Engineering:List of man-portable anti-tank systems
The following is a list of MANPATS.
Three main categories of MANPATS are in use, which are split into the following lists.
- Rocket launchers launch unguided self-propelled projectiles.
- Recoilless weapons launch unguided projectiles. They are accelerated by ejecting a counter-mass, such as a propellant gas, from the weapon's rear. There are two categories of recoilless weapons:
- Recoilless rifles have a rifled barrel and use spin stabilised projectiles (example: Carl Gustav 8.4 cm)
- Recoilless guns are smoothbore and shoot fin stabilised projectiles (examples: AT4, MATADOR RGW 90)
- Anti-tank guided missiles (ATGM)
Modern era MANPATS
List of rocket launchers that entered service after the end of the Cold War (since 1990).
| System name | Manufacturers and designers | Image | Origin | Use | In service since | Warhead calibre | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rocket launchers | |||||||
| MARA | CITEFA /
Fray Luis Beltrán munition factory |

|
Disposable | 2005 | 78 mm | [1] | |
| PF-89 | Norinco
(China North Industries Corporation) |

|
Disposable | 1993 | 80 mm | 5 warheads (HEAT, incendiary, HESH, HEAT tandem, HEAT/thermobaric tandem)[2][3] | |
| Panzerfaust 3 | Dynamit Nobel AG | 
|
Reusable | 1997 | 110 mm | Development started in 1978 | |
| M72E5 LAW | Nammo Raufoss AS in cooperation with Talley Defense (absorbed into Nammo in 2007) | 
|
Disposable | 1983[5] | 66 mm | Many variants in continuous production[6] | |
| Yasin (RPG) | Hamas | — | Reusable | 2004 | 85 mm | It is a variant of the RPG-2[7] | |
| MRO | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 2003 | 72.5 mm | Further evolution of the RPO-A Shmel
Variants:
| |
| RPG-28 | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 2011 | 125 mm | [9] | |
| RPG-30 | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 2013 | 105 mm | [10] | |
| RPG-32 Barkas | NPO Bazalt | — | Reusable | 2012 | 72.5 mm /
105 mm |
JADARA is producing it as well under license. | |
| RShG-2 "Agleni-2", or
6G31 |
NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 2003 | 72.5 mm | Evolution to the RPG-26, using a larger warhead, and a derivative of the TBG-7V thermobaric rocket for the RPG-7[12] | |
| Alcotán-100 (M2) | Instalaza SA | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1998 | 100 mm | Variants[13]
| |
| CS-70 | Instalaza SA | — | Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2023 | 72 mm | — | |
| C90-CR (M3) | Instalaza SA | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1990 | 90 mm | Warhead variants:[14]
| |
| Kestrel | NCSIST | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2015 | 110 mm | Variants:[15] | |
| PSRL-1 | AirTronicUSA | 
|
Reusable | 2017 | 93 mm | American RPG-7, warhead variants:
| |
| VE-NILANGAL | CAVIM | — | — | — | 72 mm | — | |
| Recoilless rifles | |||||||
| Carl Gustaf M4 | Saab Bofors Dynamics | 
|
Reusable | 2014 | 84 mm | [17] | |
| Recoilless guns | |||||||
| PF-98 | Norinco
(China North Industries Corporation) |

|
Reusable | 1998 | 120 mm | Successor of the Type 78 in the PLA[18][19] | |
| RGW 60 | Dynamit Nobel AG | 
|
Disposable | — | 60 mm | 4 warheads HEAT, HEAT MP (Multi-Purpose), HESH, ASM (Anti Structure Munition)[20] | |
| RGW 90 MATADOR | Dynamit Nobel AG
DSTA Rafael Advanced Defense Systems |

|
Disposable | 2000 | 90 mm | [21] | |
| RGW 110 | Dynamit Nobel AG | — | Disposable | 2023 | 110 mm | Hungary, first client of this weapon, contract 2022[22][23] | |
| Anti-tank guided missiles | |||||||
| Shershen | CJSC SRPC,
JSC Peleng. |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2012 | 130 mm
152 mm |
Belarus licensed variants of Stugna-P / Skif[24] | |
| MSS-1.2 | SIATT | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2009 | 127 mm | OTO Melara initially co-developed the missile, starting in 1985, but withdrew from the program and ceded its share[25] | |
| HJ-12 Red Arrow | Norinco
(China North Industries Corporation) |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2021 | 130 mm | [26] | |
