Hyperbolastic functions

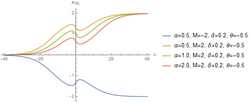
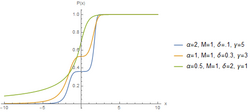

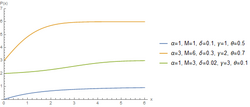
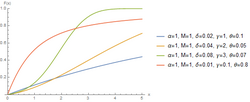
The hyperbolastic functions, also known as hyperbolastic growth models, are mathematical functions that are used in medical statistical modeling. These models were originally developed to capture the growth dynamics of multicellular tumor spheres, and were introduced in 2005 by Mohammad Tabatabai, David Williams, and Zoran Bursac.[1] The precision of hyperbolastic functions in modeling real world problems is somewhat due to their flexibility in their point of inflection.[1][2] These functions can be used in a wide variety of modeling problems such as tumor growth, stem cell proliferation, pharma kinetics, cancer growth, sigmoid activation function in neural networks, and epidemiological disease progression or regression.[1][3][4]
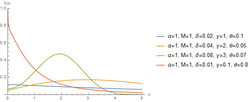
The hyperbolastic functions can model both growth and decay curves until it reaches carrying capacity. Due to their flexibility, these models have diverse applications in the medical field, with the ability to capture disease progression with an intervening treatment. As the figures indicate, hyperbolastic functions can fit a sigmoidal curve indicating that the slowest rate occurs at the early and late stages.[5] In addition to the presenting sigmoidal shapes, it can also accommodate biphasic situations where medical interventions slow or reverse disease progression; but, when the effect of the treatment vanishes, the disease will begin the second phase of its progression until it reaches its horizontal asymptote.
One of the main characteristics these functions have is that they cannot only fit sigmoidal shapes, but can also model biphasic growth patterns that other classical sigmoidal curves cannot adequately model. This distinguishing feature has advantageous applications in various fields including medicine, biology, economics, engineering, agronomy, and computer aided system theory.[6][7][8][9][10]
Function H1
The hyperbolastic rate equation of type I, denoted H1, is given by
where is any real number and is the population size at . The parameter represents carrying capacity, and parameters and jointly represent growth rate. The parameter gives the distance from a symmetric sigmoidal curve. Solving the hyperbolastic rate equation of type I for gives
where is the inverse hyperbolic sine function. If one desires to use the initial condition , then can be expressed as
- .
If , then reduces to
- .
In the event that a vertical shift is needed to give a better model fit, one can add the shift parameter , which would result in the following formula
- .
The hyperbolastic function of type I generalizes the logistic function. If the parameters , then it would become a logistic function. This function is a hyperbolastic function of type I. The standard hyperbolastic function of type I is
- .
Function H2
The hyperbolastic rate equation of type II, denoted by H2, is defined as
where is the hyperbolic tangent function, is the carrying capacity, and both and jointly determine the growth rate. In addition, the parameter represents acceleration in the time course. Solving the hyperbolastic rate function of type II for gives
- .
If one desires to use initial condition then can be expressed as
- .
If , then reduces to
- .
Similarly, in the event that a vertical shift is needed to give a better fit, one can use the following formula
- .
The standard hyperbolastic function of type II is defined as
- .
Function H3
The hyperbolastic rate equation of type III is denoted by H3 and has the form
- ,
where > 0. The parameter represents the carrying capacity, and the parameters and jointly determine the growth rate. The parameter represents acceleration of the time scale, while the size of represents distance from a symmetric sigmoidal curve. The solution to the differential equation of type III is
- ,
with the initial condition we can express as
- .
The hyperbolastic distribution of type III is a three-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with scale parameters > 0, and ≥ 0 and parameter as the shape parameter. When the parameter = 0, the hyperbolastic distribution of type III is reduced to the weibull distribution.[11] The hyperbolastic cumulative distribution function of type III is given by
- ,
and its corresponding probability density function is
- .
The hazard function (or failure rate) is given by
The survival function is given by
The standard hyperbolastic cumulative distribution function of type III is defined as
- ,
and its corresponding probability density function is
- .
Properties
If one desires to calculate the point where the population reaches a percentage of its carrying capacity , then one can solve the equation
for , where . For instance, the half point can be found by setting .
