Engineering:Progress 6
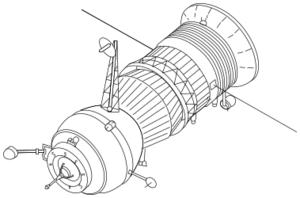 A Progress 7K-TG spacecraft | |
| Mission type | Salyut 6 resupply |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1979-039A |
| SATCAT no. | 11356[1] |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Progress (No.106) |
| Spacecraft type | Progress 7K-TG[2] |
| Manufacturer | NPO Energia |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 13 May 1979, 04:17:10 UTC[1] |
| Rocket | Soyuz-U[2] |
| Launch site | Baikonur, Site 31/6 |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Deorbited |
| Decay date | 9 June 1979, 18:52:46 UTC[3] |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Perigee altitude | 190 km[3] |
| Apogee altitude | 247 km[3] |
| Inclination | 51.6°[3] |
| Period | 88.8 minutes[3] |
| Epoch | 13 May 1979 |
| Docking with Salyut 6 | |
| Docking port | Aft[3] |
| Docking date | 15 May 1979, 06:19:22 UTC |
| Undocking date | 8 June 1979, 07:59:41 UTC |
Progress 6 (Russian: Прогресс 6) was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft. It which was launched in May 1979 to resupply the Salyut 6 space station.
Spacecraft
Progress 6 was a Progress 7K-TG spacecraft. The sixth of forty three to be launched, it had the serial number 106.[4][5] The Progress 7K-TG spacecraft was the first generation Progress, derived from the Soyuz 7K-T and intended for uncrewed logistics missions to space stations in support of the Salyut programme. On some missions the spacecraft were also used to adjust the orbit of the space station.[6]
The Progress spacecraft had a dry mass of 6,520 kilograms (14,370 lb), which increased to around 7,020 kilograms (15,480 lb) when fully fuelled. It measured 7.48 metres (24.5 ft) in length, and 2.72 metres (8 ft 11 in) in diameter. Each spacecraft could accommodate up to 2,500 kilograms (5,500 lb) of payload, consisting of dry cargo and propellant. The spacecraft were powered by chemical batteries, and could operate in free flight for up to three days, remaining docked to the station for up to thirty.[6]
Launch
Progress 6 launched on 13 May 1979 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR. It used a Soyuz-U rocket.[2][7]
Docking
Progress 6 docked with the aft port of Salyut 6 on 15 May 1979 at 06:19:22 UTC, and was undocked on 8 June 1979 at 07:59:41 UTC.[3][8]
Decay
It remained in orbit until 9 June 1979, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at 18:52:46 and the mission ended at 19:35 UTC.[3][8]
See also
- 1979 in spaceflight
- List of Progress missions
- List of uncrewed spaceflights to Salyut space stations
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Launchlog". Jonathan's Space Report. http://planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Progress 1 - 42 (11F615A15, 7K-TG)". Gunter's Space Page. https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/progress.htm.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 "Cargo spacecraft "Progress 6"". Manned Astronautics figures and facts. http://space.kursknet.ru/cosmos/english/cargoes/pr6.sht.
- ↑ Krebs, Gunter. "Progress 1 - 42 (11F615A15, 7K-TG)". Gunter's Space Page. http://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/progress.htm.
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. http://planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Hall, Rex D.; Shayler, David J. (2003). Soyuz: A Universal Spacecraft. Springer-Praxis. pp. 239–250. ISBN 1-85233-657-9.
- ↑ "Progress 6". NASA. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1979-039A.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Salyut 6". Astronautix. http://www.astronautix.com/s/salyut6.html.
 |
