Chemistry:Pingyangmycin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bleomycin A5 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intravenous, intra-arterial, intramuscular, intratumoral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | amidase |
| Elimination half-life | 1.3 hours |
| Excretion | renal (25-50%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
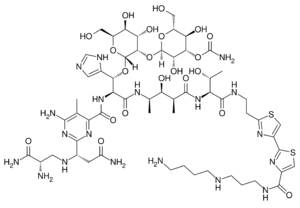
| Formula | C57H89N19O21S2 |
| Molar mass | 1440.56126 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Pingyangmycin (also known as bleomycin A5) is an antitumor glycopeptide antibiotic belonging to the bleomycin family, which is produced by Streptomyces verticillus var. pingyangensis n.sp., a variety of Streptomyces verticillus. It was discovered in 1969 at Pingyang County of Zhejiang Province in China , and was brought into clinical use in 1978.[1]
In China, pingyangmycin has largely superseded bleomycin A2 (commonly known as "bleomycin"), since according to Chinese sources it is more effective, costs less, is easier to get, can treat a larger variety of cancers (such as breast cancer and liver cancer) and causes less lung injury.[2][3] Though pingyangmycin and bleomycin can each cause pulmonary fibrosis, pingyangmycin's most serious side effect - which it does not share with bleomycin - is anaphylactic shock, which is rare, but may happen even in a low dose, and can be fatal.[4] In addition, it causes a higher incidence of fever than bleomycin; the occurrence of this complication in patients is between 20 and 50%.
References
- ↑ "[Antitumor activity and preclinical pharmacologic evaluation of pingyangmycin (author's transl)]". Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Oncology] 1 (3): 161–6. 1979. PMID 95444.
- ↑ "Intralesional injection of Pingyangmycin for vascular malformations in oral and maxillofacial regions: an evaluation of 297 consecutive patients". Oral Oncology 45 (10): 872–6. October 2009. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2009.02.011. PMID 19628423.
- ↑ "[The isolation and identification of pingyangmycin (author's transl)]". Yao Xue Xue Bao = Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 15 (10): 609–14. October 1980. PMID 6167140.
- ↑ "[Allergy caused by minidose and low concentration Pingyangmycin: a case report]". Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi = Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi = West China Journal of Stomatology 27 (5): 572–3. October 2009. PMID 19927737.
 |
