Earth:North Island Volcanic Plateau
| North Island Volcanic Plateau | |
|---|---|
| Central Plateau, Waimarino Plateau | |
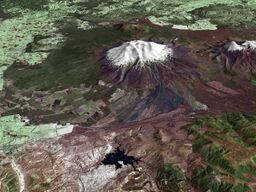 Composite satellite image of Mount Ruapehu | |
| Location | North Island, New Zealand |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 39°02′27″S 175°44′04″E / 39.04083°S 175.73444°E |
| Highest point – elevation – coordinates | Mount Ruapehu 2,797 m (9,177 ft) [ ⚑ ] 39°17′S 175°34′E / 39.283°S 175.567°E |
| Length | 125 km (78 mi) |
| Width | 60 km (37 mi) |
| Formed by | Volcanic action |
| Geology | Volcanic plateau |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Taupō Volcanic Zone |
| Elevation | above 300 m (980 ft) |
| Water bodies | Lake Taupō, Lake Rotorua, Lake Tarawera, Lake Rotoiti, Lake Rotomā, Lake Ōkataina, Lake Rotokākahi, Lake Ōkareka, Lake Tikitapu, Lake Rotomahana, Lake Rotoehu |
| River systems | Waikato River, Kaituna River, Whanganui River |
The North Island Volcanic Plateau (often called the Central Plateau and occasionally the Waimarino Plateau) is a volcanic plateau covering much of central North Island of New Zealand with volcanoes, lava plateaus, and crater lakes. It contains the Taupō caldera complex, Ōkataina caldera complex and Tongariro Volcanic Centre resulting in it being currently the most frequently active and productive area of silicic volcanism on Earth.[1] New Zealand is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Location and description
The plateau is approximately 60 km (37 mi) east–west and the north–south distance is about 125 km (78 mi).[1]
Extensive ignimbrite sheets spread east and west from the Central Taupō Volcanic Zone, centred on the huge active supervolcanic caldera of Lake Taupō, now the largest lake in New Zealand. This last erupted less than 2000 years ago. The volcanic area includes the three active peaks of Mount Tongariro, Mount Ngāuruhoe, and Mount Ruapehu in the south, and extends beyond Rotorua in the north reaching almost to the Bay of Plenty coast. North of Tongariro is the volcanic Mount Pihanga. The western boundary of the plateau forms an escarpment beside the Mamaku and Kaimai Ranges, but further south is less distinct. In the east, the plateau runs up to the foot of the Ahimanawa, Kaweka and the fertile Kaimanawa mountain ranges. West of the plateau stands the volcano Taranaki Maunga (in Egmont National Park).
Two of the country's longest rivers, the Whanganui and the Waikato have their headwaters on the plateau.
Geology
<mapframe text="Map centered to show selected surface volcanic deposits that are mainly ignimbrites sheets of the North Island Volcanic Plateau. {{Wikipedia:Map data/Northern North Island Volcanics/key}}" zoom="7" align="right" longitude="176.03" height="275" class="no-icon" latitude="-38.7" width="275">{{Wikipedia:Map data/Northern North Island Volcanics}}</mapframe>
The tallest mountain, Ruapehu, is an andesite cone that was somewhat higher but has been eroded with a 150 km3 (36 cu mi) cone and 150 km3 (36 cu mi) ring-plain.[2] It is typical of the Tongariro Volcanic Centre whose landforms are defined by the intermediate properties of its andesite magma, having a moderate amount of silica, making it more viscous than basalt, but much less viscous than rhyolite. Andesite magma in effusive eruptions cools to form dark grey lava if gas-poor or scoria if gas-rich. The explosive eruptions tend to be small or moderate sized phreatomagmatic eruptions where the hot magma turns water into steam and the magma into ash. Northwest of Ruapehu is Hauhungatahi the oldest recorded volcano in the south of the plateau.[2] The other two most prominent volcanic mountains are Tongariro and Ngāuruhoe part of a single composite stratovolcano, like Ruapehu made up of layers of lava and tephra.
