Earth:Maevarano Formation
| Maevarano Formation Stratigraphic range: Maastrichtian ~70–65.8 Ma | |
|---|---|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Sub-units | Masorobe, Anembalemba & Miadana Members |
| Underlies | Berivotra Formation |
| Overlies | Marovoay Beds |
| Thickness | >105 m (344 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sandstone |
| Other | Claystone, siltstone |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 15°54′S 46°36′E / 15.9°S 46.6°E |
| Paleocoordinates | [ ⚑ ] 30°06′S 38°24′E / 30.1°S 38.4°E |
| Region | Mahajanga Province |
| Country | Madagascar |
| Extent | Mahajanga Basin |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Maevarano River |
| Named by | Salètes |
| Year defined | 1895 |
The Maevarano Formation is a Late Cretaceous sedimentary rock formation found in the Mahajanga Province of northwestern Madagascar. It is most likely Maastrichtian in age,[1] and records a seasonal, semiarid environment with rivers that had greatly varying discharges. Notable animal fossils recovered include the theropod dinosaur Majungasaurus, the early bird Vorona, the paravian Rahonavis, the titanosaurian sauropod Rapetosaurus, and the giant frog Beelzebufo.
Description
The Maevarano Formation is well exposed in the Mahajanga Basin, in particular near the village of Berivotra near the northwestern coast of the island where its outcrops have been heavily dissected by erosion. At the time it was being deposited, its latitude was between 30°S and 25°S as Madagascar drifted northward after splitting from India about 88 million years ago. It is composed of three smaller units or members. The lowest is the Masorobe Member, which is usually reddish and is at least 80 metres (260 ft). Its rocks are mostly poorly sorted coarse-grained sandstones with some finer-grained beds. It is separated by an erosional disconformity from the next member, the Anembalemba Member. The lower portion of the Anembalemba Member is fine to coarse clay-rich sandstone, whitish or light grey in color, with cross-bedding. The upper portion of this member is made of poorly sorted clay-rich sandstone, light olive-grey in color, that lacks cross-bedding. Most vertebrate fossils come from the Anembalemba Member, especially from the upper portion. The Miadana Member, the third and uppermost member, is not always present, and is up to 25 metres (82 ft) in some places. Elsewhere, it is replaced by the marine Berivotra Formation. The Miadana Member is made up of claystone, siltstone, and sandstone, lacks cross-bedding, and has several colors of rock. The Maevarano Formation as a whole is underlain by the Marovoay beds and capped by the Berivotra Formation.[1]
The age of the Maevarano Formation has been debated; the Berivotra Formation, which is partially contemporaneous with the upper portions of the formation, shows that at least the upper part of the Maevarano is Maastrichtian in age. There is no evidence that it is Campanian,[1] despite previous reports to that effect.[2] The Berivotra Formation appears to include near its top a magnetic reversal, interpreted as the shift from Chron 30N to Chron 29R, which occurred approximately 65.8 million years ago (about 300,000 years before the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary and associated Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. This suggests that Maevarano organisms also lived shortly before (geologically speaking) the extinction event.[1]
History of exploration
The Maevarano Formation was first explored by French military physician Dr. Félix Salètes and his staff officer Landillon in 1895, and fossils and geologic data were sent to paleontologist Charles Depéret.[3] He briefly described the formation and named two dinosaurs from the remains (Titanosaurus madagascariensis and Megalosaurus crenatissimus, now Majungasaurus).[4] Similar collections were made throughout the 20th century, yielding mostly fragmentary fossils;[3] one such specimen, a rough partial skull roof, became the holotype of supposed pachycephalosaur (bonehead dinosaur) Majungatholus in 1979.[5] (This specimen was later shown to be part of the skull ornamentation of a Majungasaurus.) Large-scale expeditions (seven to date), under the banner of the Mahajanga Basin Project, began in 1993. These expeditions, conducted jointly by Stony Brook University and the University of Antananarivo, have greatly expanded knowledge of this formation and the organisms that lived while it was being deposited.[3]
Paleoenvironment

