Engineering:Kosmos 690
 Bion spacecraft | |
| Names | Бион 2 Космос 690 Bion 2 Biocosmos 2 Biokosmos 2 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Bioscience |
| Operator | Institute of Biomedical Problems |
| COSPAR ID | 1974-080A |
| SATCAT no. | 07478 [1] |
| Mission duration | 20.5 days |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Bion 2 |
| Spacecraft type | Bion |
| Bus | Zenit |
| Manufacturer | TsSKB Progress |
| Launch mass | 5,500 kg (12,100 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 20 October 1974, 17:59:59 UTC[2] |
| Rocket | Soyuz-U s/n K15000-010 |
| Launch site | Plesetsk, Site 43/4 |
| Contractor | TsSKB |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Recovered |
| Landing date | 12 November 1974, 04:48:00 UTC |
| Landing site | Steppes of Kazakhstan, Soviet Union |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit[3] |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 223 km (139 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 389 km (242 mi) |
| Inclination | 62.80° |
| Period | 90.40 minutes |
Kosmos 690 (in Russian: Бион 2, Космос 690), or Bion 2, was a Bion satellite launched by the Soviet Union.
Launch
Kosmos 690 was launched on 22 October 1974, at 17:59:59 UTC from Plesetsk Cosmodrome with a Soyuz-U launch vehicle. It was placed in low Earth orbit, with perigee of 223 km (139 mi), apogee of 389 km (242 mi) and orbital inclination of 62.80°, and orbital period of 98.40 minutes.[3]
Spacecraft
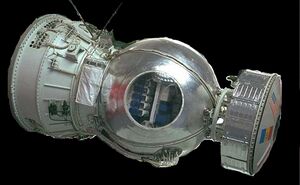
The spacecraft was based on the Zenit spy satellite with emphasis on studying the problems of radiation effects on human beings.
It carried albino rats for biomedical research. Scientists from Czechoslovakia, Romania and Soviet Union subjected the rats to daily radiation doses from a gamma source by ground command. When they were recovered 21 days later, many rats had developed lung problems and their blood and bone marrow had changed more than those of control specimens. It had an on-orbit dry mass of 5,500 kg (12,100 lb).[4][5]
An instrument module in the form of 2 connected truncated cones, weighing 2,400 kg (5,300 lb), 2.43 m (8 ft 0 in) in diameter and 2.25 m (7 ft 5 in) in length, carries in most of the auxiliary instrumentation in the hermetized part. Outwardly, ball valves with compressed nitrogen are attached to the gas nozzles of the stabilizer system. At the rear, the TDU-1 braking engine is located at a stroke of 15.83 kN and a maximum operating time of 45 seconds. Hypergolic KPL delivers a turbo pump to the combustion chamber. An auxiliary container containing chemical batteries and additional experiments, cylindrical with a diameter of 1.90 m (6 ft 3 in) and a height of 0.90 m (2 ft 11 in) is placed above the return module and dumped approximately a day before the landing.
Mission
After 21 days, Kosmos 690 returned to Earth and landing in Kazakhstan on 12 November 1974. The return module, weighing 3,100 kg (6,800 lb) and 2.3 m (7 ft 7 in) in diameter, was covered with an ablative thermal shield 3 to 18 cm thick.[5]
See also
- 1974 in spaceflight
- Kosmos (satellite)
References
- ↑ "Cosmos 690". N2yo.com. http://www.n2yo.com/satellite/?s=7478.
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Report. http://www.planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Trajectory: Bion 2 1974-080A". NASA. 14 May 2020. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/displayTrajectory.action?id=1974-080A.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ Mark Wade (2011) Bion Encyclopedia Astronautica Retrieved 2016-06-10
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Display: Bion 2 1974-080A". NASA. 14 May 2020. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1974-080A.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
Bibliography
- Kozlov, D. I. (1996), Mashnostroenie, ed.; Konstruirovanie avtomaticheskikh kosmicheskikh apparatov, Moscow, ISBN
- Melnik, T. G. (1997), Nauka, ed.; Voenno-Kosmicheskiy Sili, Moscow. ISBN
- "Bion' nuzhen lyudyam", Novosti Kosmonavtiki (6): 35, 1996
 |