The ring plain around the central volcanoes is formed from numerous volcanic deposits from slope failure or eruptions, and lahars or mudflows that occur when either the crater lake water is ejected from Ruapehu during an eruption, or snow melt is released by failure of the crater walls such as failure of an ice dam.[3] separate from an eruptive event.[2] In the case of lahars, they run down the mountain, picking up ash, lapilli, blocks and bombs as well as previously eroded rock, forming a thick, dense mud that is capable of picking up car-sized rocks. An old lahar flow is visible from the approach road to Whakapapa ski field. On Christmas Eve 1953 a sudden lahar at night on Mt Ruapehu knocked out the rail bridge at Tangiwai, causing six carriages of the Wellington-Auckland express to plunge into the Whangaehu River, killing 151 people in New Zealand's worst railway disaster.[3]
The percentage of silica is the deciding factor in the thickness or viscosity of the magma and this increases to the north and east of the Tongariro Volcanic Centre where there is a landscape of calderas and volcanic domes making up the Taupō caldera complex (Central Taupō Volcanic Zone) and Okataina caldera complex (Okataina Volcanic Centre). These produced much of the ignimbrite sheet deposits of the plateau. Ignimbrite is formed from very viscous rhyolite magma which is rich in silicon, potassium, and sodium. It in an explosive caldera forming event is the gas-rich material ejected from the ground at high speed forming a giant white hot fountain up to 55 kilometres high. When the ignimbrite falls it flows outwards at high speed (600–900 km/h) and can travel many kilometres, even going up and over hills and mountains before it cools, often trapping air inside. Especially around Lake Taupō the eroded ignimbrite includes pieces of quickly cooled pumice, a lightweight rock that floats on water. The top, unwelded layer of the ignimbrite sheet is relatively soft and easily eroded by streams and rivers, which transport the pumice to the lake. The lower, welded layers of the ignimbrite sheets are more dense, though still porous. These lower compressed layers often show the glint of heated silicon specks.[2] North of the plateau this stone, called Hinuera stone (after a quarry of origin), is produced for use for building cladding.[4] An historic eruption at the north west edge of the plateau at Mangakino about 1 million years ago produced ignimbrite that 170 km (110 mi) away in Auckland is up to 9 m (30 ft) thick.[5]
<timeline> ImageSize = width:320 height:2000 PlotArea = right:50 top:10 left:50 bottom:10 DateFormat = yyyy TimeAxis = orientation:vertical Period = from:-2300000 till:80000 AlignBars = early ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:100000 start:-2300000 Colors =
id:canvas value:rgb(1,1,0.85)
BackgroundColors = canvas:canvas PlotData =
width:15 color:white bar:test from:-2300000 till:2023#
PlotData =
at:-2299999 shift:(0,-5) text: Notable eruptions central volcanic plateau region at:80000 shift:(0,-4) text: Notable eruptions central volcanic plateau region at:80000 shift:(1,-13) fontsize:XS text: Note - The further back in time, the larger an eruption must be, to be at:80000 shift:(1,-23) fontsize:XS text: detected and assessed. Accordingly eruptions greater than 10km3 but at:80000 shift:(1,-33) fontsize:XS text: less than 100km3 DRE volume are marked at:80000 shift:(1,-43) fontsize:XS text: but other detail is omitted. at:-2220000 shift:(40,-3) fontsize:XS text: Note - The further back in time, the larger an eruption at:-2220000 shift:(40,-13) fontsize:XS text: must be, to be detected and assessed. Accordingly eruptions at:-2220000 shift:(40,-23) fontsize:XS text: greater than 10km3 but less than 100km3 DRE volume are at:-2220000 shift:(40,-33) fontsize:XS text: marked but other detail is omitted. at:-2205000 shift:(195,-5) textcolor:red text: (DRE volume) at:-2190000 shift:(195,-5) textcolor:red text: Eruptive Index at:-2175000 shift:(180,-5) textcolor:red text: 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 at:45000 shift:(195,-4) textcolor:red text: Eruptive Index at:30000 shift:(180,-5) textcolor:red text: 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 at:15000 shift:(195,-4) textcolor:red text: (DRE volume) at:233 shift:(10,-6) fontsize:XS text:233 Taupō Hatepe eruption Unit Y bar:test at:233 mark:(line,red) at:233 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(120 km ) at:233 shift:(253,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-3576 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Whakatane bar:test at:-5990 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Mamaku bar:test at:-12059 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Waiohau at:-12059 shift:(10,-5) fontsize:XS text:12059 BCE Ōkataina Caldera eg Waiohau bar:test at:-23221 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Te Rere/Kawerau at:-25580 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:25580 BCE Taupō Oruanui eruption at:-25580 shift:(215,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(530 km ) at:-25580 shift:(253,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-25580 mark:(line,red) bar:test at:-30550 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Omataroa bar:test at:-31050 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Mangaone at:-31050 shift:(10,-5) fontsize:XS text:31050 BCE Ōkataina Caldera eg Mangaone bar:test at:-34150 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Hauparu bar:test at:-34850 mark:(line,red) # Ōkataina Caldera Maketu at:-48050 