Applications
According to stem cell researchers at McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, "a newer model [called the hyperbolastic type III or] H3 is a differential equation that also describes the cell growth. This model allows for much more variation and has been proven to better predict growth."[12]
The hyperbolastic growth models H1, H2, and H3 have been applied to analyze the growth of solid Ehrlich carcinoma using a variety of treatments.[13]
In animal science,[14] the hyperbolastic functions have been used for modeling broiler chicken growth.[15][16] The hyperbolastic model of type III was used to determine the size of the recovering wound.[17]
In the area of wound healing, the hyperbolastic models accurately representing the time course of healing.[18] Such functions have been used to investigate variations in the healing velocity among different kinds of wounds and at different stages in the healing process taking into consideration the areas of trace elements, growth factors, diabetic wounds, and nutrition.[19][20]
Another application of hyperbolastic functions is in the area of the stochastic diffusion process,[21] whose mean function is a hyperbolastic curve. The main characteristics of the process are studied and the maximum likelihood estimation for the parameters of the process is considered.[22] To this end, the firefly metaheuristic optimization algorithm is applied after bounding the parametric space by a stage wise procedure. Some examples based on simulated sample paths and real data illustrate this development. A sample path of a diffusion process models the trajectory of a particle embedded in a flowing fluid and subjected to random displacements due to collisions with other particles, which is called Brownian motion.[23][24][25][26][27] The hyperbolastic function of type III was used to model the proliferation of both adult mesenchymal and embryonic stem cells;[28][29][30][31] and, the hyperbolastic mixed model of type II has been used in modeling cervical cancer data.[32] Hyperbolastic curves can be an important tool in analyzing cellular growth, the fitting of biological curves, the growth of phytoplankton, and instantaneous maturity rate.[33][34][35][36]
In forest ecology and management, the hyperbolastic models have been applied to model the relationship between DBH and height.[37]
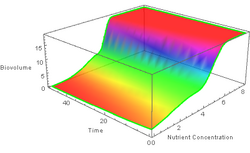
The multivariable hyperbolastic model type III has been used to analyze the growth dynamics of phytoplankton taking into consideration the concentration of nutrients.[38]
Hyperbolastic regressions
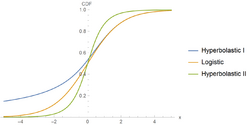

Hyperbolastic regressions are statistical models that utilize standard hyperbolastic functions to model a dichotomous or multinomial outcome variable. The purpose of hyperbolastic regression is to predict an outcome using a set of explanatory (independent) variables. These types of regressions are routinely used in many areas including medical, public health, dental, biomedical, as well as social, behavioral, and engineering sciences. For instance, binary regression analysis has been used to predict endoscopic lesions in iron deficiency anemia.[39] In addition, binary regression was applied to differentiate between malignant and benign adnexal mass prior to surgery.[40]
The binary hyperbolastic regression of type I
Let be a binary outcome variable which can assume one of two mutually exclusive values, success or failure. If we code success as and failure as , then for parameter , the hyperbolastic success probability of type I with a sample of size as a function of parameter and parameter vector given a -dimensional vector of explanatory variables is defined as , where , is given by
- .
The odds of success is the ratio of the probability of success to the probability of failure. For binary hyperbolastic regression of type I, the odds of success is denoted by and expressed by the equation
- .
The logarithm of is called the logit of binary hyperbolastic regression of type I. The logit transformation is denoted by and can be written as
- .
Shannon information for binary hyperbolastic of type I (H1)
The Shannon information for the random variable is defined as
where the base of logarithm and . For binary outcome, is equal to .
For the binary hyperbolastic regression of type I, the information is given by
- ,
where , and is the input data. For a random sample of binary outcomes of size , the average empirical information for hyperbolastic H1 can be estimated by
- ,
where , and is the input data for the observation.
Information Entropy for hyperbolastic H1
Information entropy measures the loss of information in a transmitted message or signal. In machine learning applications, it is the number of bits necessary to transmit a randomly selected event from a probability distribution. For a discrete random variable , the information entropy is defined as
where is the probability mass function for the random variable .
The information entropy is the mathematical expectation of with respect to probability mass function . The Information entropy has many applications in machine learning and artificial intelligence such as classification modeling and decision trees. For the hyperbolastic H1, the entropy is equal to
The estimated average entropy for hyperbolastic H1 is denoted by and is given by
Binary Cross-entropy for hyperbolastic H1
The binary cross-entropy compares the observed with the predicted probabilities. The average binary cross-entropy for hyperbolastic H1 is denoted by and is equal to
The binary hyperbolastic regression of type II
The hyperbolastic regression of type II is an alternative method for the analysis of binary data with robust properties. For the binary outcome variable , the hyperbolastic success probability of type II is a function of a -dimensional vector of explanatory variables given by
- ,
For the binary hyperbolastic regression of type II, the odds of success is denoted by and is defined as
The logit transformation is given by
Shannon information for binary hyperbolastic of type II (H2)
For the binary hyperbolastic regression H2, the Shannon information is given by
where , and is the input data. For a random sample of binary outcomes of size , the average empirical information for hyperbolastic H2 is estimated by
where , and is the input data for the observation.
