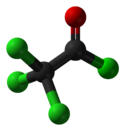
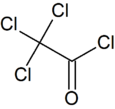Chemistry:Trichloroacetyl chloride
From HandWiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Trichloroacetyl chloride | |||
| Other names
2,2,2-Trichloroacetyl chloride
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2442 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2Cl4O | |||
| Molar mass | 181.832 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.62 g/cm3 at 20 °C | ||
| Boiling point | 117.9 °C (244.2 °F; 391.0 K) | ||
| Solubility | miscible with diethyl ether[1] | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-280.0 kJ•mol−1[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | Oxford MSDS | ||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H302, H314, H330 | |||
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P320, P330, P363, P403+233, P405 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
Trichloroacetyl chloride is the acyl chloride of trichloroacetic acid. It can be formed by reacting chlorine with acetyl chloride or acetaldehyde in the presence of activated charcoal. It is used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and plant protection compounds.[4]
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), CRC Press, pp. 3–536, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), CRC Press, pp. 5–29, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ "Trichloroacetyl chloride" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6420#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ US Patent No. 5,659,078 to Ebmeyer et al., "Process for the preparation of trichloroacetyl chloride," issued August 19, 1997 (as reproduced by freepatentsonline.com and retrieved on October 23, 2007).
 |