Damping
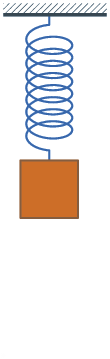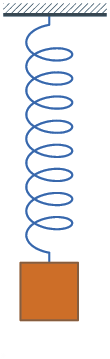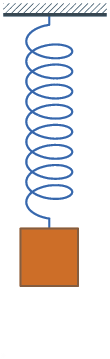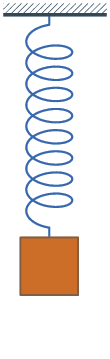
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation.[1] Examples include viscous drag in mechanical systems, resistance in electronic oscillators, and absorption and scattering of light in optical oscillators. Damping not based on energy loss can be important in other oscillating systems such as those that occur in biological systems and bikes.[2]
The damping ratio is a dimensionless measure describing how oscillations in a system decay after a disturbance. Many systems exhibit oscillatory behavior when they are disturbed from their position of static equilibrium. A mass suspended from a spring, for example, might, if pulled and released, bounce up and down. On each bounce, the system tends to return to its equilibrium position, but overshoots it. Sometimes losses (e.g. frictional) damp the system and can cause the oscillations to gradually decay in amplitude towards zero or attenuate. The damping ratio is a measure describing how rapidly the oscillations decay from one bounce to the next.
The damping ratio is a system parameter, denoted by ζ (zeta), that can vary from undamped (ζ = 0), underdamped (ζ < 1) through critically damped (ζ = 1) to overdamped (ζ > 1).
The behaviour of oscillating systems is often of interest in a diverse range of disciplines that include control engineering, chemical engineering, mechanical engineering, structural engineering, and electrical engineering. The physical quantity that is oscillating varies greatly, and could be the swaying of a tall building in the wind, or the speed of an electric motor, but a normalised, or non-dimensionalised approach can be convenient in describing common aspects of behavior.
Oscillation cases
Depending on the amount of damping present, a system exhibits different oscillatory behaviors.
- Where the spring–mass system is completely lossless, the mass would oscillate indefinitely, with each bounce of equal height to the last. This hypothetical case is called undamped.
- If the system contained high losses, for example if the spring–mass experiment were conducted in a viscous fluid, the mass could slowly return to its rest position without ever overshooting. This case is called overdamped.
- Commonly, the mass tends to overshoot its starting position, and then return, overshooting again. With each overshoot, some energy in the system is dissipated, and the oscillations die towards zero. This case is called underdamped.
- Between the overdamped and underdamped cases, there exists a certain level of damping at which the system will just fail to overshoot and will not make a single oscillation. This case is called critical damping. The key difference between critical damping and overdamping is that, in critical damping, the system returns to equilibrium in the minimum amount of time.
Damped sine wave

A damped sine wave or damped sinusoid is a sinusoidal function whose amplitude approaches zero as time increases, corresponding to the underdamped case of damped second-order systems, or underdamped second-order differential equations.[3] Damped sine waves are commonly seen in science and engineering, wherever a harmonic oscillator is losing energy faster than it is being supplied. A true sine wave starting at time = 0 begins at the origin (amplitude = 0). A cosine wave begins at its maximum value due to its phase difference from the sine wave. A given sinusoidal waveform may be of intermediate phase, having both sine and cosine components. The term "damped sine wave" describes all such damped waveforms, whatever their initial phase.
The most common form of damping, and that usually assumed, is the form found in linear systems, which is exponential damping, in which the outer envelope of the successive peaks is an exponential decay curve. The general equation for an exponentially damped sinusoid may be represented as:
where:
- is the instantaneous amplitude at time t;
- is the initial amplitude of the envelope;
- is the decay rate, in the reciprocal of the time units of the independent variable t;
- is the phase angle at t = 0;
- is the angular frequency.
Other important parameters include:
- Frequency: , the number of cycles per time unit. It is expressed in inverse time units , or hertz.
- Time constant: , the time for the amplitude to decrease by the factor of e.
- Half-life is the time it takes for the exponential amplitude envelope to decrease by a factor of 2. It is equal to which is approximately .
- Damping ratio: is a non-dimensional characterization of the decay rate relative to the frequency, approximately , or exactly .
- Q factor: is another non-dimensional characterization of the amount of damping; high Q indicates slow damping relative to the oscillation.
Damping ratio definition

The damping ratio is a parameter, usually denoted by ζ (zeta),[4] that characterizes the frequency response of a second-order ordinary differential equation. It is particularly important in the study of control theory. It is also important in the harmonic oscillator.