The Maevarano Formation is interpreted as a low-relief alluvial plain that over time was covered by a marine transgression. Broad, shallow rivers flowed to the northwest from central highlands; evidence for debris flows suggests that the discharges of the rivers varied greatly, with periods of dilute water flow, and periods of rapid erosion dumping sediment into the channels. Paleosols are reddish and include root casts. The paleosols and other sedimentologic evidence indicate well-drained floodplains with abundant vegetation adapted to a relatively dry climate, strongly seasonal (rainy and dry seasons) and at times semiarid (not unlike the present climate of the area).[1]
Paleofauna
Animals found in the formation include frogs (including Beelzebufo ampinga),[6] turtles, snakes, lizards, at least seven species of crocodyliforms (including species of Mahajangasuchus and Miadanasuchus), abelisaurid theropod Majungasaurus, noasaurid Masiakasaurus, two types of titanosaurian sauropods (Rapetosaurus and Vahiny), and at least five species of bird-like dinosaurs, including Rahonavis. The 6 to 7 metres (20 to 23 ft) long Majungasaurus was likely the apex predator in the terrestrial environment. Crocodyliforms were very diverse and abundant.[1]
Template:Paleobiota-key-compact
Invertebrates
| Invertebrates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Cubiculum[7] | C. ornatus | Ovoid chambers in dinosaur bones | A trace fossil, possibly puppal chambers of carrion beetles | |||
| Ethmosestheria[8] | E. mahajangaensis | Anembalemba Member | A species of antronstheriid clam shrimp | |||
| Osteocallis[7] | O. mandibulus | Curved grooves on dinosaur bones | A trace fossil, possibly feeding marks by a similar insect as Cubiculum ornatus | |||
Fish
Osteichthyes
| Osteichthyes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxon | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Albula[9] | A. sp. | Tooth plates and dentaries | A species of bonefish | |||
| Characiformes indet.[9] | Partial jaw | |||||
| Coelodus[9] | C. sp. | A tooth plate | A species of pycnodontid | |||
| Cypriniformes?[9] | ||||||
| Dipnoi indet.[10] | Masorobe and Anembalemba Members | Burrows | ||||
| Egertonia[9] | E. sp. | Partial toothplates | ||||
| Enchodus[9] | E. sp. | Teeth | ||||
| Lepisosteus[11] | L. sp. | Scales, fin rays, teeth, vertebrae, skull bones | A type of gar | |||
| Paralbula[9] | P. sp. | Lac Kinkony Member | Partial tooth plates | A species of bonefish | ||
| Sciaenidae indet.[9] | A species of croaker | |||||
| Siluriformes indet.[9] | Vertebrae | A type of catfish | ||||
| Vango[12] | V. fahiny | Lac Kinkony Member | Referred material is hyomandibulae, although other partial remains of gonorynchiform probably belongs to this taxa as well | A chanid gonorynchiform, milkfish | ||
Amphibians
| Amphibians | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Beelzebufo | Beelzebufo ampinga | locality MAD98-25[13] | A large frog |  | ||
Dinosaurs
Indeterminate Lithostrotia remains formerly attributed to Titanosauridae. Undescribed Lithostrotia form. Indeterminate Enantiornithes remains. A rich avifauna with several undescribed taxa are known, including pengornithid enantiornithes and putative omnivoropterygids.[14]
Ornithischians
| Ornithischians of the Maevarano Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Stegosaurus[15] | S. madagascariensis[15] | "Teeth"[16] | An indeterminate thyreophoran.[17] | |||
Sauropods
| Sauropods of the Maevarano Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Rapetosaurus[15] | R. krausei[15] | "[Three] skulls, at least [one] postcranial skeleton."[18] | A titanosaur |  | ||
| Titanosaurus[15] | T. madagascariensis[15] | |||||
| Vahiny[19] | V. depereti[19] | "Partial braincase"[19] | A titanosaur | |||
Theropods
| Theropods of the Maevarano Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Falcatakely[20] | F. forsterae | "Partial skull" | A member of Enantiornithes |  | ||
| Majungasaurus[15] | M. crenatissimus[15] | "Scattered remains leading to nearly most of the animal."[21] | An abelisaur | |||
| Masiakasaurus[15] | M. knopfleri[15] | "Disarticulated remains of at least 6 individuals," as well as other isolated fossils.[22] | A noasaurid abelisaur | 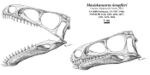 | ||
| Rahonavis[15] | R. ostromi[15] | "Partial postcranial skeleton"[23] | A paravian of unclear phylogenetic placement |  | ||
| Vorona[15] | V. berivotrensis[15] | "Partial hindlimbs"[24] | An ornithuromorph | |||
Crocodylomorphs
| Crocodylomorphs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Mahajangasuchus | M. insignis | disarticulated postcranial skeleton, multiple skull remains | A mahajangasuchid |  | ||
| Miadanasuchus | M. oblita | A peirosaurid. Formerly known as Trematochampsa oblita | ||||
| Simosuchus | S. clarki | multiple specimens representing most of the skeleton | A ziphosuchian |  | ||
