Medicine:Ectopic ureter
| Ectopic ureter | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ureteral ectopia |
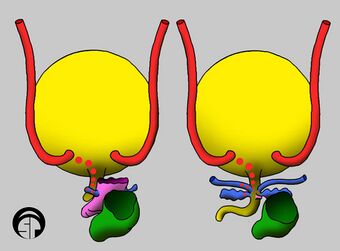 | |
| These two illustrations are posterior views of all the possible locations of ectopic ureter insertion (red dots) in a female (left illustration) and a male (right illustration). The different colors indicate embryologic origin of structure: a) red = metanephric duct (ureter), b) yellow = urogenital sinus (bladder and urethra), c) blue = Wolffian duct (Gartner's ducts in female, seminal vesicles and vasa deferentia in male), pink = Müllerian ducts (vagina in female, prostatic utricle in male), green = hindgut (rectum). | |
| Specialty | Urology |
Ectopic ureter (or ureteral ectopia) is a medical condition where the ureter, rather than terminating at the urinary bladder, terminates at a different site.[1][2] In males this site is usually the urethra, in females this is usually the urethra or vagina.[3] It can be associated with renal dysplasia,[4] frequent urinary tract infections, and urinary incontinence (usually continuous drip incontinence).[5] Ectopic ureters are found in 1 of every 2000–4000 patients,[6] and can be difficult to diagnose, but are most often seen on CT scans.[7]
Ectopic ureter is commonly a result of a duplicated renal collecting system, a duplex kidney with 2 ureters. In this case, usually one ureter drains correctly to the bladder, with the duplicated ureter presenting as ectopic.[8]
The embryology that explains the pathology of an ectopic ureter is a cephalad origin of the ureteral bud on the mesonephric duct. With an abnormally long common excretory duct, the ureter never becomes incorporated into the bladder, and, therefore, remains ectopic. In the female, the most common locations of an ectopic ureter are the bladder neck, urethra, or Gartner's duct which lies between the urethra and the anterior vaginal wall.[9]
See also
- Ectopia (disambiguation)
References
- ↑ "Definition: ectopic ureter from Online Medical Dictionary". http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?ectopic+ureter.
- ↑ "An Ectopic Ureter". http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/405340_2.
- ↑ "UrologyHealth.org - Pediatric Conditions: Abnormalities - Ectopic Ureter". http://www.urologyhealth.org/pediatric/index.cfm?cat=01&topic=71.
- ↑ "Abnormal Ureteric Development". http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/Meded/urology/abnurtdv.htm.
- ↑ "Constant urinary dribbling due to an ectopic ureter and delays in diagnosis". Clin Pediatr (Phila) 46 (6): 544–6. 2007. doi:10.1177/0009922807299311. PMID 17579108.
- ↑ "Duplicated Ectopic Ureter". http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/reprint/189/5/W272.pdf.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ "Diagnosis Of Ectopic Ureter As A Cause Of Urinary Incontinence". http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/67464.php.
- ↑ "Duplicated Collecting System". http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/378075-overview.
- ↑ Schmoldt A, Benthe HF, Haberland G (1975). "Digitoxin metabolism by rat liver microsomes.". Biochemical Pharmacology 24 (17): 1639–41. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(75)90094-5. PMID 10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

