Engineering:Reciprocating motion
From HandWiki
Short description: Repetitive back-and-forth linear motion
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (May 2022) |
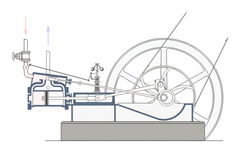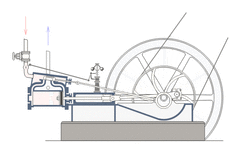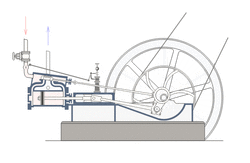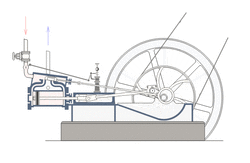
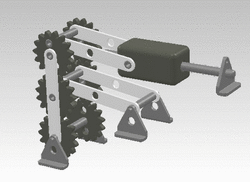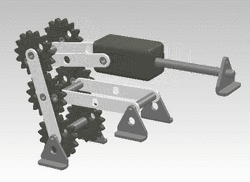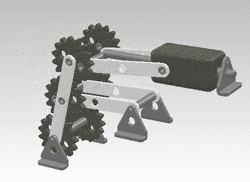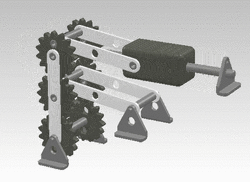
A crank can be used to convert into reciprocating motion, or conversely turn reciprocating motion into circular motion. [1]
For example, inside an internal combustion engine (a type of reciprocating engine), the expansion of burning fuel in the cylinders periodically pushes the piston down, which, through the connecting rod, turns the crankshaft. The continuing rotation of the crankshaft drives the piston back up, ready for the next cycle. The piston moves in a reciprocating motion, which is converted into the
See also
- Oscillation – Repetitive variation of some measure about a central value
- Engineering:Stroboscope – Instrument used to make a cyclically moving object appear to be slow-moving, or stationary
- Engineering:Reciprocating saw – Type of machine powered saw
- Engineering:Reciprocating engine – Engine utilising one or more reciprocating pistons
- Rotary reciprocating saw – Type of mechanical saw
- Agitation – Device or mechanism which shakes or stirs something
- Engineering:Scotch yoke – Mechanism to convert between rotational and reciprocating motion
- Crank – Simple machine transferring motion to or from a rotating shaft at a distance from the centreline
- Engineering:Crankshaft – Mechanism for converting reciprocating motion to rotation
- Engineering:Swashplate
- Engineering:Trip hammer – Type of blacksmithing tool
- Engineering:Slider-crank linkage – Mechanism for converting rotary motion into linear motion
- Physics:Straight line mechanism – Mechanisms generating real or approximate straight line motion
- Engineering:Reciprocating compressor – Device used to pump gases at high pressure
- Engineering:Sun and planet gear – Type of gear used in early beam engines
References
- ↑ Mobley, Keith R (2001). Plant Engineer's Handbook. USA: Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 723-755. ISBN 0 7506 7328 1.
 |
