Earth:Ganigobis Formation
| Ganigobis Formation Stratigraphic range: Gzhelian-Artinskian 302–297 Ma | |
|---|---|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Dwyka Group |
| Sub-units | Ganigobis Shale Member |
| Underlies | Ecca Group |
| Overlies | Nama Group |
| Thickness | up to 240 m (790 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Shale, conglomerate, sandstone |
| Other | Tuff |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 25°54′S 18°00′E / 25.9°S 18.0°E |
| Paleocoordinates | [ ⚑ ] 56°00′S 35°54′W / 56.0°S 35.9°W |
| Region | ǁKaras Region Northern Cape |
| Country | |
| Extent | Aranos & Karoo Basins Kalahari Craton |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Ganigobis |
| Location | Ganigobis, Fish River Canyon |
| Thickness at type section | 155 m (509 ft) |
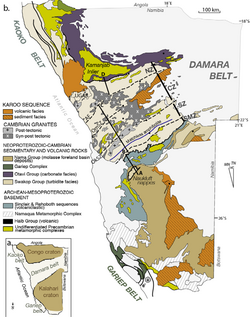 Geologic map of Namibia with the Ganigobis Formation partly cropping out in the southern area (orange) | |
The Ganigobis Formation is a Late Carboniferous (Gzhelian) to Early Permian (Artinskian) geologic formation of the Dwyka Group in the ǁKaras Region of southeastern Namibia and the Northern Cape of South Africa . The widespread formation was deposited in the Aranos and Karoo Basins of southern Africa.
Description
The Ganigobis Formation is an extensive unit with a maximum thickness of 240 metres (790 ft) evidenced in the Vreda borehole.[1] The conglomerates, sandstones, shales and tuff of the formation were deposited in a glacio-lacustrine to marine environment.[2][3] The Ganigobis Formation provides fossil fish as well as bivalves (e.g. Nuculopsis), gastropods (e.g. Peruvispira), scyphozoa (e.g. Conularia), crinoid stalks, foraminifera (Hyperammina, Ammodiscus, Glomospira, Ammobacculites and Spiroplectammina),[4] sponges and sponge spicules, radiolaria, coprolites and permineralised wood.[5]
Zircons of the Ganigobis Shale Member yield SHRIMP-ages of 302-300 Ma. This dates the uppermost part of the second deglaciation sequence in southern Namibia to the Late Carboniferous (Gzelian) and provides a minimum age for the onset of Karoo-equivalent marine deposition. The age of the uppermost argillaceous part of the third deglaciation sequence (297 Ma) was determined from zircons of a tuffaceous bed sampled in a roadcut in the Western Cape Province, South Africa.[5]
Fossil content
Among others, the following fossils are reported from the formation:[6][7][8]
- Fish
- Acrolepis addamsi
- Namaichthys schroederi
- Watsonichthys lotzi
See also
- List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Namibia
- List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in South Africa
- Geology of Namibia
- Geology of South Africa
- Irati Formation
References
- ↑ Bangert et al., 2000, p.266
- ↑ Ganigobis Formation at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ Bangert, 2000, p.21
- ↑ Bangert, 2000, p.60
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Bangert, 2000, p.3
- ↑ Ganigobis at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ Wesselton Mine, Kimberley at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ Ganigobis, near Tses Station at Fossilworks.org
Bibliography
- Bangert, B.; H. Stollhofen; M. Geiger, and V. Lorenz. 2000. Fossil record and high-resolution tephrostratigraphy of Carboniferous glaciomarine mudstones, Dwyka Group, southern Namibia. Communications of the Geological Survey of Namibia 12. 265–276. Accessed 2018-08-26.
- Bangert, Berthold. 2000. Tephrostratigraphy, petrography, geochemistry, age and fossil record of the Ganigobis Shale Member and associated glaciomarine deposits of the Dwyka Group, Late Carboniferous, southern Africa (PhD thesis), 1–242. Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg. Accessed 2018-08-26.
Further reading
- B. G. Gardiner. 1962. Namaichthys schroederi Gürich and other Palaeozoic Fishes from South Africa. Palaeontology 5(1):9-21
 |