| Eryx | Aérospatiale then,
MBDA France now |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1993 | 136 mm | [27] | |
| Akeron MP | MBDA France Saab Bofors Dynamics Switzerland |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2017 | 140 mm | The missile design is French, the warhead is close to the one of the NLAW, developed and manufactured by Saab in Switzerland (former RUAG) | |
| PARS 3 MR | MBDA Deutschland, Diehl BGT Defence |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | Cancelled | 159 mm | France, the UK and the Netherlands withdrew from the common development program.[31]
Infantry variant therefore cancelled, only the PARS-3 LR variant used by German Army Tiger Helicopter. | |
| MBDA Deutschland | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2024 | 90 mm | A light guided missile, with some potential alternative variants are to be developed.[32]
TDW warhead. | ||
| Amogha missile | Bharat Dynamics Limited | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | In development | — | 3 variants[33] | |
| MPATGM | DRDO
VEM Technologies |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2023-4 | 120 mm | [34][35] | |
| Spike | Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 
Spike LR |
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | — | 110 mm
130 mm |
Multiple variants that are in this MANPATS category:
| |
| Type 01 LMAT
(or XATM-5) |
Defense Agency Technical Research and Development Institute | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2001 | 140 mm | [36] | |
| Terminator | Jadara EDS,
KADDB |
— | Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2020 | 107 mm | Partnership with Azerbaijan in discussion[37] | |
| Pirat PPK
Light ATGM |
Kyiv Design Bureau "Luch",
Mesko, CRW Telesystem-Mesko |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2025 | 107 mm | Ordered by Poland[38] | |
| MOSKIT
Long range ATGM |
Kyiv Design Bureau "Luch",
Mesko, CRW Telesystem-Mesko |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2025 | — | Ordered by Poland[38] | |
| 9M133 Kornet | Degtyarev plant,
KBP Instrument Design Bureau |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1998 | 152 mm | Five variants used (HEAT, thermobaric, or blast fragmentation warheads)[39] | |
| AT-1K Raybolt | Hanwha Defense
LIG Nex1 |
File:(K-weapon source) 전차잡는 빛의 화살 현궁(Raybolt) 1편.webm | Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2017 | 150 mm | [40] | |
| RBS 56 BILL 2 | Saab Bofors Dynamics | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1999 | 150 mm | Major upgrade with OTA capacity with special warhead made by RUAG.[41]
Saab acquired the designer / manufacturer of the warhead in 2007 and maintained the activity locally.[42] | |
| NLAW | Saab Bofors Dynamics Saab Bofors Dynamics Switzerland Thales Air Defence UK |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2009 | 150 mm | [43] | |
| Karaok | Roketsan | — | Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2022 | 125 mm | [44][45] | |
| OMTAS | Roketsan | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2017 | 160 mm | [46] | |
| Stugna-P | Kyiv Design Bureau "Luch" | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2011 | 130 mm | [47] | |
| RK-3 Corsar | Kyiv Design Bureau "Luch" | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2017 | 107 mm | [48] | |
| LMM Martlet | Thales Air Defence | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2021 | 76 mm | Multi-role missile, usable against air targets, light boats, and armoured vehicles, laser guided. The anti-armout surface-to-surface variant isn't its primary role though[49] | |
| FGM-148 Javelin | Texas Instruments Martin Marietta (now Raytheon Technologies & Lockheed Martin) |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1996 | 127 mm | [50] | |
| FGM-172 SRAW | Lockheed Martin | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 2002 | 193 mm | Only 960 produced, used by USA and Israel, remained 4 years in service[51] | |
Cold War era MANPATS
List of MANPATS that entered service during the Cold War (1946–1989).