shift:(10,-6) fontsize:XS text:48050 BCE Rotoiti/Rotoehu eruption bar:test at:-48050 mark:(line,red) at:-48050 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(130 km ) at:-48050 shift:(253,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-220000 mark:(line,red) # Maroa Caldera Mokai ignimbrite at:-238000 shift:(10,12) fontsize:XS text:238000 BCE Kaingaroa Formation at:-238000 shift:(215,10) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(100 km ) at:-238000 shift:(253,13) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-238000 mark:(line,red) at:-239000 shift:(10,3) fontsize:XS text:239000 BCE Ohakuri Formation at:-239000 shift:(215,1) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(100 km ) at:-239000 shift:(253,3) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-239000 mark:(line,red) at:-240000 shift:(10,-6) fontsize:XS text:240000 BCE Mamaku Formation at:-240000 shift:(215,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(145 km ) at:-240000 shift:(253,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-240000 mark:(line,red) at:-275000 shift:(10,0) fontsize:XS text:275000 BCE Pokai Formation bar:test at:-275000 mark:(line,red) at:-275000 shift:(214,0) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(100 km ) at:-275000 shift:(253,2) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 at:-280000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:280000 BCE Matahina Formation bar:test at:-280000 mark:(line,red) at:-280000 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(150 km ) at:-280000 shift:(253,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-310000 mark:(line,red) # Kapenga Caldera chimp 50 km3 DRE at:-310000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:310000 BCE Chimp Ignimbrite bar:test at:-325000 mark:(line,red) at:-325000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:325000 BCE Mananui/Te Whaiti bar:test at:-325000 mark:(line,red) at:-325000 shift:(214,1) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(100+km ) at:-325000 shift:(255,3) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 at:-335000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:335000 BCE Whakamaru/Rangitawa bar:test at:-335000 mark:(line,red) at:-335000 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(1500 km ) at:-335000 shift:(258,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 at:-555000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:555000 BCE Utu Caldera bar:test at:-555000 mark:(line,red) at:-555000 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(100+km ) at:-555000 shift:(255,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-680000 mark:(line,red) # Kapenga Caldera Matahana Ignimbrite at:-680000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:680000 BCE Matahana Ignimbrite bar:test at:-710000 mark:(line,red) # Kapenga Caldera Waiotapu Ignimbrite at:-710000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:710000 BCE Waiotapu Ignimbrite bar:test at:-770000 mark:(line,red) # Kapenga Caldera Rahopaka Ignimbrite at:-770000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:770000 BCE Rahopaka Ignimbrite bar:test at:-890000 mark:(line,red) # Kapenga Caldera Tikorangi /Pukerimu Ignimbrite at:-890000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:890000 BCE Tikorangi /Pukerimu Ignimbrite bar:test at:-950000 mark:(line,red) # Mangakino caldera complex Marshall Formation at:-950000 shift:(10,-1) fontsize:XS text:950000 BCE Marshall Formation at:-1010000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1010000 BCE Kidnappers/Raepahu bar:test at:-1010000 mark:(line,red) at:-1010000 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(1200 km ) at:-1010000 shift:(258,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 at:-1050000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1050000 BCE Rocky Hill bar:test at:-1050000 mark:(line,red) at:-1050000 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(200 km ) at:-1050000 shift:(253,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-1160000 mark:(line,red) # Mangakino caldera complex Mangaokewa Formation at:-1160000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1160000 BCE Mangaokewa Formation bar:test at:-1310000 mark:(line,red) # Mangakino caldera complex Ngaroma Formation at:-1310000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1310000 BCE Ngaroma Formation at:-1370000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1370000 BCE Ongatiti/Oparau bar:test at:-1370000 mark:(line,red) at:-1370000 shift:(214,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(1000 km ) at:-1370000 shift:(258,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-1530000 mark:(line,red) # Mangakino caldera complex Tolley Formation at:-1530000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1530000 BCE Tolley Formation bar:test at:-1600000 mark:(line,red) # Link Formation at:-1600000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1600000 BCE Link Formation bar:test at:-1680000 mark:(line,red) # Mangakino caldera complex Pouakani Formation at:-1680000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:1680000 BCE Pouakani Formation bar:test at:-1900000 mark:(line,red) # Tauranga Volcanic Centre Papamoa ignimbrites at:-1900000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:2290000 BCE Papamoa ignimbrites at:-2100000 shift:(10,-3) fontsize:XS text:2100000 BCE Waiteariki at:-2100000 shift:(215,-11) textcolor:red fontsize:S text:(870 km ) at:-2100000 shift:(253,-9) textcolor:red fontsize:XS text:3 bar:test at:-2100000 mark:(line,red) bar:test at:-2290000 mark:(line,red) # Tauranga Volcanic Centre Waiteariki ignimbrite at:-2290000 shift:(10,4) fontsize:XS text:~2290000 BCE Waiteariki ignimbrite
