Chemistry:Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride
From HandWiki
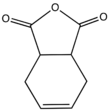
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3aR,7aS)-3a,4,7,7a-Tetrahydro-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2698 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.149 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white or colorless solid |
| Melting point | 97–103 °C (207–217 °F; 370–376 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H317, H318, H334, H412 | |
| P261, P272, P273, P280, P285, P302+352, P304+341, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P333+313, P342+311, P363, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C6H8C2O3. The compound exists as two isomers, this article being focused on the more common cis isomer. It is a precursor to other compounds including the dicarboxylic acid tetrahydrophthalic acid as well the tetrahydrophthalimide, which is a precursor to the fungicide Captan. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, the cis isomer, is prepared by the Diels-Alder reaction of butadiene and maleic anhydride.[1]
References
- ↑ Arthur C. Cope; Elbert C. Herrick (1950). "cis-Δ4-Tetrahydrophthalic Anhydride". Org. Synth. 50: 93. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.030.0093.
 |

