Chemistry:Seaborgium hexacarbonyl
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hexacarbonylseaborgium
| |
| Other names
Seaborgium carbonyl
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
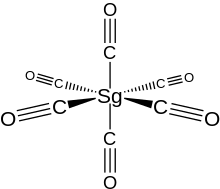
| Sg(CO) 6 | |
| Molar mass | 437 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Radioactive |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Chromium hexacarbonyl Molybdenum hexacarbonyl Tungsten hexacarbonyl |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Seaborgium hexacarbonyl (also called seaborgium carbonyl) is the organometallic compound with the formula Sg(CO)
6. Like its chromium, molybdenum, and tungsten analogs, it is a volatile derivative of seaborgium in its zero oxidation state.[1] Seaborgium hexacarbonyl has little practical usage, outside of scientific interest, where it and other transactinide compounds are studied to shed light on relativistic effects on electronic structure as a consequence of high nuclear charge.
Synthesis
Sg(CO)
6 can be prepared by passing seaborgium atoms through a helium and carbon monoxide mixture:[1]
- Sg + 6 CO → Sg(CO)
6
Reactivity
Seaborgium hexacarbonyl reacts and interacts with a SiO
2 surface in ways closely resembling its lighter congeners, molybdenum hexacarbonyl and tungsten hexacarbonyl.[1]
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 Even, J.; Yakushev, A.; Dullmann, C. E.; Haba, H.; Asai, M.; Sato, T. K.; Brand, H.; Di Nitto, A. et al. (2014). "Synthesis and detection of a seaborgium carbonyl complex". Science 345 (6203): 1491–3. doi:10.1126/science.1255720. PMID 25237098. Bibcode: 2014Sci...345.1491E. (Subscription content?)
 |