LineData =
at:233 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-25580 frompos:240 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-48050 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-238000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-239000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-240000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-275000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-280000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-325000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-335000 frompos:230 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-555000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-1050000 frompos:260 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-1010000 frompos:235 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-1370000 frompos:240 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 at:-2100000 frompos:237 tillpos:320 color:red width:2 </timeline>
The last massive eruption in the area was the Hatepe eruption from the Lake Taupō volcanic complex 1800 years ago, which ejected lava and especially wind-blown tephra over a wide area to the north and northeast of the North Island. About 30 km3 (7.2 cu mi) of material was ejected in the space of a few minutes, in what is thought to be New Zealand's largest eruption in last 20,000 years, but the entire eruption sequence ejected over 120 km3 (29 cu mi) in a little longer period which might have lasted several years. As is typical after such degassing events which are separated in considerable time, dome building by effusive eruption of low gas viscous rhyolite magma then occurred resulting in this case the formation of the Horomatangi Reefs about 200 years later. Another example in Lake Taupo of such a volcanic dome is Motutaiko Island and towards the north west of the plateau is the lava dome of Mount Tarawera which was split in half by a later relatively small explosive eruption as recently as 1886 with the greatest loss of human life documented from an eruption in New Zealand history. A subsequent risk assessment suggests the Tarawera containing Okataina caldera complex as the highest risk volcanic field in New Zealand to man.[6]
The entire area of the plateau is above 300 metres, with a considerable proportion of it more than 800 metres above sea level.
Climate
The plateau has a mild climate although the temperature regularly falls below freezing in winter and snow can fall between March and October. Of all North Island regions, the Volcanic Plateau is closest to having a continental climate.[7] The period of maximum snow is July to September. Sudden blizzard conditions can be experienced on the volcanoes in winter. Such conditions have killed climbers as recently as 2019.[8] The Desert Road on State Highway 1 is often closed by snow in winter for brief periods.
Flora
The natural vegetation of the area includes the podocarp conifers including rimu (Dacrydium cupressinum), miro (Prumnopitys ferruginea), matai (Prumnopitys taxifolia), totara (Podocarpus totara) and kahikatea (Dacrycarpus dacrydioides) and hardwoods that once covered this whole area before the eruption of Taupō and other volcanoes. To the west of the three large volcanoes, the land is rough forested hill country, while the north close to Lake Taupō is more fertile and undulating and much has been cleared for farming. The forest used to extend to the west coast and there are still patches of natural vegetation in wetlands including the Horowhenua floodplains.[9]
However to the south of Taupō the barren, ash-laden soils and harsh alpine climate leave the high land largely bare and unprofitable, capable of growing only scrubby plants. This area is known as the Rangipo Desert although it is not a true desert as the annual rainfall is over 1,000mm PA and the real reason for the low and sparse vegetation was the mass sterilization of seeds caused by the 26,000-year-old Taupō eruption, which swept white-hot ignimbrite through this valley. Prior to this cataclysmic event this area was forested and stumps of charcoalized trees can be seen where soil has eroded. Around Taupō itself there are geothermal areas with specialised plant life such as the prostrate kanuka (a subspecies of kunzea ericoides).[10]
Further to the east of the plateau lies more rough hill country in the Kaimanawa Ranges, a popular hunting area for wild red and sika deer. The tops of the mountains are open and tussock covered. Helicopters and light aircraft can land on a rough air strip. Hunting range in the bush is often 50 m or less but in the open tops the range can be much further. The area to the south, around Lake Moawhango is richer in plant life. Finally there are areas of beech forest and alpine vegetation at higher elevations throughout the region.[11]
Fauna
The northern side of the plateau especially is home to wildlife including birds such as the North Island kōkako wattlebird (Callaeas wilsoni), New Zealand kaka, and large populations of brown kiwi (Apteryx australis) and blue duck (Hymenolaimus malacorhynchos). The area to the south of the plateau and down to Wellington is home to a variety of lizards including Whitaker's skink (Cyclodina whitakeri), forest gecko (Hoplodactylus granulatus) and Wellington green gecko (Naultinus elegans punctatus). Wetlands throughout the region support waterbirds and fish including the endemic brown mudfish.
