Medicine:List of foramina of the human body
From HandWiki
Short description: none
This article lists foramina that occur in the human body.
Skull
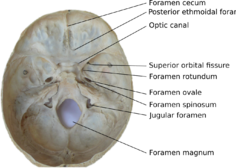
The human skull has numerous openings (foramina), through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. These foramina vary in size and number, with age.[1][2]
| Bone | Cranial fossa | Foramina | Number | Vessels | Nerves |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| frontal | - | supraorbital foramen | 2 | supraorbital artery supraorbital vein | supraorbital nerve |
| frontal | anterior cranial fossa | foramen cecum | 1 | emissary veins to superior sagittal sinus from the upper part of the nose[3] | |
| ethmoid | anterior cranial fossa (osama) | foramina of cribriform plate | ~20 | - | olfactory nerve bundles (I) |
| ethmoid | anterior cranial fossa | anterior ethmoidal foramen | 2 | anterior ethmoidal artery anterior ethmoidal vein |
anterior ethmoidal nerve |
| ethmoid | anterior cranial fossa | posterior ethmoidal foramen | 2 | posterior ethmoidal artery posterior ethmoidal vein |
posterior ethmoidal nerve |
| sphenoid | - | optic canal | 2 | ophthalmic artery | optic nerve (II) |
| sphenoid | middle cranial fossa | superior orbital fissure | 2 | superior ophthalmic vein | oculomotor nerve (III) trochlear nerve (IV) lacrimal, frontal and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic nerve (V1) abducent nerve (VI) |
| sphenoid | middle cranial fossa | foramen rotundum | 2 | - | maxillary nerve (V2) |
| maxilla | - | incisive foramen/canal/Stenson/Scarpa | 4 | terminal branch of descending palatine artery | Terminal part of[3] nasopalatine nerve (V2) |
| palatine | - | greater palatine foramen | 2 | greater palatine artery greater palatine vein |
greater palatine nerve |
| palatine and sphenoid | - | foramen sphenopalatinum | 2 | sphenopalatine artery sphenopalatine vein |
nasopalatine nerve rami nasales posteriores superiores (V2) |
| palatine and maxilla | - | lesser palatine foramina | 4 | lesser palatine arteries lesser palatine vein |
lesser palatine nerve, greater palatine nerve[3] |
| sphenoid and maxilla | - | inferior orbital fissure | 2 | inferior ophthalmic veins infraorbital artery infraorbital vein, tributary of pterygoid plexus |
zygomatic nerve and infraorbital nerve of maxillary nerve (V2) orbital branches of pterygopalatine ganglion |
| maxilla | - | infraorbital foramen | 2 | infraorbital artery infraorbital vein, tributary of pterygoid plexus |
infraorbital nerve |
| sphenoid | middle cranial fossa | foramen ovale | 2 | accessory meningeal artery, emissary vein connecting cavernous sinus with pterygoid plexus | mandibular nerve (V3) lesser petrosal nerve (occasionally)[3] |
| sphenoid | middle cranial fossa | foramen spinosum | 2 | middle meningeal artery | meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (V3) |
| sphenoid | middle cranial fossa | foramen lacerum | 2 | artery of pterygoid canal, Meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery, emissary vein | nerve of pterygoid canal through its anterior wall |
| temporal | middle cranial fossa | carotid canal | 2 | internal carotid artery | internal carotid plexus, sympathetics from the superior cervical ganglion |
| temporal | posterior cranial fossa | internal acoustic meatus | 2 | labyrinthine artery | facial nerve (VII), vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) |
| temporal | posterior cranial fossa | jugular foramen | 2 | internal jugular vein, inferior petrosal sinus, sigmoid sinus | glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), vagus nerve (X), accessory nerve (XI) |
| temporal | posterior cranial fossa | stylomastoid foramen | 2 | stylomastoid artery | facial nerve (VII) |
| occipital | posterior cranial fossa | hypoglossal canal | 2 | - | hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
| occipital | posterior cranial fossa | foramen magnum | 1 | anterior and posterior spinal arteries, vertebral arteries | lowest part of medulla oblongata, three meninges, ascending spinal fibers of accessory nerve (XI)[3] |
| occipital | posterior cranial fossa | condylar canal | 1 | occipital emissary vein, meningeal branch of occipital artery |
-
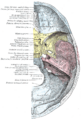
Base of the skull, upper surface
-
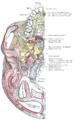
Base of the skull, inferior surface, attachment of muscles marked in red
Spine
Within the vertebral column (spine) of vertebrates, including the human spine, each bone has an opening at both its top and bottom to allow nerves, arteries, veins, etc. to pass through.
Other
- Apical foramen, the opening at the tip of the root of a tooth
- Foramen ovale (heart), an opening between the venous and arterial sides of the fetal heart
- Foramen transversarium, one of a pair of openings in each cervical vertebra, in which the vertebral artery travels
- Greater sciatic foramen, a major foramen of the pelvis
- Interventricular foramen, channels connecting ventricles in the brain
- Intervertebral foramen, foramina formed between vertebrae
- Lesser sciatic foramen, an opening between the pelvis and the posterior thigh
- Obturator foramen, the opening created by the ischium and pubis bones of the pelvis
- Vertebral foramen, the foramen formed by the anterior segment (the body), and the posterior part, the vertebral arch
References
- ↑ Kalmey JK1, ThewissenJG, Dluzen DE (July 1998). "Age-related size reduction of foramina in the cribriform plate". Anat. Rec. 251 (3): 326–9. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-0185(199807)251:3<326::aid-ar7>3.3.co;2-#. PMID 9669759.
- ↑ "The forgotten foramina: a study of the anterior cribriform plate". Surg Radiol Anat 37 (7): 835–40. Sep 2015. doi:10.1007/s00276-015-1471-2. PMID 25823692.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Chaurasia, BD (2013). BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy Volume 3. New Delhi: CBS Publishers and Distributors PVT Ltd. pp. 56–57. ISBN 9788123923321.
 |