Medicine:Congenital fiber type disproportion
| Congenital fiber type disproportion | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Congenital myopathy with fiber type disproportion, CFTD, CFTDM. |
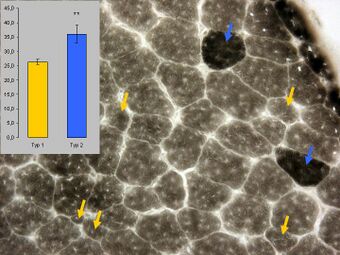 | |
| Histopathology of congental muscle fibre dysproportion showing predominance of type 1 fibres which appear to be atrophic (yellow arrows) and few type 2 fibres. ATPase staining (pH 4) of a muscle biopsy. | |
| Specialty | Neurology Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | contractures, lordosis, scoliosis, hypotonia and weakness, kyphoscoliosis, high-arched palate, dislocated hips, short stature, and feet deformities.[1] |
| Complications | Dilated cardiomyopathy[2] |
| Causes | Genetic mutations.[2] |
| Diagnostic method | Muscle biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Other types of congenital myopathy. |
| Treatment | Symptomatic. |
Congenital fiber type disproportion (CFTD) is an inherited form of myopathy with small type 1 muscle fibers that may occur in a number of neurological disorders.[3] It has a relatively good outcome and follows a stable course.[4] While the exact genetics is unclear, there is an association with mutations in the genes TPM3, ACTA1 and SEPN1.[5] It is a rare condition.[6]
Signs and symptoms
Congenital fiber-type disproportion can cause contractures as well as lordosis or scoliosis. Approximately 30% of people with this disorder have mild to severe respiratory issues due to weakness of breathing muscles. Some people with these breathing issues need noninvasive mechanical ventilation at night and on occasion during the day. Due to throat muscle weakness, approximately 30% of those affected have difficulty swallowing. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a rare complication of this condition.[2]
Other symptoms include congenital nonprogressive hypotonia and weakness, kyphoscoliosis, high-arched palate, dislocated hips, short stature, and feet deformities.[1]
Causes
A positive family history has been reported in approximately 40% of cases, however, the inheritance pattern remains unknown. Both autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant inheritance patterns have been proposed.[7] Some CFTD children appear to "grow out" of their hypotonia and weakness during childhood, and this can often be accompanied by a normalization of type 1 fiber size.[3]
According to the current literature, patients are most likely to carry mutations in TPM3, RYR1, ACTA1, and possibly TPM2 and SEPN1 in that order. It is worth noting that nearly every patient with known genetic causes have at least 40% fiber size disproportion.[8] TPM3 mutation is the most prevalent cause of CFTD reported so far.[5]
Diagnosis
To be diagnosed with CFTD, the main diagnostic abnormality must be a disproportion in fiber sizes, and the diagnosis is only appropriate after every other type of congenital myopathy has been ruled out. Before CFTD is diagnosed, a number of other neuromuscular (and systemic) disorders must be taken into account and ruled out as possible causes of mild cases of fiber size disproportion (FSD). These factors make CFTD a diagnosis of exclusion.[8]
A consistent difference in size between type 1 fibers, which are small in comparison to type 2 fibers, and type 2 fibers on muscle biopsy is the defining feature of CFTD, but only when it is the primary diagnostic abnormality.[8] The best threshold for the degree of fiber size disproportion required to diagnose CFTD is still being debated, but it is generally agreed that it should be greater than 12%.[5]
Treatment
Similar to other types of congenital myopathy, there is currently no known treatment that can strengthen muscles or stop the natural progression of muscle weakness. Nonetheless, much can be done to help people with CFTD maintain their health and well-being.[8]
Patients who experience nocturnal hypoventilation in childhood or adulthood nearly always react favorably to noninvasive nocturnal ventilation.[5]
To ensure proper nutrition, some patients with severe dysphagia and generalized weakness need to be fed through a gastrostomy tube.[9]
Patients will occasionally develop severe scoliosis that requires surgical correction, most commonly in connection with mutations in RYR1 and TPM3.[5]
Patients with CFTD may develop contractures of the Achilles tendons as a result of RYR1 and TPM3 mutations; in these cases, surgical tendon lengthening may be necessary. Physiotherapy to maintain ankle and other joint range of motion is frequently beneficial.[8]
History
Brooke coined the term congenital fiber type disproportion (CFTD) in 1971 to describe children whose biopsies revealed an abnormal size disparity between type 1 and type 2 fibers in the absence of any other obvious histologic abnormalities.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Clancy, Robert R.; Kelts, K.Alan; Oehlert, John W. (1980). "Clinical variability in congenital fiber type disproportion". Journal of the Neurological Sciences (Elsevier BV) 46 (3): 257–266. doi:10.1016/0022-510x(80)90050-7. ISSN 0022-510X. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7381515/. Retrieved November 21, 2023.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Congenital fiber-type disproportion: MedlinePlus Genetics". May 1, 2016. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/congenital-fiber-type-disproportion/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Congenital fiber type dispropsortion—30 years on". J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62 (10): 977–89. October 2003. doi:10.1093/jnen/62.10.977. PMID 14575234. https://academic.oup.com/jnen/article/62/10/977/2916428?login=false. Retrieved November 20, 2023.
- ↑ "Comparison of clinical characteristics between congenital fiber type disproportion myopathy and congenital myopathy with type 1 fiber predominance". Yonsei Med. J. 47 (4): 513–8. August 2006. doi:10.3349/ymj.2006.47.4.513. PMID 16941741.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Clarke, Nigel F.; Kolski, Hanna; Dye, Danielle E.; Lim, Esther; Smith, Robert L. L.; Patel, Rakesh; Fahey, Michael C.; Bellance, Rémi et al. (2008). "Mutations in TPM3 are a common cause of congenital fiber type disproportion". Annals of Neurology (Wiley) 63 (3): 329–337. doi:10.1002/ana.21308. ISSN 0364-5134. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18300303/. Retrieved November 20, 2023.
- ↑ "Congenital fiber type disproportion: a rare type of congenital myopathy: a report of four cases". Neurol India 52 (2): 254–6. June 2004. PMID 15269486. https://www.neurologyindia.com/article.asp?issn=0028-3886;year=2004;volume=52;issue=2;spage=254;epage=256;aulast=Sharma. Retrieved November 20, 2023.
- ↑ Sobrido, M. J.; Fernández, J. M.; Fontoira, E.; Pérez-Sousa, C.; Cabello, A.; Castro, M.; Teijeira, S.; Álvarez, S. et al. (April 27, 2005). "Autosomal dominant congenital fibre type disproportion: a clinicopathological and imaging study of a large family". Brain (Oxford University Press (OUP)) 128 (7): 1716–1727. doi:10.1093/brain/awh511. ISSN 1460-2156.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Clarke, Nigel F. (2011). "Congenital Fiber-Type Disproportion". Seminars in Pediatric Neurology (Elsevier BV) 18 (4): 264–271. doi:10.1016/j.spen.2011.10.008. ISSN 1071-9091. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1071909111000933. Retrieved November 21, 2023.
- ↑ Clarke, Nigel F.; Waddell, Leigh B.; Cooper, Sandra T.; Perry, Margaret; Smith, Robert L.L.; Kornberg, Andrew J.; Muntoni, Francesco; Lillis, Suzanne et al. (May 11, 2010). "Recessive mutations in RYR1 are a common cause of congenital fiber type disproportion". Human Mutation (Hindawi Limited) 31 (7): E1544–E1550. doi:10.1002/humu.21278. ISSN 1059-7794. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20583297/. Retrieved November 21, 2023.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