| System name | Manufacturers and designers | Image | Origin | Use | In service since | Warhead calibre | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rocket launchers | |||||||
| FHJ-84 | Norinco
(China North Industries Corporation) |
— | Reusable | 1984 | 62 mm | [52] | |
| Type 69 RPG | Norinco
(China North Industries Corporation) |

|
Reusable | 1970 | 85 mm | ||
| RPG-75 | Zeveta a.s. | 
|
Disposable | 1975 | 68 mm | [53] | |
| AC 300 Jupiter | Luchaire SA MBB |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | Mid 1980s | 115 mm | A MILAN 2 warhead was mounted to an Armbrust launcher, but never placed in production | |
| Dard 120 | Societe Europeenne de Propulsion
(which became SNECMA) |
— | Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | Mid 1980s | 120 mm | Competition lost with the Jupiter 300 against the APILAS for a rocket launcher with more power than the LRAC F1.[55]
The French Army has used it, but more information is needed. Evolution of the DARD 90, very similar to LRAC F1. | |
| LRAC F1 | Luchaire SA /
Manufacture Nationale d'Armes de Saint-Etienne |

|
Reusable | 1972 | 89 mm | [56] | |
| LRAC 73 mm Modèle 1950 | — | 
|
Reusable | 1950 | 73 mm | Development financed by the Marshall Plan[57] | |
| SARPAC | Hotchkiss-Brandt | 
|
Disposable | 1975 | 68 mm | Limited production[58] | |
| WASP 58 | Luchaire SA | — | Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1987 | 58 mm | [59] | |
| Panzerfaust 2 /Panzerfaust 44 mm | Dynamit Nobel AG | 
|
Reusable | 1963 | 44 mm | HEAT warhead named Panzerfaustgeschoß DM32 | |
| ARIS IV | Elliniki Biomihania Oplon | — | Disposable | Cancelled | 113 mm | [61] | |
| B-300 | Israel Military Industries | 
|
Reusable | 1980 | 82 mm | [62] | |
| RPG-76 Komar | Zakład Sprzętu Precyzyjnego | 
|
Disposable | 1985 | 40 mm
68 mm |
[63] | |
| RPG-2 | Kovrov Mechanical Plant | 
|
Reusable | 1949 | 82 mm | [64] | |
| RPG-7 | NPO Bazalt and
ZiD |

|
Reusable | 1961 | 40 – 105 mm | Many variants of warheads in service[65] | |
| RPG-16 | NPO Bazalt | — | Reusable | 1976 | 58.3 mm | Used mostly by special forces[66] | |
| RPG-18 | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 1972 | 64 mm | [67] | |
| RPG-22 | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 1985 | 72.5 mm | [68] | |
| RPG-26 | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 1985 | 72.5 mm | [69] | |
| RPG-27 | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Disposable | 1989 | 105 mm | [70] | |
| RPG-29 | NPO Bazalt | 
|
Reusable | 1989 | 105 mm | [71] | |
| LAW 80 | Hunting Engineering | 
|
Disposable | 1987 | 94 mm | [72] | |
| FGR-17 Viper | General Dynamics | 
|
Disposable | 1983 | 70 mm | Poor performance, few delivered, quickly cancelled, the Army requirements were the source of the result[73] | |
| M202A1 FLASH | Northrop Corporation (Electro-Mechanical Division) | 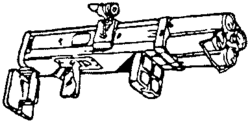
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1978 | 4 × 66 mm | Multiple-barrel incendiary rocket launcher[74] | |
| M72 LAW | Talley Defense Systems | 
|
Disposable | 1963 | 66 mm | [75] | |
| MK-153 (SMAW) | McDonnell Douglas
Talley Defense Systems |

|
Reusable | 1984 | 83 mm | Derivative of IMI B-300[76] | |
| M80 Zolja | Sloboda | 
|
Disposable | 1980 | 64 mm | [77] | |
| Recoilless rifles | |||||||
| Carl Gustaf M1 – M3 | Saab Bofors Dynamics(at first, Carl Gustafs stads gevärsfaktori) | 
|
Reusable | 1946 | 84 mm | [17] | |
| Miniman | Saab Bofors Dynamics | 
|
Reusable | 1968 | 74 mm | [78] | |