Information Entropy for hyperbolastic H2
For the hyperbolastic H2, the information entropy is equal to
and the estimated average entropy for hyperbolastic H2 is
Binary Cross-entropy for hyperbolastic H2
The average binary cross-entropy for hyperbolastic H2 is
Parameter estimation for the binary hyperbolastic regression of type I and II
The estimate of the parameter vector can be obtained by maximizing the log-likelihood function
where is defined according to one of the two types of hyberbolastic functions used.
The multinomial hyperbolastic regression of type I and II
The generalization of the binary hyperbolastic regression to multinomial hyperbolastic regression has a response variable for individual with categories (i.e. ). When , this model reduces to a binary hyperbolastic regression. For each , we form indicator variables where
- ,
meaning that whenever the response is in category and otherwise.
Define parameter vector in a -dimensional Euclidean space and .
Using category 1 as a reference and as its corresponding probability function, the multinomial hyperbolastic regression of type I probabilities are defined as
and for ,
Similarly, for the multinomial hyperbolastic regression of type II we have
and for ,
where with and .
The choice of is dependent on the choice of hyperbolastic H1 or H2.
Shannon Information for multiclass hyperbolastic H1 or H2
For the multiclass , the Shannon information is
- .
For a random sample of size , the empirical multiclass information can be estimated by
- .
Multiclass Entropy in Information Theory
For a discrete random variable , the multiclass information entropy is defined as
where is the probability mass function for the multiclass random variable .
For the hyperbolastic H1 or H2, the multiclass entropy is equal to
The estimated average multiclass entropy is equal to
Multiclass Cross-entropy for hyperbolastic H1 or H2
Multiclass cross-entropy compares the observed multiclass output with the predicted probabilities. For a random sample of multiclass outcomes of size , the average multiclass cross-entropy for hyperbolastic H1 or H2 can be estimated by
The log-odds of membership in category versus the reference category 1, denoted by , is equal to
where and . The estimated parameter matrix of multinomial hyperbolastic regression is obtained by maximizing the log-likelihood function. The maximum likelihood estimates of the parameter matrix is
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Tabatabai, Mohammad; Williams, David; Bursac, Zoran (2005). "Hyperbolastic growth models: Theory and application". Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling 2: 14. doi:10.1186/1742-4682-2-14. PMID 15799781.
- ↑ Himali, L.P.; Xia, Zhiming (2022). "Performance of the Survival models in Socioeconomic Phenomena". Vavuniya Journal of Science 1 (2): 9–19. doi:10.4038/vjs.v1i2.9. ISSN 2950-7154.
- ↑ Acton, Q. Ashton (2012). Blood Cells—Advances in Research and Application: 2012 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. ISBN 978-1-4649-9316-9.
- ↑ Wadkin, L. E.; Orozco-Fuentes, S.; Neganova, I.; Lako, M.; Parker, N. G.; Shukurov, A. (2020). "An introduction to the mathematical modelling of iPSCs". Recent Advances in IPSC Technology 5.
- ↑ Albano, G.; Giorno, V.; Roman-Roman, P.; Torres-Ruiz, F. (2022). "Study of a General Growth Model". Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation 107. doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2021.106100. Bibcode: 2022CNSNS.10706100A.
- ↑ Neysens, Patricia; Messens, Winy; Gevers, Dirk; Swings, Jean; De Vuyst, Luc (2003). "Biphasic kinetics of growth and bacteriocin production with Lactobacillus amylovorus DCE 471 occur under stress conditions". Microbiology 149 (4): 1073–1082. doi:10.1099/mic.0.25880-0. PMID 12686649.
- ↑ Chu, Charlene; Han, Christina; Shimizu, Hiromi; Wong, Bonnie (2002). "The Effect of Fructose, Galactose, and Glucose on the Induction of β-Galactosidase in Escherichia coli". Journal of Experimental Microbiology and Immunology 2: 1–5. https://www.microbiology.ubc.ca/sites/default/files/roles/drupal_ungrad/JEMI/2/2-1.pdf.
- ↑ Tabatabai, M. A.; Eby, W. M.; Singh, K. P.; Bae, S. (2013). "T model of growth and its application in systems of tumor-immunedynamics". Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 10 (3): 925–938. doi:10.3934/mbe.2013.10.925. PMID 23906156.