| Araripesuchus | A. tsangatsangana | Anembalemba Member | multiple specimen including several skulls and one almost complete specimen | A notosuchian |  | |
Squamates
| Squamates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Adinophis | A. fisaka | A madtsoiid snake | ||||
| Indophis | I. fanambinana | A nigerophid snake | ||||
| Kelyophis | K. hechti | A nigerophiid snake | ||||
| Konkasaurus | K. mahalana | A cordylid lizard | ||||
| Madtsoia | M. madagascariensis | A madtsoiid snake | ||||
| Menarana | M. nosymena | Vertebrae and rib fragments | A madtsoiid snake | |||
Turtles
| Turtles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Kinkonychelys | K. rogersi | A side-necked turtle | ||||
| Sahonachelys | S. mailakavava | A sahonachelyid side-necked turtle |  | |||
| Sokatra | S. antitra | A sahonachelyid side-necked turtle | ||||
Mammals
Mammal remains include an undescribed gondwanathere,[25] a broken tooth UA 8699, which has been interpreted both as metatherian and as eutherian, a non-gondwanathere multituberculate tooth fragment, a non-gondwanathere multituberculate femur,[26] and a yet undescribed mammal known from an articulated skeleton.[27] Some taxa are particularly large sized herbivores, exemplifying the diversity of Mesozoic mammals.[28]
| Mammals | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Adalatherium | A. hui | A nearly-complete skeleton | A gondwanatherian | 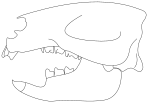 | ||
| Lavanify | L. miolaka | Multiple teeth and dentition | A gondwanatherian | |||
| Vintana | V. sertichi | A gondwanatherian |  | |||
See also
- Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Africa
- List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Madagascar
- Geology of Madagascar
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Rogers et al., 2007
- ↑ Weishampel et al., 2004
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Krause et al., 2007b
- ↑ Depéret, 1896
- ↑ Sues & Taquet, 1979
- ↑ Evans, Susan E.; Jones, Marc E. H.; Krause, David W. (2008). "A giant frog with South American affinities from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105 (8): 2951–2956. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707599105. PMID 18287076. Bibcode: 2008PNAS..105.2951E.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Roberts, E.M.; Rogers, R.R.; Foreman, B.Z. (2007). "Continental insect borings in dinosaur bone: Examples from the late Cretaceous of Madagascar and Utah". Journal of Paleontology 81 (1): 201–208. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2007)81[201:CIBIDB2.0.CO;2].
- ↑ Stigall, A.L.; Hartman, J.H. (2008). "A New Spinicaudatan Genus (Crustacea: 'Conchostraca') from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar". Palaeontology 51 (5): 1053–1067. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2008.00799.x. Bibcode: 2008Palgy..51.1053S.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 Ostrowski, S.A. (2012). "The teleost ichthyofauna from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar: systematics, distributions, and implications for Gondwanan biogeography". Michigan State University. Geological Sciences. https://d.lib.msu.edu/etd/1842/datastream/OBJ/download/The_teleost_ichthyofauna_from_the_Late_Cretaceous_of_Madagascar___systematics__distributions__and_implications_for_Gondwanan_biogeography.pdf. Retrieved 2022-01-28.
- ↑ Marshall, M.S.; Rogers, R.R. (2013). "Lungfish Burrows from the Upper Cretaceous Maevarano Formation, Mahajanga Basin, Northwestern Madagascar". PALAIOS 27 (12): 857–866. doi:10.2110/palo.2012.p12-018r. Bibcode: 2013Palai..27..857M.
- ↑ Gottfried, M.D.; Krause, D.W. (1998). "First record of gars (Lepisosteidae, Actinopterygii) on Madagascar: Late Cretaceous remains from the Mahajanga Basin.". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 18 (2): 275–279. doi:10.1080/02724634.1998.10011056. Bibcode: 1998JVPal..18..275G.
- ↑ Murray, Alison M.; Brinkman, Donald B.; Friedman, Matt; Krause, David W. (2023-10-17). "A large, freshwater chanid fish (Ostariophysi: Gonorynchiformes) from the Upper Cretaceous of Madagascar". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. doi:10.1080/02724634.2023.2255630. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ↑ Evans et al., 2014, p.5
- ↑ O'Connor and Forster, 2010. A Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) avifauna from the Maevarano Formation, Madagascar. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30(4), 1178-1201.
- ↑ 15.00 15.01 15.02 15.03 15.04 15.05 15.06 15.07 15.08 15.09 15.10 15.11 15.12 15.13 "83.2 Faritany Majunga, Madagascar; 3. Maevarano Formation," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.605
- ↑ "Table 14.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 326.
