Chemistry:Potassium hydrogenoxalate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium 2-hydroxy-2-oxoacetate
| |
| Other names
Potassium bioxalate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2HKO4 | |
| Molar mass | 128.124 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.0 g/cm3 |
| 2.5 g/100 g | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in alcohol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
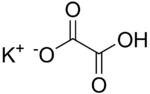
Potassium hydrogenoxalate is a salt with formula KHC2O4 or K+·HO2C-CO2−. It is one of the most common salts of the hydrogenoxalate anion, and can be obtained by reacting potassium hydroxide with oxalic acid in 1:1 mole ratio.
The salt is also known as: potassium hydrogen oxalate, potassium bioxalate, acid potassium oxalate, or monobasic potassium oxalate. In older literature, it was also called: Salt of sorrel,[1] sorrel salt, sel d'oseille,[2][3] sal acetosella; or, inaccurately, salt of lemon (due to the similar acidic “lemony” taste of the edible common sorrel or garden sorrel)[4]
Potassium hydrogenoxalate occurs in some plants, notably sorrel. It is a commercial product used in photography, marble grinding, and removing ink stains.
Properties
The anhydrous product is a white, odorless, crystalline solid, hygroscopic and soluble in water (2.5 g/100 g at room temperature). The solutions are basic. Below 50 °C the much less soluble "potassium tetraoxalate" K+[C
2HO
4]−•C
2H
2O
4 forms and precipitates out of solution.[5]
The monohydrate KHC2O4·H2O starts losing the water at 100 °C.[6]
The anhydrous salt was found to have remarkable elastic anisotropy, due to its crystal structure that consists of relatively rigid columns of hydrogen-bonded hydrogenoxalate anions, joined into sheets by ionic K–O bonds.[7]
Toxicity
Potassium hydrogenoxalate is strongly irritating to eyes, mucoses and gastrointestinal tract. It may cause cardiac failure and death.[5]
See also
- Potassium bicarbonate
- Potassium hydrogenacetylenedicarboxylate
References
- ↑ "Die Net Dictionary: "Salt of Sorrel"". http://dictionary.die.net/salt%20of%20sorrel. Retrieved 19 May 2012. (retrieved via Internet Archive)
- ↑ "Selency: Old bottle at pharmacy—‘Salt of Sorrel". https://www.selency.nl/product/DxMFZuL/old-bottle-at-pharmacy-salt-of-sorrel.html. Salt of Sorrel labelled “sel d'oseille”.
- ↑ "Salt of Sorrel: labelled ‘sel d'oseille’". https://selency.imgix.net/8bd30dba-d2c2-41bf-b186-96481fedb166/old-bottle-at-pharmacy-salt-of-sorrel_original.png?bg=FFF&fit=fill&auto=format,compress&w=579&h=475&meta_format=product_gallery_main&fm=jpg. Old dark-amber glass vial marked “sel d'oseille” with protective leaden cap.
- ↑ "kitchn™ It’s Fresh, Green, and Super Tangy: Sorrel Is In Season!". https://www.thekitchn.com/its-green-fresh-and-super-tang-144842. “This fresh, “lemony” sourness has been highly prized in cuisines all over the world.”
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 ChemicalBook (2007) Potassium binoxalate Product Description
- ↑ Mark Dugan (2009) Potassium binoxalate product data sheet Hummel Croton
- ↑ H. Koppers (1973), 'The Elastic Constants of Monoclinic Potassium Hydrogen Oxalate Acta Crystallographica,volume A29, p. 415
 |