Threats and preservation
The lowland areas are quite highly populated and therefore urban development, agriculture and forestry are a major threat to natural habitats there. One block of lowland forest remains in and around Whanganui National Park and large areas of the uplands are protected either by Maori tradition or in national parks of which Te Urewera is the largest. The four North Island national parks, which surround the plateau, are Te Urewera, Whanganui, Egmont and New Zealand's first national park, the World Heritage listed Tongariro National Park. Introduced species and livestock grazing are now major threats to some endemic species. Rats, cats and stoats prey on native reptiles and birds (including the kokako, blue duck and brown kiwi), while imported plants such as old man's beard, banana passionfruit and gorse can take over from indigenous species. Finally grazing by goats and possums can eradicate others such as kamahi, kaikawaka (Libocedrus bidwillii) and mountain tōtara. Therefore, smaller islands off the coast of Wellington have been used as a refuge for North Island birds and reptiles whose habitats may be threatened now or in the future.
Also the Volcanic Plateau region has the largest area of man made forest in the Southern Hemisphere. Nearly all the trees are Pinus radiata which were bought in for trials at Rotorua in 1899 from Kew Gardens, London. The tree, a native of Monterey, California, grew very fast in the poor soils. Mass planting was initially carried out by prisoners in the 1920s and then by the unemployed on a large scale during the Great Depression. After World War II scientists from Norway settled in the region and helped develop ways of treating the soft pine to prevent rotting using pressure treatment with chemicals. They also introduced selective breeding methods which was the standard way of improving the trees until tissue culture was introduced in the 1990s. Trees take 25–30 years to reach full height. Most plantations use growth factor (GF) trees to guarantee very high quality (straight and knot-free) timber, however treatment by chemical salts is still required to stop rotting. This is done by either dipping or more usually, pressure treatment. New Zealand has pioneered the use of Radiata timber and plywood in small craft boatbuilding. Untreated clear timber or plywood is used that is then encapsulated in epoxy resin after construction. The key reason is the low cost of the wood rather than any inherent properties of the wood which is of moderate weight but fractures easily when bent, when dried to 12% moisture. One of the largest ply factories in New Zealand is located on the Volcanic Plateau at Tokoroa. Although planting by hand is still done on steeper land, most seedlings are now planted with the help of machines.
Urban areas in the region include the towns of Taihape in the south, Ohakune the carrot-growing capital of NZ in the west, and Taupō in the north, with Tūrangi a major trout fishing base at the south of Lake Taupō and by the Kaweka Ranges in the east, The majority of the population of the area lives close to the shores of Lake Taupō, with some smaller settlements to the east of the volcanoes. These make their living largely through tourism, including skiing in the winter season, trout fishing, especially on the Tongariro river or by forestry in the plateau's northeast, which includes the Kaingaroa Forest or by working on the extensive hydro electric power system.
History
The Māori population during the Archaic period was sparse. Only two moa hunter period sites have been discovered to date. The best known is the Whakamoenga cave near Taupō. The cave was in use about 600 years ago and three moa bones, obsidian flakes, hollow pumice stone ash holders, pumice floats, a fishing net, bird spears, pieces of hue (gourd) and bracken remains have been found. The other moa hunter site is at Tokoroa.[12]
The tangata whenua are the Ngāti Tūwharetoa. Their paramount chief is Sir Tumu te Heuheu. They moved into this area after splitting away from the Arawa tribe on the east coast. The boundary between Arawa and Tuwharetoa is a small island 400 metres north of Huka Falls on the Waikato River. Their main marae is on the southern shores of Lake Taupō at Waihi near the Tokaanu geothermal area. They still retain ownership of the peaks of the mountains which are considered sacred, as well as the Ketetahi hot springs on the north slope of Mt Tongariro. The Māori people considered the volcanoes sacred and in traditional times wore woven flax eye shields to avoid looking at the peaks.
