Chemistry:Tert-Butyl acetate
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
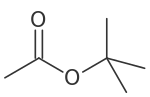
tert-Butyl acetate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 116.160 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fruity |
| Density | 0.8593 g/cm3[1] |
| Boiling point | 97.8 °C (208.0 °F; 370.9 K)[1] |
| 0.8 wt% at 22 °C | |
| Solubility in ether and ethanol | Miscible[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| Flash point | 22 °C; 72 °F; 295 K[2] |
| Explosive limits | From 1.5% to unknown[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 200 ppm (950 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 200 ppm (950 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1500 ppm[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
tert-Butyl acetate, t-butyl acetate or TBAc is a colorless flammable liquid with a camphor- or blueberry-like smell. It is used as a solvent in the production of lacquers, enamels, inks, adhesives, thinners and industrial cleaners. It has recently gained EPA volatile organic compound (VOC) exempt status.[3]
It is manufactured from acetic acid and isobutylene.[1] An attempt at Fischer esterification would lead to elimination of tert-butyl alcohol to isobutylene.
Butyl acetate has four isomers (or five, including stereoisomers): tert-butyl acetate, n-butyl acetate, isobutyl acetate, and sec-butyl acetate (two enantiomers).
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 tert-Butyl acetate (11th ed.). p. 236.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0074". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0074.html.
- ↑ "Update: U.S. EPA Exempt Volatile Organic Compounds" (in en-US). 2018-01-30. https://www.paint.org/voc-exempt/.
External links
 |

