Medicine:Photoacoustic imaging
| Photoacoustic imaging | |
|---|---|
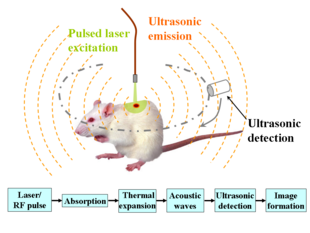 Schematic illustration of photoacoustic imaging |
Photoacoustic imaging or optoacoustic imaging is a biomedical imaging modality based on the photoacoustic effect. Non-ionizing laser pulses are delivered into biological tissues and part of the energy will be absorbed and converted into heat, leading to transient thermoelastic expansion and thus wideband (i.e., megahertz-order bandwidth) ultrasonic emission. The generated ultrasonic waves are detected by ultrasonic transducers and then analyzed to produce images. It is known that optical absorption is closely associated with physiological properties, such as hemoglobin concentration and oxygen saturation.[1] As a result, the magnitude of the ultrasonic emission (i.e. photoacoustic signal), which is proportional to the local energy deposition, reveals physiologically specific optical absorption contrast. 2D or 3D images of the targeted areas can then be formed.[2]
Biomedical imaging

The optical absorption in biological tissues can be due to endogenous molecules such as hemoglobin or melanin, or exogenously delivered contrast agents. As an example, Fig. 2 shows the optical absorption spectra of oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2) and deoxygenated hemoglobin (Hb) in the visible and near infrared region.[3] Since blood usually has orders of magnitude higher absorption than surrounding tissues, there is sufficient endogenous contrast for photoacoustic imaging to visualize blood vessels. Recent studies have shown that photoacoustic imaging can be used in vivo for tumor angiogenesis monitoring, blood oxygenation mapping, functional brain imaging, skin melanoma detection, methemoglobin measuring, etc.[2]
| Δf | Primary contrast | Δz | δz | δx | Speed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hz | mm | μm | μm | Mvx/s | ||
| Photoacoustic microscopy | 50 M | Optical absorption | 3 | 15 | 45 | 0.5 |
| Photoacoustic tomography | 5 M | Optical absorption | 50 | 700 | 700 | 0.5 |
| Confocal microscopy | Fluorescence, scattering | 0.2 | 3-20 | 0.3-3 | 10-100 | |
| Two-photon microscopy | Fluorescence | 0.5-1.0 | 1-10 | 0.3-3 | 10-100 | |
| Optical coherence tomography | 300 T | Optical scattering | 1-2 | 0.5-10 | 1-10 | 20-4.000 |
| Scanning laser acoustic microscopy | 300 M | Ultrasonic scattering | 1-2 | 20 | 20 | 10 |
| Acoustic microscopy | 50 M | Ultrasonic scattering | 20 | 20-100 | 80-160 | 0.1 |
| Ultrasonography | 5 M | Ultrasonic scattering | 60 | 300 | 300 | 1 |
| Table 1. Comparison of contrast mechanisms, penetration depth (Δz), axial resolution (δz), lateral resolution (δx=δy) and imaging speed of confocal microscopy, two-photon microscopy, optical coherence tomography (300 THz), ultrasound microscopy (50 MHz), ultrasound imaging (5 MHz), photoacoustic microscopy (50 MHz), and photoacoustic tomography (3.5 MHz). Speeds in megavoxel per second of non-parallel techniques. | ||||||
Two types of photoacoustic imaging systems, photoacoustic/thermoacoustic computed tomography (also known as photoacoustic/thermoacoustic tomography, i.e., PAT/TAT) and photoacoustic microscopy (PAM), have been developed. A typical PAT system uses an unfocused ultrasound detector to acquire the photoacoustic signals, and the image is reconstructed by inversely solving the photoacoustic equations. A PAM system, on the other hand, uses a spherically focused ultrasound detector with 2D point-by-point scanning, and requires no reconstruction algorithm.
Photoacoustic computed tomography
General equation
Given the heating function , the generation and propagation of photoacoustic wave pressure in an acoustically homogeneous inviscid medium is governed by
where is the speed of sound in medium, is the thermal expansion coefficient, and is the specific heat capacity at constant pressure. Eq. (1) holds under thermal confinement to ensure that heat conduction is negligible during the laser pulse excitation. The thermal confinement occurs when the laser pulsewidth is much shorter than the thermal relaxation time.[4]
The forward solution of Eq. (1) is given by
In stress confinement, which occurs when the laser pulsewidth is much shorter than the stress relaxation time,[4] Eq. (2) can be further derived as
where is the initial photoacoustic pressure.
Universal reconstruction algorithm
In a PAT system, the acoustic pressure is detected by scanning an ultrasonic transducer over a surface that encloses the photoacoustic source. To reconstruct the internal source distribution, we need to solve the inverse problem of equation (3) (i.e. to obtain ). A representative method applied for PAT reconstruction is known as the universal backprojection algorithm.[5] This method is suitable for three imaging geometries: planar, spherical, and cylindrical surfaces.
