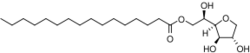
Chemistry:Sorbitan monopalmitate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,4-Anhydro-D-glucitol 6-hexadecanoate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R)-2-[(2R,3R,4S)-3,4-Dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]-2-hydroxyethyl hexadecanoate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H42O6 | |
| Molar mass | 402.572 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 46–47 °C (115–117 °F; 319–320 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 113 °C (235 °F; 386 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sorbitan monopalmitate (SMP) is a food additive,[2] permitted by the EU. It is entry E495 in the E number list of permitted food additives.[3] It is also known under the trade name Span 40.[4]
Synopsis
Sorbitan monopalmitate has been known since at least 1959.[5]
Around 2000, SMP was permitted by the EU in bakery products, icings, marmalades, simulations of milk and cream, beverage whiteners, liquid concentrates of fruit and herbs, sorbets, emulsified sauces, food supplements and chewing gum amongst others.[3]
SMP is a polysorbate that is derived from the mixture of partial esters of sorbitol treated with palmitic acid. SMP is a lipophilic surfactant. It may be found in combination with polysorbates. It is used to modify crystallisation of fats.[3] It is insoluble in water.[6] Up to 25 mg/kg bodyweight can be processed by humans. SMP is metabolized to sorbitol and palmitic acid, without any apparent side effects. The use of animal fats, like pork, in the production of SMP is possible.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Sorbitan monopalmitate". Sigma-Aldrich. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/388920.
- ↑ "Compound Summary for CID 14927 - Sorbitan Monopalmitate". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/14927.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "E495 - Sorbitan monopalmitate, polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monopalmitate, polyoxethylene, Tween 40, sorbitan, monohexadecanoate.Polysorbate 40". http://www.ukfoodguide.net/e495.htm.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "E 495: Sorbitane mono palmitate". http://www.food-info.net/uk/e/e495.htm.
- ↑ BELL Jr., JT (1959). "Polyoxyethylene sorbitan monopalmitate (tween 40) as a vehicle for oil red O fat stain". Stain Technology 34 (4): 219–21. doi:10.3109/10520295909114678. PMID 13668771.
- ↑ "E495 (Sorbitan Monopalmitate) (SMP)". ERVESA. http://www.ervesa.com/index.php/home/83-products/123-e495-sorbitan-monopalmitat.
 |