The Rangipo region is largely uninhabited. It is used by the New Zealand Army, based at Waiouru in the south, and by the Rangipo prison farm in the north and Rangipo underground HEP station to the east. During the 1960s the Tongariro Power Scheme redirected the flow of water from many of the streams and rivers that drain the central peaks. The water was channelled into canals, tunnels and storage lakes to provide water for 2 HEP stations at Rangipo and Tokaanu. The water then flowed into Lake Taupō increasing its input by 20%. Most of the Tongariro river flow is not included in the power scheme due to its importance as a breeding area for brown and rainbow trout. The extra water boosted the amount of water available to the 10 other HEP stations on the Waikato River which flows from the north end of the lake and is its only exit.
The productivity of pasture on the plateau was greatly improved in the 1950s once it was realised that the "bush sickness" suffered by local livestock was due to cobalt deficient volcanic soils. The diagnosis and cure for this was discovered by work of New Zealand scientists ( Grimmett and Shorland, senior chemists at the Department of Agriculture in 1934) who found that the iron ore which gave the best results contained significant amounts of cobalt, and went against popular wisdom by dosing animals with cobalt, with spectacular results. Australians Underwood and Filmer in 1936 confirmed this and solved a similar issue in cattle in Australia.[13] However the application of cobalt at the rate of 30cc per Ha was only possible after World War II making use of war surplus planes and ex WW2 pilots for aerial topdressing. The cobalt was mixed with crushed phosphate rock which was obtained cheaply from Nauru Island in the West Pacific. The resulting mix was called Super Phosphate.
The largest farm - as measured by effective area farmed - in the North Island including 13,800 hectares of land with about 9,500 hectares of developed farm land was established off the Taupō-Napier road and is called Lochinver Station. The station was largely developed by construction millionaire Bill Stephenson and his family using heavy earthmoving equipment in the 1960s and 1970s. In 2015 it was sold to Rimanui Farms after a bid by Chinese interests was blocked by the government.[14] The high country sheep and cattle station has several airstrips, 21 houses and 200 km of roading. It historically carried 100,000 breeding ewes and about 8,000 cattle but now carries about a third of these. It has extensive shelter belts of contorta pine, improved rye-grass pasture and grows crops of swedes and barley. It previously was open to tourist and school group bus tours.
Popular culture
Tourism is an economic mainstay of the region with a wide range of largely outdoor attractions from trout fishing, flyfishing on Tongariro River or harling on Lake Taupō, tramping, Mountain biking centred on National Park, deer or pig hunting, horse riding to snowskiing/boarding on Mt Ruapehu.
The Sir Edmund Hillary Outdoor Pursuits Centre of New Zealand is located on the site of an old Italian tunneling construction camp. Started by mountaineer Graeme Dingle in the 1970s, this centre offers valuable outdoor training experience and skills to secondary school groups and others.
The Raurimu Spiral is a railway spiral traveling upwards 122 m (400 ft) in 1.6 km (0.99 mi),[15] via tunnels and 180-degree hairpin bends so the passengers near the head of the train can see the rear carriages heading in the opposite direction.[16] At the time of construction it was considered a masterpiece of engineering.[16]:5 This was the last stage to be built in the main trunk railway line completed in 1908.[16]:{{{1}}}
Cold Kiwi Motorcycle Rally
The Cold Kiwi Motorcycle Rally, advertised as NZ's longest running motorcycle rally,[17] has been held on the Plateau since 1972.[18] The event is run by The Ruapehu Motorcycle Club in early September each year. Bikers sleep in their own tents despite the average temperature being −8 °C at night, but the club provides hot food and drinks, a bonfire, as well as competitions, souvenirs, live bands and toilet facilities.
