Chemistry:Xylylene dichloride
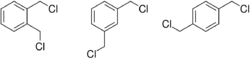 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-xylylene dichloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 2928, 2811 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8Cl2 | |
| Molar mass | 175.05 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.202 |
| Melting point | 34–37 °C (93–99 °F; 307–310 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H314, H315, H317, H319, H330, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P284, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P320, P321, P330, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P391 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The chemical compound xylylene dichloride (C6H4(CH2Cl)2) is a white to light yellow sandlike solid.[1] This compound can be classified as a benzyl halide.[2][3] Xylylene dichloride is used as a vulcanizing agent to harden rubbers. It catalyzes the crosslinking of phenolic resins.[2]
Structure and reactivity
The structure of xylylene dichloride is characterized by an benzene ring with two chloromethyl groups and four hydrogen atoms bound to it.[4] The chloromethyl groups can be located on different sites on the ring, leading to a few different possible forms. These forms are:[3]
- o-xylylene dichloride: 1,2-bis(chloromethyl)benzene
- m-xylylene dichloride: 1,3-bis(chloromethyl)benzene
- p-xylylene dichloride: 1,4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene
The reactive groups of xylylene dichloride are the two CH2Cl groups.
Synthesis
Xylylene dichloride can be synthesized from benzenedimethanol by reaction with hydrogen chloride.[5] It has also been produced by photochemical chlorination of ortho-xylene.[6]
Related compounds
- Xylylene dibromide, the dibromo analogue of the title compound.
References
- ↑ Xylylene dichloride. New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "XYLYLENE DICHLORIDE – National Library of Medicine HSDB Database". https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/a?dbs+hsdb:@term+@DOCNO+6349.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Pubchem. "1,4-Bis(chloromethyl)benzene". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/12171.
- ↑ Blinnikova, Z. K.; Golding, I. R.; Tsyurupa, M. P.; Fomkin, A. A.; Pulin, A. L.; Davankov, V. A. (1 January 2018). "Hypercrosslinked Polycondensation Networks: Copolymers of p-Xylylene Dichloride". Polymer Science, Series B 60 (1): 91–98. doi:10.1134/S1560090418010013.
- ↑ "Hydroxyl Group Substitution". 2 October 2013. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_(Organic_Chemistry)/Alcohols/Reactivity_of_Alcohols/Hydroxyl_Group_Substitution.
- ↑ "1, 4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene synthesis technology" (2015) Chinese patent N105384595A
 |