| RAK 74 "Raketenrohre NORA" | Waffenfabrik Bern | — | Reusable | 1974 | 83 mm | Project abandoned[79] | |
| M40 recoilless rifle | Watervliet Arsenal | 
|
Reusable | 1955 | 105 mm | [80] | |
| Recoilless guns | |||||||
| APILAS"Armour Piercing Infantry Light Arm System" | GIAT | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1985 | 112 mm | Also known as "RAC 112" in the French Army. | |
| Armbrust | Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm | 
|
Disposable | 1978 | 67 mm | [83] | |
| RPO-A Shmel | Tula (now KDB) | 
|
Disposable | 1980s | 93 mm | [8] | |
| AT4 | Saab Bofors Dynamics | 
|
Disposable | 1987 | 84 mm | [84] | |
| Raketenrohr 80 | Société Anonyme Constructions Mécaniques du Léman (CML) | 
|
Reusable | 1980 | 83 mm | [79] | |
| Anti-tank guided missiles | |||||||
| Mathogo | CITEFA | 
|
— | 1978 | 102 mm | [85] | |
| HJ-8 | Norinco
(China North Industries Corporation) |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1984 | 120 mm | [86] | |
| SS.10 | Nord Aviation | 
|
— | 1955 | 160 mm | [87] | |
| ENTAC | DTAT
Aérospatiale |

|
— | 1957 | 152 mm | [87] | |
| MILAN | At first made by Euromissile (JV Aérospatiale and DaimlerChrysler Aerospace AG),
now MBDA |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1972 | 103 mm,
115 mm |
Made under licence by Bharat Dynamics (India) and BAe Dynamics (United Kingdom) | |
| MAPATS
(or "Hutra") |
IMI Systems | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1985 | 156 mm | [89] | |
| Type 64 MAT
(or KAM-3) |
Defense Agency Technical Research and Development Institute | 
|
— | 1964 | 120 mm | [90] | |
| Type 79 Jyu-MAT
(or KAM-9) |
Defense Agency Technical Research and Development Institute
Daicel |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1984 | 153 mm | [91] | |
| Type 87 Chū-MAT
(or Shin Chu-MAT) |
Defense Agency Technical Research and Development Institute
Mitsubishi Motors |

|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1989 | 110 mm | [92] | |
| ZT3 Ingwe | Denel Dynamics | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1987 | 127 mm | [93] | |
| 9M14 Malyutka | Tula Machinery Design Bureau (Tula KBP) | 
|
— | 1963 | 125 mm | [94] | |
| 9K111 Fagot | Tula Machinery Design Bureau (Tula KBP) | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1970 | 120 mm | [95] | |
| 9M113 Konkurs | Tula Machinery Design Bureau (Tula KBP) – Tulsky Oruzheiny Zavod | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1974 | 135 mm | [96] | |
| 9K115 Metis | Tula Machinery Design Bureau (Tula KBP) – Tulsky Oruzheiny Zavod | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1982 | 94 mm | [97] | |
| RBS 56 BILL | Bofors | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1988 | 150 mm | [41] | |
| RB 53 Bantam | Bofors | 
|
Reusable | 1963 | 110 mm | [98] | |
| Cobra | Contraves AG Oerlikon, Bölkow |

|
— | 1957 | 100 mm | Considered as most effective anti-tank missile in the 50s[99] | |
| Mamba | Contraves AG Oerlikon, Bölkow |

|
— | 1957 | 120 mm | [99] | |
| Mosquito | Contraves AG Oerlikon, Bölkow |

|
— | 1964 | 120 mm | Licensed produced in Italy (Contraves Italiana SpA)[100] | |
| Vigilant | Vickers | Reusable | 1963 | 131 mm | [101] | ||
| BGM-71 TOW | Hughes Aircraft Company | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1970 | 152 mm | [102] | |
| M47 Dragon | Raytheon | 
|
Fire unit resuable, tube disposable | 1975 | 127 mm | [103] | |
Second World War era rocket launchers
List of rocket launchers that entered service during World War II (1939–1945).