The damping ratio provides a mathematical means of expressing the level of damping in a system relative to critical damping. For a damped harmonic oscillator with mass m, damping coefficient c, and spring constant k, it can be defined as the ratio of the damping coefficient in the system's differential equation to the critical damping coefficient:
where the system's equation of motion is
and the corresponding critical damping coefficient is
or
where
- is the natural frequency of the system.
The damping ratio is dimensionless, being the ratio of two coefficients of identical units.
Derivation
Using the natural frequency of a harmonic oscillator and the definition of the damping ratio above, we can rewrite this as:
This equation is more general than just the mass–spring system, and also applies to electrical circuits and to other domains. It can be solved with the approach.
where C and s are both complex constants, with s satisfying
Two such solutions, for the two values of s satisfying the equation, can be combined to make the general real solutions, with oscillatory and decaying properties in several regimes:
- Undamped
- Is the case where corresponds to the undamped simple harmonic oscillator, and in that case the solution looks like , as expected.
- Underdamped
- If s is a pair of complex values, then each complex solution term is a decaying exponential combined with an oscillatory portion that looks like . This case occurs for , and is referred to as underdamped.
- Overdamped
- If s is a pair of real values, then the solution is simply a sum of two decaying exponentials with no oscillation. This case occurs for , and is referred to as overdamped.
- Critically damped
- The case where is the border between the overdamped and underdamped cases, and is referred to as critically damped. This turns out to be a desirable outcome in many cases where engineering design of a damped oscillator is required (e.g., a door closing mechanism).
Q factor and decay rate
The Q factor, damping ratio ζ, and exponential decay rate α are related such that[5]
When a second-order system has (that is, when the system is underdamped), it has two complex conjugate poles that each have a real part of ; that is, the decay rate parameter represents the rate of exponential decay of the oscillations. A lower damping ratio implies a lower decay rate, and so very underdamped systems oscillate for long times.[6] For example, a high quality tuning fork, which has a very low damping ratio, has an oscillation that lasts a long time, decaying very slowly after being struck by a hammer.
Logarithmic decrement
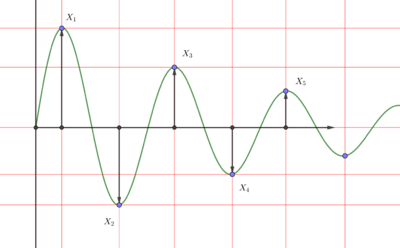
For underdamped vibrations, the damping ratio is also related to the logarithmic decrement . The damping ratio can be found for any two peaks, even if they are not adjacent.[7] For adjacent peaks:[8]
- where
where x0 and x1 are amplitudes of any two successive peaks.
As shown in the right figure:
where , are amplitudes of two successive positive peaks and , are amplitudes of two successive negative peaks.
Percentage overshoot
In control theory, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value.[9] For a step input, the percentage overshoot (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the overshoot is just the maximum value of the step response minus one.
The percentage overshoot (PO) is related to damping ratio (ζ) by:
Conversely, the damping ratio (ζ) that yields a given percentage overshoot is given by:
References
- ↑ Steidel (1971). An Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations. John Wiley & Sons. p. 37. "damped, which is the term used in the study of vibration to denote a dissipation of energy"
- ↑ J. P. Meijaard; J. M. Papadopoulos; A. Ruina; A. L. Schwab (2007). "Linearized dynamics equations for the balance and steer of a bicycle: a benchmark and review". Proceedings of the Royal Society A 463 (2084): 1955–1982. doi:10.1098/rspa.2007.1857. Bibcode: 2007RSPSA.463.1955M. "lean and steer perturbations die away in a seemingly damped fashion. However, the system has no true damping and conserves energy. The energy in the lean and steer oscillations is transferred to the forward speed rather than being dissipated.".
- ↑ Douglas C. Giancoli (2000). [Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics (3rd Edition)]. Prentice Hall. p. 387 ISBN 0-13-021517-1
- ↑ Alciatore, David G. (2007). Introduction to Mechatronics and Measurement (3rd ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-296305-2.
- ↑ William McC. Siebert. Circuits, Signals, and Systems. MIT Press.
- ↑ Ming Rao and Haiming Qiu (1993). Process control engineering: a textbook for chemical, mechanical and electrical engineers. CRC Press. p. 96. ISBN 978-2-88124-628-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=NOpmEHNRH98C&pg=PA96.
- ↑ https://www.brown.edu/Departments/Engineering/Courses/En4/Notes/vibrations_free_damped/vibrations_free_damped.htm
- ↑ https://pm-engr.com/damping-evaluation-2/
- ↑ Kuo, Benjamin C & Golnaraghi M F (2003). Automatic control systems (Eighth ed.). NY: Wiley. p. §7.3 p. 236–237. ISBN 0-471-13476-7. http://worldcat.org/isbn/0471134767.
 |
