Engineering:Progress 7K-TG
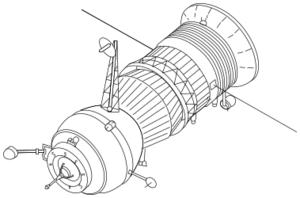 A Progress 7K-TG spacecraft | |
| Manufacturer | NPO Energia |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | USSR |
| Operator | NPO Energia |
| Applications | Space stations resupply |
| Specifications | |
| Design life | 33 to 75 days |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Production | |
| Status | Retired |
| Built | 43 |
| Launched | 43 |
| Retired | 43 |
| Maiden launch | Progress 1 (1978) |
| Last launch | Progress 42 (1990) |
| Last retirement | Progress 42 (1990) |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | Soyuz 7K-T |
| Derivatives | Progress-M |
Progress 7K-TG (Russian: Прогресс 7К-ТГ, GRAU index 11F615A15), was a Soviet uncrewed spacecraft used to resupply space stations in low Earth orbit. Forty three flew,[1] delivering cargo to Salyut 6, Salyut 7, and Mir.[2] It was the first version of the Progress spacecraft to fly, and spawned later derivatives including the Progress-M which replaced it, and the later Progress-M1.

The Progress 7K-TG spacecraft was derived from the crewed Soyuz 7K-T ferry spacecraft, which had been designed for the Salyut programme. The descent module of the Soyuz spacecraft was replaced with a new section designated Otsek Komponentov Dozapravki, or OKD. This contained fuel tanks and pumps used for refuelling the space station that it docked with. Like the Soyuz 7K-T, the Progress was not equipped with solar panels, and instead relied on batteries for power. Early spacecraft had a design life of 33 days, including three in free flight, and the rest docked with a space station. Later spacecraft flew longer missions, with the longest, Progress 38, spending almost 75 days in orbit.[2]
The first Progress 7K-TG spacecraft, Progress 1, was launched on 20 January 1978. The first twelve spacecraft flew to Salyut 6, with the next thirteen, including the Kosmos 1669 spacecraft - a Progress spacecraft which was given a Kosmos designation and omitted from the sequence of Progress designations - going to Salyut 7. The last eighteen flew to Mir. With the exception of Progress 20, all of the flights to Salyut stations were launched by Soyuz-U carrier rockets. Progress 20 and all of the Mir flights used the more powerful Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket.[1][3] The last spacecraft, Progress 42, was launched on 5 May 1990. It was deorbited on 27 May 1990, breaking up in the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean at around 12:27 UTC.[2]
Some Progress 7K-TG launches used the payload fairing developed for the Soyuz spacecraft, including the launch escape tower, but with the motors in the tower removed, and no stabilisers on the sides of the fairing. Officially this was done to preserve the rocket's aerodynamic properties, however it was reported that on several flights the tower was used to support tests of the K-36M ejection seat under development for the Buran programme.[2] In addition to their regular cargoes, the Progress 7 spacecraft was used to transport the KRT-10 radio telescope to Salyut 6, and Progress 17 delivered the Iskra 3 satellite to Salyut 7 for deployment.[1]
See also
- Automated Transfer Vehicle
- Cygnus spacecraft
- H-II Transfer Vehicle
- Soyuz programme
- SpaceX Dragon
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Krebs, Gunter. "Progress 1 - 42 (11F615A15, 7K-TG)". Gunter's Space Page. http://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/progress.htm.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Wade, Mark. "Progress". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/craft/progress.htm.
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. http://planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt.
 |

