Chemistry:Thorin
From HandWiki
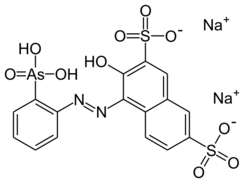
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Disodium 3-hydroxy-4-[(2-arsonophenyl)diazenyl]naphthalene-2,7-disulfonate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Disodium 4-[2-(2-arsonophenyl)hydrazin-1-ylidene]-3-oxo-3,4-dihydronaphthalene-2,7-disulfonate | |
| Other names
Disodium 4-[2-(2-arsonophenyl)hydrazin-1-ylidene]-3-oxonaphthalene-2,7-disulfonate
2-(3,6-Disulfo-2-hydroxy-1-naphthylazo)benzenearsonic acid disodium salt | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 2957648 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1557 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H11AsN2O10S2 | |
| Molar mass | 530.31 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange-yellow crystals |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H331, H410 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+310, P304+340, P311, P321, P330, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Thorin (also called thoron or thoronol) is an indicator used in the determination of barium, beryllium, lithium, uranium and thorium compounds. Being a compound of arsenic, it is highly toxic.[1]
References
- ↑ Haartz, J. C.; Eller, Peter M.; Hornung, Richard W. (1 November 1979). "Critical parameters in the barium perchlorate/Thorin titration of sulfate". Analytical Chemistry 51 (13): 2293–2295. doi:10.1021/ac50049a056.
External links