| System name | Manufacturers and designers | Image | Origin | Use | In service since | Warhead calibre | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rocket launchers | |||||||
| 44M Buzogányvető | Weiss Manfréd Factory | 
|
Reusable | 1944 | — | One of the most effective anti-tank weapon during WW2 | |
| Type 4 | Unknown | 
|
Reusable | 1944 | 70 mm | ||
| PanzerschreckRaketenpanzerbüchse 54 | Enzinger Union, HASAG and Jackel |  
|
Reusable | 1943 | 88 mm | [104] | |
| M1 Bazooka | Several manufacturers over time | 
|
Reusable | 1942 | 60 mm | [105] | |
| M20 Super bazooka | Several manufacturers over time | 
|
Reusable | 1945 | 89 mm | [106] | |
| Recoilless rifles | |||||||
| Carl Gustaf 20 mm recoilless rifle | Carl Gustafs stads gevärsfaktori | 
|
Reusable | 1942 | 20 mm | [107] | |
| Recoilless guns | |||||||
| Panzerfaust | HASAG, Werk Schlieben | 
|
Disposable | 1942 | 100mm
106 mm 149 mm |
[108] | |
| Anti-tank missiles | |||||||
| X-7 Rotkäppchen (de) | Ruhrstahl AG (de) | 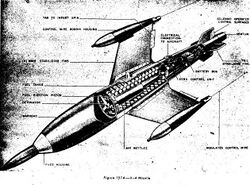 X-7 missile based on air-to-air X-4 shown above, modifications on the tail, remote controlled X-7 missile based on air-to-air X-4 shown above, modifications on the tail, remote controlled
|
Fire unit resuable | 1945 | 150 mm | First anti-tank missile, few reports of its use on the Eastern Front, but seems successful.[109] | |
| Other category | |||||||
| PIAT | Imperial Chemical Industries | 
|
Reusable | 1942 | 83 mm | [110] | |
References
- ↑ "MARA Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/mara.htm.
- ↑ "PF-89 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/pf_89.htm.
- ↑ "CAT-UXO – 80mm pf 89 rocket" (in en). https://cat-uxo.com/explosive-hazards/rockets/80mm-pf-89-rocket.
- ↑ "Panzerfaust 3 – Dynamit Nobel Defence GmbH" (in de-DE). https://dn-defence.com/schulterwaffen/panzerfaust-3/.
- ↑ D. Kyle, Armed Forces Journal International, November 1983, "Viper Dead, Army Picks AT-4 Antitank Missile", page 21
- ↑ "M72 Enhanced Capacity" (in en-US). https://www.nammo.com/product/our-products/shoulder-fired-systems/m72-series/m72-enhanced-capacity/.
- ↑ "Yasin Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/yasin.htm.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "RPO-A Shmel Thermobaric Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpo_a_shmel.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-28 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_28.htm.
- ↑ TAB (2022-10-23). "RPG-30: Russia's Dual Tube Rocket Launcher" (in en). https://armourersbench.com/2022/10/23/rpg-30-russias-dual-tube-rocket-launcher/.
- ↑ "RPG-32 Barkaz Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_32.htm.
- ↑ "RShG-2" (in en). https://weaponsystems.net/system/1072-RShG-2.
- ↑ "ALCOTAN-100 (M2)" (in en-US). 2023-06-15. https://instalaza.com/producto/alcotan/?lang=en.
- ↑ "C90 Family" (in en-US). https://instalaza.com/c90/?lang=en.
- ↑ "NCSIST". https://www.ncsist.org.tw/eng/csistdup/products/product.aspx?catalog=41&product_id=284.