- ↑ Parmoon, Ghasem; Moosavi, Seyed; Poshtdar, Adel; Siadat, Seyed (2020). "Effects of cadmium toxicity on sesame seed germination explained by various nonlinear growth models". Oilseeds & Fats Crops and Lipids 27 (57): 57. doi:10.1051/ocl/2020053.
- ↑ Kronberger, Gabriel; Kammerer, Lukas; Kommenda, Michael (2020). Computer Aided Systems Theory – EUROCAST 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 12013. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-45093-9. ISBN 978-3-030-45092-2.
- ↑ Kamar SH, Msallam BS. Comparative Study between Generalized Maximum Entropy and Bayes Methods to Estimate the Four Parameter Weibull Growth Model. Journal of Probability and Statistics. 2020 Jan 14;2020:1–7.
- ↑ "Proliferative heterogeneity in stem cell populations". Live Cell Imaging Laboratory, McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine. n.d.. https://www.engineering.pitt.edu/Departments/Bioengineering/_Documents/Undergraduate-research/Intramural-Internships/(2131)---Fall2012/Abstract_Roehrs.
- ↑ Eby, Wayne M.; Tabatabai, Mohammad A.; Bursac, Zoran (2010). "Hyperbolastic modeling of tumor growth with a combined treatment of iodoacetate and dimethylsulphoxide". BMC Cancer 10: 509. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-509. PMID 20863400.
- ↑ France, James, ed (2008). Mathematical Modelling in Animal Nutrition. Wallingford: CABI. ISBN 978-1-84593-354-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/40802178.
- ↑ Ahmadi, H.; Mottaghitalab, M. (2007). "Hyperbolastic Models as a New Powerful Tool to Describe Broiler Growth Kinetics". Poultry Science 86 (11): 2461–2465. doi:10.3382/ps.2007-00086. PMID 17954598.
- ↑ Tkachuk, S. A.; Pasnichenko, O. S.; Savchok, L. B. (2021). "Approximation of Growth Indicators and Analysis of Individual Growth Curves by Linear Dimensions of Tubular Bones in Chickens of Meat Production Direction During Postnatal Period of Ontogenesis". Ukrainian Journal of Veterinary Sciences 12 (4). doi:10.31548/ujvs2021.04.002.
- ↑ Choi, Taeyoung; Chin, Seongah (2014). "Novel Real-Time Facial Wound Recovery Synthesis Using Subsurface Scattering". The Scientific World Journal 2014: 1–8. doi:10.1155/2014/965036. PMID 25197721.
- ↑ Kiziloz, S.; Ward, E.J.; Hawthorne, D. (2025). "Ti3C2Tx MXene augments osmo-adaptive repression of the inflammatory stress response for improved wound repair". Nanoscale: 1-31. doi:10.1039/d4nr04622f.
- ↑ Tabatabai, M.A.; Eby, W.M.; Singh, K.P. (2011). "Hyperbolastic modeling of wound healing". Mathematical and Computer Modelling 53 (5–6): 755–768. doi:10.1016/j.mcm.2010.10.013.
- ↑ Ko, Ung Hyun; Choi, Jongjin; Choung, Jinseung; Moon, Sunghwan; Shin, Jennifer H. (2019). "Physicochemically Tuned Myofibroblasts for Wound Healing Strategy". Scientific Reports 9 (1): 16070. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-52523-9. PMID 31690789. Bibcode: 2019NatSR...916070K.
- ↑ Barrera, Antonio; Román-Román, Patricia; Torres-Ruiz, Francisco (2021). "Hyperbolastic Models from a Stochastic Differential Equation Point of View". Mathematics 9 (16): 1835. doi:10.3390/math9161835.
- ↑ Barrera, Antonio; Román-Román, Patricia; Torres-Ruiz, Francisco (2020). "Diffusion Processes for Weibull-Based Models". Computer Aided Systems Theory – EUROCAST 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 12013. pp. 204–210. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-45093-9_25. ISBN 978-3-030-45092-2.
- ↑ Barrera, Antonio; Román-Román, Patricia; Torres-Ruiz, Francisco (2018). "A hyperbolastic type-I diffusion process: Parameter estimation by means of the firefly algorithm". Biosystems 163: 11–22. doi:10.1016/j.biosystems.2017.11.001. PMID 29129822. Bibcode: 2018BiSys.163...11B.
- ↑ Barrera, Antonio; Román-Roán, Patricia; Torres-Ruiz, Francisco (2020). "Hyperbolastic type-III diffusion process: Obtaining from the generalized Weibull diffusion process". Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 17 (1): 814–833. doi:10.3934/mbe.2020043. PMID 31731379.
