenate of neodymium with the chemical formula of NdAsO4. In this compound, neodymium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It has good thermal stability, and its pKsp,c is 21.86±0.11.[2]
Preparation
Neodymium arsenate can be obtained from the reaction between sodium arsenate (Na3AsO4) and neodymium chloride (NdCl3) in solution:[3]
- Na3AsO4 + NdCl3 → 3 NaCl + NdAsO4↓
See also
References
- ↑ See https://www.americanelements.com/neodymium-arsenate-15479-84-2
- ↑ Firsching, F. Henry. Solubility products of the trivalent rare-earth arsenates. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 1992. 37 (4): 497-499. DOI:10.1021/je00008a028
- ↑ Gabisoniya, Ts. D.; Nanobashvili, E. M.. Synthesis of rare earth metal arsenates. Soobshcheniya Akademii Nauk Gruzinskoi SSR (1980), 97(2), 345-8. ISSN 0002-3167
 |