- ↑ "AirTronic USA | AirTronic PSRL-1 USA" (in en). https://airtronic-usa.com/products/airtronic-rpg-7-usa/.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Carl-Gustaf system is a weapon system that is a recoilless and also a multi-purpose weapon system" (in en). https://www.saab.com/products/carl-gustaf-m4.
- ↑ "PF-98 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/pf_98.htm.
- ↑ "An Introduction To The PF-98 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher" (in en). 2016-03-25. https://21stcenturyasianarmsrace.com/2016/03/25/an-introduction-to-the-pf-98-anti-tank-rocket-launcher/.
- ↑ "RGW 60 – Dynamit Nobel Defence GmbH" (in de-DE). https://dn-defence.com/rgw-60/.
- ↑ "RGW 90 – Dynamit Nobel Defence GmbH" (in de-DE). https://dn-defence.com/rgw-90/.
- ↑ ESD (2022-12-15). "Hungary to Become the First Customer for DND RGW 110" (in en-US). https://euro-sd.com/2022/12/news/28730/hungary-to-become-the-first-customer-for-dnd-rgw-110/.
- ↑ "RGW 110". https://dn-defence.com/schulterwaffen/rgw-110-2/.
- ↑ Sof, Eric (2023-06-26). "Shershen ATGM: A Belarusian version of Skif with additional capabilities" (in en-US). https://special-ops.org/shershen-atgm/.
- ↑ "MSS 1.2 Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/mss_1_2.htm.
- ↑ "HJ-12 Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/hj_12.htm.
- ↑ "Eryx Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/eryx.htm.
- ↑ "MMP Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/mmp.htm.
- ↑ "Saab Signs Warhead Contract" (in en). https://www.saab.com/newsroom/press-releases/2015/saab-signs-warhead-contract.
- ↑ Valpolini, Paolo (2022-11-14). "Saab further develops its knowledge in warhead technology" (in en-GB). https://www.edrmagazine.eu/saab-further-develops-its-knowledge-in-warhead-technology.
- ↑ "Trigat MR/Trigan" (in en-US). https://www.army-technology.com/projects/mr_trigat/.
- ↑ "ENFORCER | MOUNTED AND DISMOUNTED, Battlefield Engagement" (in en-US). https://www.mbda-systems.com/product/enforcer/.
- ↑ "AMOGHA – III ATGM | BHARAT DYNAMICS LIMITED INDIA". https://bdl-india.in/amogha.
- ↑ "India successfully tests man-portable anti-tank guided missile: All you need to know about it" (in en). 2022-01-12. https://www.firstpost.com/india/india-successfully-tests-man-portable-anti-tank-guided-missile-all-you-need-to-know-about-it-10278551.html.
- ↑ "Aero India 2023: DRDO plans lightweight MPATGM" (in en). https://www.janes.com/defence-news/news-detail/aero-india-2023-drdo-plans-lightweight-mpatgm.
- ↑ "XATM-5 Light Anti-Tank Missile". 2009-08-26. http://www.fas.org/man/dod-101/sys/missile/row/atm-5.htm.
- ↑ "Jordan Can Now Build Anti-Tank Missiles" (in en). 2018-08-03. https://21stcenturyasianarmsrace.com/2018/08/03/jordan-can-now-build-anti-tank-missiles/.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "Ukraine conflict: Russia's invasion raises short-term consequences for Poland's defence capabilities" (in en). https://www.janes.com/defence-news/news-detail/ukraine-conflict-russias-invasion-raises-short-term-consequences-for-polands-defence-capabilities.
- ↑ "Kornet Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/kornet.htm.
- ↑ "South Korea Can Export The Raybolt (Almost) Anywhere" (in en). 2022-07-21. https://21stcenturyasianarmsrace.com/2022/07/22/south-korea-can-export-the-raybolt-almost-anywhere/.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "RBS 56 BILL Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/bill.htm.
