Chemistry:Retinyl acetate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
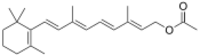
| IUPAC name
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-yl acetate
| |
| Other names
Retinol acetate; Vitamin A acetate; Vitamin A1 acetate; Acetylretinol; all-trans-Retinol acetate; all-trans-Retinyl acetate; all-trans-Vitamin A acetate;
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1915439 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H32O2 | |
| Molar mass | 328.496 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 57 to 58 °C (135 to 136 °F; 330 to 331 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H361, H413 | |
| P201, P202, P264, P273, P280, P281, P302+352, P308+313, P321, P332+313, P362, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Retinyl acetate (retinol acetate, vitamin A acetate) is a natural[dubious ] form of vitamin A which is the acetate ester of retinol. It has potential antineoplastic and chemopreventive activities.[2][3]
In the United States, retinyl acetate is classified generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in the amounts used to fortify foods with vitamin A.[4][5]
Toxicology
World Health Organization "Recommendations for preformed vitamin A supplements for mothers during pregnancy" states that "health benefits are expected for the mother and her developing fetus with little risk of detriment to either, from a daily supplement not exceeding 10,000 IU vitamin A (3000mcg RE) at any time during pregnancy." Preformed Vitamin A refers to retinol and retinyl esters, such as retinyl palmitate and retinyl acetate.[6]
References
- ↑ Retinyl acetate from Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Moon, Richard C.; Grubbs, Clinton J.; Sporn, Michael B.; Goodman, Dawn G. (1977). "Retinyl acetate inhibits mammary carcinogenesis induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea". Nature 267 (5612): 620–1. doi:10.1038/267620a0. PMID 876383. Bibcode: 1977Natur.267..620M.
- ↑ Retinyl acetate, National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary
- ↑ Select Committee on GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Opinion: Vitamin A, United States Food and Drug Administration
- ↑ 21 C.F.R. 184.1930
- ↑ World Health Organization Nutrition Unit (1998). Safe vitamin A dosage during pregnancy and lactation. World Health Organization.
 |