- ↑ Maidment, Susannah; Norman, David; Barrett, Paul; Upchurch, Paul (2008). "Systematics and phylogeny of Stegosauria (Dinosauria: Ornithischia)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 6 (4): 367–407. doi:10.1017/S1477201908002459. Bibcode: 2008JSPal...6..367M.
- ↑ "Table 13.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 270.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Rogers & Wilson, 2014
- ↑ Patrick M. O'Connor; Alan H. Turner; Joseph R. Groenke; Ryan N. Felice; Raymond R. Rogers; David W. Krause; Lydia J. Rahantarisoa (2020). "Late Cretaceous bird from Madagascar reveals unique development of beaks". Nature 588 (7837): 272–276. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2945-x. PMID 33239782. Bibcode: 2020Natur.588..272O.
- ↑ "Table 3.1," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.50
- ↑ "Table 3.1," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.49
- ↑ "Table 11.1," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.211
- ↑ "Table 11.1," in Weishampel et al., 2004, p.212
- ↑ Krause et al, 2014
- ↑ Krause, David W.; Hoffmann, Simone; Werning, Sarah (December 2017). "First postcranial remains of Multituberculata (Allotheria, Mammalia) from Gondwana". Cretaceous Research 80: 91–100. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2017.08.009. Bibcode: 2017CrRes..80...91K.
- ↑ Krause, David W.; O'Connor, Patrick M.; Rogers, Kristina Curry; Sampson, Scott D.; Buckley, Gregory A.; Rogers, Raymond R. (23 August 2006). "Late Cretaceous terrestrial vertebrates from Madagascar: Implications for Latin American biogeography". Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 93 (2): 178–208. doi:10.3417/0026-6493(2006)93[178:LCTVFM2.0.CO;2]. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/part/390696.
- ↑ Krause et al., 2020
Bibliography
- Depéret, Charles (1896), "Note sur les Dinosauriens Sauropodes et Théropodes du Crétacé supérieur de Madagascar" (in French), Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 21: 176–194
- Evans, Susan E.; Groenke, Joseph R.; Jones, Marc E. H.; Turner, Alan H.; Krause, David W.; Claessens, Leon (2014), "New Material of Beelzebufo, a Hyperossified Frog (Amphibia: Anura) from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar", PLoS ONE 9 (1), doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0087236, PMID 24489877, Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...987236E Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...987236E
- Krause, David W.; Hoffmann, Simone; Hu, Yaoming; Wible, John R.; Rougier, Guillermo W.; Kirk, E. Christopher; Groenke, Joseph R.; Rogers, Raymond R. et al. (2020), "Skeleton of a Cretaceous mammal from Madagascar reflects long-term insularity", Nature 581 (7809): 1–7, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2234-8, PMID 32461642, Bibcode: 2020Natur.581..421K
- Krause, David W.; Hoffmann, Simone; Wible, John R.; Kirk, E. Christopher; Schultz, Julia A.; von Koenigswald, Wighart; Groenke, Joseph R.; Rossie, James B. et al. (2014), "First cranial remains of a gondwanatherianmammal reveal remarkable mosaicism", Nature 525
- Krause, David W.; Sampson, Scott D.; Carrano, Matthew T.; O'Connor, Patrick M. (2007b), "Overview of the history of discovery, taxonomy, phylogeny, and biogeography of Majungasaurus crenatissimus (Theropoda: Abelisauridae) from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar", Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 27 (sup2): 1–20, doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[1:OOTHOD2.0.CO;2]
- Rogers, K.C.; Wilson, J.A. (2014), "Vahiny depereti, gen. et sp. nov., a new titanosaur (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous Maevarano Formation, Madagascar", Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 34 (3): 606, doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.822874, Bibcode: 2014JVPal..34..606R, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262070167, retrieved 2020-05-04
- Rogers, Raymond R.; Krause, David W.; Rogers, Kristina Curry; Rasoamiaramanana, Armand H.; Rahantarisoa, Lydia (2007), "Paleoenvironment and Paleoecology of Majungasaurus crenatissimus (Theropoda: Abelisauridae) from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar", Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 27 (sup2): 21–31, doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[21:PAPOMC2.0.CO;2]
- Sues, Hans-Dieter; Taquet, Phillipe (1979), "A pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from Madagascar and a Laurasia−Gondwanaland connection in the Cretaceous", Nature 279 (5714): 633–635, doi:10.1038/279633a0, Bibcode: 1979Natur.279..633S Bibcode: 1979Natur.279..633S
- Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; Osmólska, Halszka (2004), The Dinosauria, 2nd edition, Berkeley: University of California Press, pp. 1–880, ISBN 0-520-24209-2, https://books.google.com/books?id=vtZFDb_iw40C, retrieved 2019-02-21
 |