- ↑ "Saab becomes established in Switzerland" (in en). https://www.saab.com/newsroom/press-releases/2007/saab-becomes-established-in-switzerland.
- ↑ "NLAW - Anti-tank weapon" (in en). https://www.saab.com/products/nlaw.
- ↑ "KARAOK Omuzdan Atılan Tanksavar Füzesi | SavunmaSanayiST" (in tr). 2018-11-18. https://www.savunmasanayist.com/karaok-omuzdan-atilan-tanksavar-fuzesi/.
- ↑ Insight, Global Defense (2022-08-07). "Turkiye's Latest Anti Tank Guided Missile "KARAOK"" (in en-US). https://defensetalks.com/turkiyes-latest-anti-tank-guided-missile-karaok/.
- ↑ "Turkish army adopts home-grown anti-tank missile system". https://www.aa.com.tr/en/science-technology/turkish-army-adopts-home-grown-anti-tank-missile-system/838182.
- ↑ "Stugna-P Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/stugna_p.htm.
- ↑ "Korsar Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/korsar.htm.
- ↑ "Martlet ( Lightweight Multirole Missile) - Think Defence" (in en-GB). 2022-11-12. https://www.thinkdefence.co.uk/2022/11/martlet-lightweight-multirole-missile/.
- ↑ "Javelin Weapon System" (in en). https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/products/javelin.html.
- ↑ "Lockheed Martin FGM-172 SRAW". https://www.designation-systems.net/dusrm/m-172.html.
- ↑ "FHJ-84 Incendiary Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/fhj_84.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-75". 2016-03-07. http://www.saafmuseum.org/armament/310-rpg-75.
- ↑ note – AC300 Jupiter was a mid-1980s development of MBB of Germany and Luchaire of France where a MILAN 2 warhead was mounted to an Armbrust launcher, but never placed in production
- ↑ "DARD 120 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/dard_120.htm.
- ↑ "LRAC F1 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/lrac_f1.htm.
- ↑ LRAC 73 mm Mle 50 monsieur-legionnaire.org
- ↑ "SARPAC Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/sarpac.htm.
- ↑ "Wasp 58 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/wasp_58.htm.
- ↑ "Rocket, Anti-tank, Panzerfaust 44, Demonstration | National Air and Space Museum" (in en). https://airandspace.si.edu/collection-objects/rocket-anti-tank-panzerfaust-44-demonstration/nasm_A19890579000.
- ↑ "ARIS IV Anti-Tank Rocker Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/aris_4.htm.
- ↑ "IMI B-300". https://www.militaryfactory.com/smallarms/detail.php?smallarms_id=117.
- ↑ "RPG-76 Komar Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_76_komar.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-2 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_2.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-7 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_7.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-16 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_16.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-18 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_18.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-22 Single-Use Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_22.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-26 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_26.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-27 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_27.htm.
- ↑ "RPG-29 Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/rpg_29.htm.
- ↑ "LAW-80" (in en). https://weaponsystems.net/system/182-LAW-80.
- ↑ "FGR-17 Viper Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/fgr17_viper.htm.
- ↑ "M202 Multiple-Barrel Incendiary Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/m202.htm.
- ↑ "M-72 Light Anti-tank Weapon (LAW)". https://man.fas.org/dod-101/sys/land/m72.htm.
- ↑ "Mk.153 SMAW Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/mk153_smaw.htm.
- ↑ "Rocket launcher RBR 64 mm M80 - ZOLJA | EUROKOMPOZIT". 2018-01-09. http://www.eurokompozit.mk/product/en/rocket-launcher-rbr-64-mm-m80-zolja/.
- ↑ "Miniman Single-Use Anti-Tank Recoilless Rifle | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/miniman.htm.
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 Dok Panzerabwehr 2009 armeemuseum.ch
- ↑ "M40, 105 mm Recoilless Rifle | Estrella Warbird Museum". https://www.ewarbirds.org/armament/m40recoilless.shtml.
- ↑ "APILAS Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/firearms/apilas.htm.
- ↑ "RAC 112 APILAS". https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/europe/apilas.htm.
