Medicine:Pacman dysplasia
From HandWiki
| Pacman dysplasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Epiphyseal stippling with osteoclastic hyperplasia |
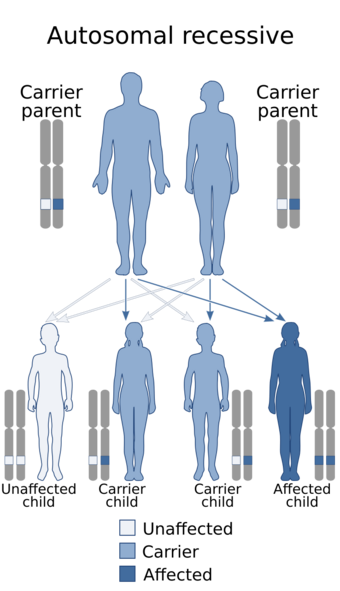 | |
| Pacman dysplasia is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner | |
Pacman dysplasia is a lethal autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia. The dysplasia is present during fetal development.[1]
References
Further reading
- "Distinguishing Pacman dysplasia from mucolipidosis II: comment on Saul et al. [2005]". Am J Med Genet A 135 (3): 333. 2005. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.30717. PMID 15887286.
- "Prenatal mucolipidosis type II (I-cell disease) can present as Pacman dysplasia". Am J Med Genet A 135 (3): 328–32. 2005. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.30716. PMID 15887289.
- "Pacman dysplasia: report of two affected sibs". Am J Med Genet 77 (4): 272–6. 1998. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980526)77:4<272::AID-AJMG4>3.0.CO;2-P. PMID 9600734.
- "New epiphyseal stippling syndrome with osteoclastic hyperplasia". Am J Med Genet 45 (5): 558–61. 1993. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320450506. PMID 8456823.
- "Pacman dysplasia: a lethal skeletal dysplasia with variable radiographic features". Pediatr Radiol 33 (4): 256–60. 2003. doi:10.1007/s00247-002-0859-4. PMID 12709756.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

