Chemistry:Persin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
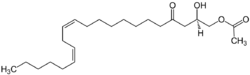
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2R,12Z,15Z)-2-Hydroxy-4-oxohenicosa-12,15-dien-1-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H40O4 | |
| Molar mass | 380.569 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Persin is a fungicidal toxin present in the avocado.[1] Persin is an oil-soluble compound structurally similar to a fatty acid, a colourless oil, and it leaches into the body of the fruit from the seeds.
The relatively low concentrations of persin in the ripe pulp of the avocado fruit is generally considered harmless to humans. Negative effects in humans are primarily in allergic individuals. When persin is consumed by domestic animals through the leaves or bark of the avocado tree, or skins and seeds of the avocado fruit, it is toxic and dangerous.[2][3]
Presence in the avocado plant
All parts of the avocado — the fruit, leaves, stems, and seeds — contain the toxin. The leaves are the most dangerous part.[4]
| Leaves | 0.9 to 1%[5] |
| Fruit | ~0.08% to 0.15%[6][citation needed] |
Toxicity
Consumption of the leaves and bark of the avocado tree, or the skin and pit of the avocado fruit have been shown to have the following effects:[2][7]
- In birds, which are particularly sensitive to the avocado toxin, the symptoms are: increased heart rate, myocardial tissue damage, subcutaneous edema of the neck and pectoral regions, labored breathing, disordered plumage, unrest, weakness, apathy and anorexia. High doses cause acute respiratory syndrome (asphyxia), with death approximately 12 to 48 hours after consumption.[7] Caged birds seem to be more sensitive to the effects of persin, whereas, for example, turkeys and chickens seem more resistant.[7]
- Lactating rabbits and mice: non-infectious mastitis and agalactia after consumption of leaves or bark.
- Rabbits: cardiac arrhythmia, submandibular edema and death after consumption of leaves.
- Cows and goats: mastitis, decreased milk production after consumption of leaves or bark. Goats develop severe mastitis after ingesting 20 g/kg of leaves, and 30 g/kg of leaves usually results in cardiac injury.[7]
- Horses: clinical effects occur mainly in mares, and includes noninfectious mastitis, as well as occasional gastritis and colic. Swelling of the head, tongue, and brisket may also be present.[7]
- Cats, dogs: mild stomach upset may occur, with potential to cause heart damage.[2] Dogs might be more resistant.[7]
- Hares, pigs, rats, sheep, ostriches, chickens, turkeys and fish: symptoms of intoxication similar to those described above. The lethal dose is not known; the effect is different depending upon the animal species.[8]
- Mice: non-fatal injury to the lactating mammary gland from 60 to 100 mg/kg of persin. Necrosis of myocardial fibres with 100 mg/kg of persin. 200 mg/kg of persin is lethal.[1]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of avocado toxicosis relies on history of exposure and clinical signs. There are no readily available specific tests that confirm diagnosis.[9]
Treatment
NSAIDs, pain relievers, medications for congestive heart failure.[7]
Additional pharmacology
Animal studies show that exposure to persin leads to apoptosis in certain types of breast cancer cells.[10] It has also been shown to enhance the cytotoxic effect of tamoxifen in vitro.[11] Persin is however highly insoluble in aqueous solutions and more research will be needed to put it into a soluble tablet form.[11]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Isolation and identification of a compound from avocado (Persea americana) leaves which causes necrosis of the acinar epithelium of the lactating mammary gland and the myocardium". Nat. Toxins 3 (5): 344–9. 1995. doi:10.1002/nt.2620030504. PMID 8581318. "non-fatal injury to the lactating mammary gland of the mouse is from 60 to 100 mg/kg. At doses of person above 100 mg/kg, necrosis of myocardial fibres may occur and areas of myocardial fibrosis can be observed in animals surviving for seven days. Hydrothorax and/or pulmonary oedema may be present in more severely affected animals. [..] there have been few attempts to investigate the cause of possible toxic effects of the plant in mammals.".
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 ASPCA Poison Control: Avocado on aspca.org
- ↑ Morton, Julia F.. "NewCROP - Avocado Persea americana". Purdue University. https://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/morton/avocado_ars.html.
- ↑ "Food Hazards - Special Pet Topics" (in en). https://www.msdvetmanual.com/special-pet-topics/poisoning/food-hazards.
- ↑ Oelrichs, Peter B.; Ng, Jack C.; Seawright, Alan A.; Ward, Annemarie; Schäffeler, Lothar; Macleod, John K. (September 1995). "Isolation and identification of a compound from avocado ( Persea americana ) leaves which causes necrosis of the acinar epithelium of the lactating mammary gland and the myocardium" (in en). Natural Toxins 3 (5): 344–349. doi:10.1002/nt.2620030504. ISSN 1056-9014. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/nt.2620030504.
- ↑ from calculation based on amount of phenolic content related to persin numbers from values found online multiple from sources
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 "Avocado Toxicosis in Animals - Toxicology" (in en). https://www.msdvetmanual.com/toxicology/food-hazards/avocado-toxicosis-in-animals.
- ↑ Clipsham, R. "Avocado Toxicity". http://kgkat.tripod.com/avocado.html.
- ↑ "Avocado Toxicosis in Animals - Toxicology". https://www.merckvetmanual.com/toxicology/food-hazards/avocado-toxicosis-in-animals.
- ↑ "A novel plant toxin, persin, with in vivo activity in the mammary gland, induces Bim-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells". Mol Cancer Ther 5 (9): 2300–9. 2006. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0170. PMID 16985064. http://mct.aacrjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/5/9/2300.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Synergistic cytotoxicity between tamoxifen and the plant toxin persin in human breast cancer cells is dependent on Bim expression and mediated by modulation of ceramide metabolism". Mol. Cancer Ther. 6 (10): 2777–85. October 2007. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0374. PMID 17913853. http://mct.aacrjournals.org/content/6/10/2777.full.
 |
