Chemistry:Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid
From HandWiki
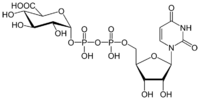
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-[(5′-Deoxyuridin-5′-yl)oxy]-1,3-dihydroxy-1,3-dioxo-1λ5,3λ5-diphosphoxan-1-yl α-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(3-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-Dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy}-1,3-dihydroxy-1,3-dioxo-1λ5,3λ5-diphosphoxan-1-yl)oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | UDP+glucuronic+acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H22N2O18P2 | |
| Molar mass | 580.285 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
UDP-glucuronic acid is a sugar used in the creation of polysaccharides and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid (except in primates and guinea pigs). It also participates in the heme degradation process of human.
It is made from UDP-glucose by UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.22) using NAD+ as a cofactor. It is the source of the glucuronosyl group in glucuronosyltransferase reactions.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Specific protein-1 is a universal regulator of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase expression: its positive involvement in transforming growth factor-beta signaling and inhibition in hypoxia". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 278 (24): 21566–75. Jun 2003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209366200. PMID 12682078.
- ↑ "Characterization of human UDP-glucose dehydrogenase. CYS-276 is required for the second of two successive oxidations". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (22): 23590–6. May 2004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401928200. PMID 15044486.
 |