- ↑ "Armbrust" (in en). https://weaponsystems.net/system/1074-Armbrust.
- ↑ "AT4 Family | Saab" (in en). https://www.saab.com/products/at4.
- ↑ "Anti-tank Missiles - ATGMs" (in en-US). 2015-02-18. https://world-defense.com/threads/anti-tank-missiles-atgms.1317/.
- ↑ "HJ-8 Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/hj8.htm.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 "The United States Army | Redstone Arsenal Historical Information". https://history.redstone.army.mil/miss-entac.html.
- ↑ "MILAN Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/milan.htm.
- ↑ "MAPATS Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/mapats.htm.
- ↑ "Type 64 MAT" (in en). https://weaponsystems.net/system/1364-Type+64+MAT.
- ↑ "Defense & Security Intelligence & Analysis: IHS Jane's | IHS". 2017-10-19. http://articles.janes.com/notice.html.
- ↑ "Type 87 Chu-MAT" (in en). https://weaponsystems.net/system/1078-Type+87+Chu-MAT.
- ↑ "ZT3 Ingwe Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/ingwe.htm.
- ↑ "Malyutka (AT-3 Sagger) Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/malyutka.htm.
- ↑ "Fagot Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/fagot.htm.
- ↑ "Konkurs Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/konkurs.htm.
- ↑ "9K115 Metis" (in en). https://weaponsystems.net/system/89-9K115+Metis.
- ↑ Michael J.H. Taylor (1980). Missile's of the World. Charles Scribner's Sons. ISBN 0-684-16593-7.
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 "missile antichar sol-sol Oerlikon Cobra armée américaine | Le QG 1/72e de Twist Again". https://www.loutan.net/olivier/archives/2022/10/16/missile-antichar-sol-sol-oerlikon-cobra-armee-americaine/.
- ↑ "Mosquito ATGM". https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/europe/mosquito-atgm.htm.
- ↑ Forbat 2006, p. 262.
- ↑ "M-220 Tube-launched, Optically tracked, Wire-guided missile (TOW)". https://man.fas.org/dod-101/sys/land/tow.htm.
- ↑ "M47 Dragon Anti-Tank Guided Missile | MilitaryToday.com". https://www.militarytoday.com/missiles/m47_dragon.htm.
- ↑ https://www.facebook.com/stern+(2020-03-08).+"Panzerschreck – der wirksamste deutsche Panzerkiller war das Plagiat einer US-Waffe" (in de). https://www.stern.de/digital/technik/panzerschreck---der-wirksamste-deutsche-panzerkiller-war-das-plagiat-einer-us-waffe-9172948.html.
- ↑ "M1 (Bazooka) / (2.36-inch Rocket Launcher M1)". https://www.militaryfactory.com/smallarms/detail.php?smallarms_id=69.
- ↑ "M20 Super-Bazooka" (in en). 2011-03-27. https://modernfirearms.net/en/grenade-launchers/u-s-a-grenade-launchers/m20-super-bazooka-eng/.
- ↑ "Carl Gustav m/42" (in en). 2010-10-27. https://modernfirearms.net/en/anti-tank-rifles/sweden-anti-tank-rifles/carl-gustav-m42-eng/.
- ↑ "Die Panzerfaust – Geschichte einer deutschen Waffe" (in de). Mar 27, 2021. https://www.mdr.de/geschichte/ns-zeit/panzerfaust-hasag-wehrmacht-zweiter-weltkrieg-100.html.
- ↑ "X7 Rotkäppchen (Red Riding Hood) Anti-tank Missile". https://www.wehrmacht-history.com/luftwaffe/missiles/x7-rotkaeppchen-anti-tank-missile.html.
- ↑ "PIAT" (in en). 2011-04-10. https://modernfirearms.net/en/grenade-launchers/united-kingdom-grenade-launchers/piat-eng/.
Bibliography
- Forbat, John (2006). The 'Secret' World of Vickers Guided Weapons. Tempus. ISBN 0-7524-3769-0.
 |


