Chemistry:Plutonium borides
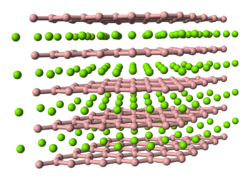
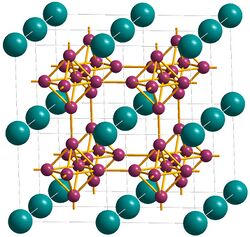
Several plutonium borides can be formed by direct combination of plutonium and boron powders in an inert atmosphere at reduced pressure.
PuB was reported to form at 1200 °C with a range of 40–70% boron. It supposedly has a Pu-B bond length of 2.46 Å and the NaCl structure, as do TiB, ZrB and HfB.[1] The existence of PuB was contested later based on several arguments.[2]
PuB2 is formed at 800 °C and has a similar structure to most other metal diborides.
At 1200 °C with 70–85% boron, mixtures of PuB4 and PuB6 are formed, with more of the latter as the temperature increases; PuB4 has the tetragonal structure (same as UB4), and PuB6 has cubic structure, same as all hexaborides (CaB6, LaB6 etc.).[1]
The most remarkable plutonium boride is arguably PuB66, previously misidentified as PuB100.[3] Its existence[2] demonstrates the importance of contamination in boride research because as little as 1% of an impurity is capable of changing its crystal structure.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 B. J. McDonald; W. I. Stuart (1960). "The crystal structures of some plutonium borides". Acta Crystallogr. 13 (5): 447–448. doi:10.1107/S0365110X60001059. Bibcode: 1960AcCry..13..447M.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 H. A. Eick (1965). "Plutonium Borides". Inorganic Chemistry 4 (8): 1237–1239. doi:10.1021/ic50030a037.
- ↑ Clark, David L.; Hecker, Siegfried S.; Jarvinen, Gordon D.; Neu, Mary P. (2011). "Plutonium". The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-0211-0_7. ISBN 978-94-007-0211-0. https://www.xylenepower.com/THE_CHEMISTRY_OF_THE_ACTINIDE_AND_TRANSA.pdf.
 |