Tongariro Alpine Crossing
The one-day Tongariro Alpine Crossing from the Mangatepopo Valley across Mt Ngāuruhoe and Mt Tongariro is named one of the greatest one-day walks in the world by the Department of Conservation. The 19.2 km track is well marked in summer and popular but trampers should be quite fit and well equipped as the route is exposed, especially during the winter months (April to September) when the route poles are sometimes hidden by snow or blown away. There are two well equipped huts near the ends of route. Detailed guidance is available from the Mt Ruapehu Department of Conservation Visitors Centre.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wilson, C. J. N.; Gravley, D. M.; Leonard, G. S.; Rowland, J. V. (2009) (in en). Volcanism in the central Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand: tempo,styles and controls. Geological Society of London. pp. 226–231. doi:10.1144/IAVCEl002.12. ISBN 9781862396241. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsl/books/book/1733/Studies-in-VolcanologyThe-Legacy-of-George-Walker.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Leonard, Graham S.; Cole, Rosie P.; Christenson, Bruce W.; Conway, Chris E.; Cronin, Shane J.; Gamble, John A.; Hurst, Tony; Kennedy, Ben M. et al. (2021-05-02). "Ruapehu and Tongariro stratovolcanoes: a review of current understanding" (in en). New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics 64 (2–3): 389–420. doi:10.1080/00288306.2021.1909080.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Odell, N. E. (1955). "Mount Ruapehu, New Zealand: Observations on its Crater Lake and Glaciers" (in en). Journal of Glaciology 2 (18): 601–605. doi:10.3189/002214355793702181. Bibcode: 1955JGlac...2..601O.
- ↑ "Hinuera Natural Stone". https://www.hinuera.co.nz/.
- ↑ "GUIDEBOOK FOR LAND AND LAKES FIELD TRIP". New Zealand Society of Soil Science. 2006-11-28. https://sciencedocbox.com/Geology/79493941-Land-and-lakes-guidebook-for-land-and-lakes-field-trip-tuesday-28-th-november-2006.html.
- ↑ Doherty, Angela Louise (2009). "Blue‐sky eruptions, do they exist? Implications for monitoring New Zealand's volcanoes.". University of Canterbury. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/35460853.pdf.
- ↑ "Geology and climate – Volcanic Plateau region". The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. 30 November 1999. http://www.teara.govt.nz/en/volcanic-plateau-region/2..
- ↑ "Multiple mistakes led to death on Tongariro Alpine Crossing, says coroner.". https://www.mountainsafety.org.nz/read/multiple-mistakes-led-to-death-on-tongariro-alpine-crossing-says-coroner/.
- ↑ "Love ancient forests Love Taupō". https://www.lovetaupo.com/en/discover/highlights/pureora-forest-park.
- ↑ "Geothermal plants". https://www.nzpcn.org.nz/ecosystems/plant-communities/scrub-shrublands/geothermal/geothermal-plants/.
- ↑ "North Island temperate forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. http://worldwildlife.org/ecoregions/aa0405.
- ↑ Anne Leahy Study, University of Auckland, 1962/63
- ↑ Lowe, D. J.; Balks }first2= M. R. (2019). "Introduction to Tephra-Derived Soils and Farming, Waikato-Bay of Plenty, North Island, New Zealand". https://researchcommons.waikato.ac.nz/bitstream/handle/10289/12297/Lowe%20and%20Balks%202019%20Intro%20to%20tephra-derived%20soils%20and%20farming%2c%20NZ_final.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y.
- ↑ "Lochinver Station sold to New Zealand company Rimanui Farms". 2015-11-05. https://www.stuff.co.nz/business/industries/73743157/lochinver-station-sold-to-new-zealand-company-rimanui-farms.
- ↑ Wright, Matthew. "Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand: Engineering, 19th-century engineering". https://teara.govt.nz/en/engineering/page-2.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 McPherson, C.; Astwood, K. (8 February 2012). "IPENZ Engineering Heritage Register Report: Raurimu Spiral". https://d2rjvl4n5h2b61.cloudfront.net/media/documents/raurimu_spiral_register_report.pdf.
- ↑ [1], www.coldkiwi.co.nz
- ↑ Cold Kiwi , www.kiwibiker.co.nz
- Geology - South Auckland Land District, from An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand, edited by A. H. McLintock, originally published in 1966. Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, updated 26 September 2006. Accessed 2007-07-06.
- Landscape - North Island, from An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand, edited by A. H. McLintock, originally published in 1966. Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, updated 26 September 2006. Accessed 2007-07-06.
- Chapters 1-3, The Volcanic Plateau, District Report 07, Rangahaua Whanui, Waitangi Tribunal. Accessed 2007-07-06.
- Ignimbrite cliffs, from Eileen McSaveney and Simon Nathan.
- 'Geology – overview', Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, updated 13 April 2007. Accessed 2007-07-06.
- Tony Nightingale. 'Government and agriculture - State-funded research', Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, updated 20 November 2008.
 |




