Inverse-chi-squared distribution
|
Probability density function 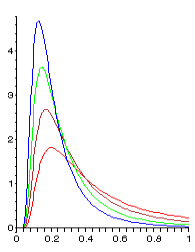 | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function 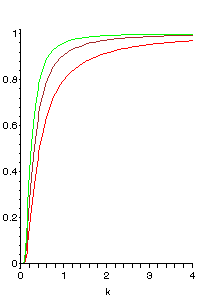 | |||
| Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean | for | ||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | for | ||
| Skewness | for | ||
| Kurtosis | for | ||
| Entropy |
| ||
| MGF | ; does not exist as real valued function | ||
| CF | |||
In probability and statistics, the inverse-chi-squared distribution (or inverted-chi-square distribution[1]) is a continuous probability distribution of a positive-valued random variable. It is closely related to the chi-squared distribution. It is used in Bayesian inference as conjugate prior for the variance of the normal distribution.[2]
Definition
The inverse chi-squared distribution (or inverted-chi-square distribution[1] ) is the probability distribution of a random variable whose multiplicative inverse (reciprocal) has a chi-squared distribution.
If follows a chi-squared distribution with degrees of freedom then follows the inverse chi-squared distribution with degrees of freedom.
The probability density function of the inverse chi-squared distribution is given by
In the above and is the degrees of freedom parameter. Further, is the gamma function.
The inverse chi-squared distribution is a special case of the inverse-gamma distribution. with shape parameter and scale parameter .
Related distributions
- chi-squared: If and , then
- scaled-inverse chi-squared: If , then
- Inverse gamma with and
- Inverse chi-squared distribution is a special case of type 5 Pearson distribution
See also
- Scaled-inverse-chi-squared distribution
- Inverse-Wishart distribution
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bernardo, J.M.; Smith, A.F.M. (1993) Bayesian Theory, Wiley (pages 119, 431) ISBN 0-471-49464-X
- ↑ Gelman, Andrew et al. (2014). "Normal data with a conjugate prior distribution". Bayesian Data Analysis (Third ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. pp. 67–68. ISBN 978-1-4398-4095-5.
External links
- InvChisquare in geoR package for the R Language.
 |