- ↑ Barrera, Antonio; Román-Román, Patricia; Torres-Ruiz, Francisco (2020). "Two Stochastic Differential Equations for Modeling Oscillabolastic-Type Behavior". Mathematics 8 (2): 155. doi:10.3390/math8020155.
- ↑ Stochastic Processes with Applications. 2019. doi:10.3390/books978-3-03921-729-8. ISBN 978-3-03921-729-8. https://digitalcommons.uri.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1006&context=nonequilibrium_statistical_physics.
- ↑ Barrera, Antonio; Román-Román, Patricia; Torres-Ruiz, Francisco (2021). "T-Growth Stochastic Model: Simulation and Inference via Metaheuristic Algorithms". Mathematics 9 (9): 959. doi:10.3390/math9090959.
- ↑ Tabatabai, Mohammad A.; Bursac, Zoran; Eby, Wayne M.; Singh, Karan P. (2011). "Mathematical modeling of stem cell proliferation". Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing 49 (3): 253–262. doi:10.1007/s11517-010-0686-y. PMID 20953843.
- ↑ Eby, Wayne M.; Tabatabai, Mohammad A. (2014). "Methods in Mathematical Modeling for Stem Cells". Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 12. 12. pp. 201–217. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-8032-2_18. ISBN 978-94-017-8031-5.
- ↑ Wadkin, L. E.; Orozco-Fuentes, S.; Neganova, I.; Lako, M.; Shukurov, A.; Parker, N. G. (2020). "The recent advances in the mathematical modelling of human pluripotent stem cells". SN Applied Sciences 2 (2): 276. doi:10.1007/s42452-020-2070-3. PMID 32803125.
- ↑ Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 12. 12. 2014. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-8032-2. ISBN 978-94-017-8031-5.
- ↑ Tabatabai, Mohammad A.; Kengwoung-Keumo, Jean-Jacques; Eby, Wayne M.; Bae, Sejong; Guemmegne, Juliette T.; Manne, Upender; Fouad, Mona; Partridge, Edward E. et al. (2014). "Disparities in Cervical Cancer Mortality Rates as Determined by the Longitudinal Hyperbolastic Mixed-Effects Type II Model". PLOS ONE 9 (9). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107242. PMID 25226583. Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...9j7242T.
- ↑ Veríssimo, André; Paixão, Laura; Neves, Ana; Vinga, Susana (2013). "BGFit: Management and automated fitting of biological growth curves". BMC Bioinformatics 14: 283. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-283. PMID 24067087.
- ↑ Tabatabai, M. A.; Eby, W. M.; Bae, S.; Singh, K. P. (2013). "A flexible multivariable model for Phytoplankton growth". Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 10 (3): 913–923. doi:10.3934/mbe.2013.10.913. PMID 23906155.
- ↑ Yeasmin, Farhana; Daw, Ranadeep; Chakraborty, Bratati (2021). "A New Growth Rate Measure in Identifying Extended Gompertz Growth Curve and Development of Goodness-of-fit Test". Calcutta Statistical Association Bulletin 73 (2): 127–145. doi:10.1177/00080683211037203.
- ↑ Arif, Samiur (2014). Modeling Stem Cell Population Dynamics (Thesis). Old Dominion University. doi:10.25777/thnx-6q07.
- ↑ Eby, Wayne M.; Oyamakin, Samuel O.; Chukwu, Angela U. (2017). "A new nonlinear model applied to the height-DBH relationship in Gmelina arborea". Forest Ecology and Management 397: 139–149. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2017.04.015. Bibcode: 2017ForEM.397..139E.
- ↑ Tabatabai, M. A.; Eby, W. M.; Bae, S.; Singh, K. P. (2013). "A flexible multivariable model for Phytoplankton growth". Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 10 (3): 913–923. doi:10.3934/mbe.2013.10.913. PMID 23906155.
- ↑ Majid, Shahid; Salih, Mohammad; Wasaya, Rozina; Jafri, Wasim (2008). "Predictors of gastrointestinal lesions on endoscopy in iron deficiency anemia without gastrointestinal symptoms". BMC Gastroenterology 8: 52. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-8-52. PMID 18992171.
- ↑ Timmerman, Dirk; Testa, Antonia C.; Bourne, Tom; Ferrazzi, Enrico; Ameye, Lieveke; Konstantinovic, Maja L.; Van Calster, Ben; Collins, William P. et al. (2005). "Logistic Regression Model to Distinguish Between the Benign and Malignant Adnexal Mass Before Surgery: A Multicenter Study by the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis Group". Journal of Clinical Oncology 23 (34): 8794–8801. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.01.7632. PMID 16314639.
 |
