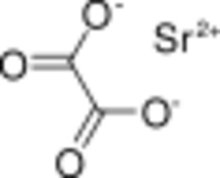
Chemistry:Strontium oxalate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Strontium oxalate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| SrC 2O 4 | |
| Molar mass | 175.64 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder[1] |
| Density | 2.08 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | Decomposes above 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| Insoluble in water | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Skin and eye irritant. Inhaling the compound irritates mucous membrane in the lungs. |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| HH302Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH312Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |
| PP264Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP270Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP280Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP301+P317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP302+P352Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP321Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP330Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP362+P364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP501Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Strontium oxalate is a compound with the chemical formula SrC
2O
4. Strontium oxalate can exist either in a hydrated form (SrC
2O
4 · nH
2O) or as the acidic salt of strontium oxalate (SrC
2O
4 · mH
2C
2O
4 · nH
2O).[2]
Use in pyrotechnics
With the addition of heat, strontium oxalate will decompose based on the following reaction:[3]
- SrC
2O
4 → SrO + CO
2 + CO
Strontium oxalate is a good agent for use in pyrotechnics since it decomposes readily with the addition of heat. When it decomposes into strontium oxide, it produces a red flame color. Since this reaction produces carbon monoxide, which can undergo a further reduction with magnesium oxide, strontium oxalate is an excellent red flame color producing agent in the presence of magnesium. If it is not in the presence of magnesium, strontium carbonate has been found to be a better option to produce an even greater effect.
References
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Strontium-oxalate
- ↑ Knaepen, E. "Preparation and Thermal Decomposition of Various Forms of Strontium Oxalate". Thermochimica Acta 284.1 (1996): 213-27.
- ↑ Kosanke, K. "Chemical Components of Fireworks Compositions". Pyrotechnic Chemistry. Whitewater, CO: Journal of Pyrotechnics, 2004. 1-11.
 |