The universal back projection formula is
where is the solid angle subtended by the entire surface with respect to the reconstruction point inside , and
Simple system
A simple PAT/TAT/OAT system is shown in the left part of Fig. 3.[where?] The laser beam is expanded and diffused to cover the whole region of interest. Photoacoustic waves are generated proportional to the distribution of optical absorption in the target, and are detected by a single scanned ultrasonic transducer. A TAT/OAT system is the same as PAT except that it uses a microwave excitation source instead of a laser. Although single-element transducers have been employed in these two systems, the detection scheme can be extended to use ultrasound arrays as well.
Biomedical applications
Intrinsic optical or microwave absorption contrast and diffraction-limited high spatial resolution of ultrasound make PAT and TAT promising imaging modalities for wide biomedical applications:
Brain lesion detection
Soft tissues with different optical absorption properties in the brain can be clearly identified by PAT.[6]
Hemodynamics monitoring
Since HbO2 and Hb are the dominant absorbing compounds in biological tissues in the visible spectral range, multiple wavelength photoacoustic measurements can be used to reveal the relative concentration of these two chromophores.[6][7] Thus, the relative total concentration of hemoglobin (HbT) and the hemoglobin oxygen saturation (sO2) can be derived. Therefore, cerebral hemodynamic changes associated with brain function can be successfully detected with PAT.
Breast cancer diagnosis
By utilizing low scattered microwave for excitation, TAT is capable of penetrating thick (several cm) biological tissues with less than mm spatial resolution.[8] Since cancerous tissue and normal tissue have about the same responses to radio frequency radiation, TAT has limited potential in early breast cancer diagnosis.
Photoacoustic microscopy
The imaging depth of photoacoustic microscopy is mainly limited by the ultrasonic attenuation. The spatial (i.e. axial and lateral) resolutions depend on the ultrasonic transducer used. An ultrasonic transducer with high central frequency and broader bandwidth are chosen to obtain high axial resolution. The lateral resolution is determined by the focal diameter of the transducer. For instance, a 50 MHz ultrasonic transducer provides 15 micrometre axial and 45 micrometre lateral resolution with ~3 mm imaging depth.
Photoacoustic microscopy has multiple important applications in functional imaging: it can detect changes in oxygenated/deoxygenated hemoglobin in small vessels.[9][10]
Other applications
Photoacoustic imaging was introduced recently in the context of artwork diagnostics with emphasis on the uncovering of hidden features such as underdrawings or original sketch lines in paintings. Photoacoustic images, collected from miniature oil paintings on canvas, illuminated with a pulsed laser on their reverse side, revealed clearly the presence of pencil sketch lines coated over by several paint layers.[11]
Advances in photoacoustic imaging
Gold nanocages have been presented as a promising contrast agent for photoacoustic tomography due to their tunable optical properties.[12] Photoacoustic imaging has seen recent advances through the integration of deep learning principles and compressed sensing. For more information, see Deep learning in photoacoustic imaging.
See also
- Multispectral optoacoustic tomography
- Photoacoustic microscopy
- Deep learning in photoacoustic imaging
- Photoacoustic effect
References
- ↑ A. Grinvald (1986). "Functional architecture of cortex revealed by optical imaging of intrinsic signals". Nature 324 (6095): 361–364. doi:10.1038/324361a0. PMID 3785405. Bibcode: 1986Natur.324..361G.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 M. Xu; L.H. Wang (2006). "Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine". Review of Scientific Instruments 77 (4): 041101–041101–22. doi:10.1063/1.2195024. Bibcode: 2006RScI...77d1101X. https://authors.library.caltech.edu/72157/1/1.2195024.pdf.
- ↑ Optical Properties Spectra
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 L.H. Wang; H.I. Wu (2007). Biomedical Optics. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-74304-0.
- ↑ M. Xu (2005). "Universal back-projection algorithm for photoacoustic-computed tomography". Physical Review E 71 (1). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.71.016706. PMID 15697763. Bibcode: 2005PhRvE..71a6706X. https://authors.library.caltech.edu/67913/1/PhysRevE.71.016706.pdf.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 X. Wang (2003). "Non-invasive laser-induced photoacoustic tomography for structural and functional imaging of the brain in vivo". Nature Biotechnology 21 (7): 803–806. doi:10.1038/nbt839. PMID 12808463. https://authors.library.caltech.edu/67790/2/nbt839-S1.pdf.
- ↑ X. Wang (2006). "Non-invasive imaging of hemoglobin concentration and oxygenation in the rat brain using high-resolution photoacoustic tomography". Journal of Biomedical Optics 11 (2): 024015. doi:10.1117/1.2192804. PMID 16674205. Bibcode: 2006JBO....11b4015W. https://authors.library.caltech.edu/72156/1/024015_1_2006.pdf.
- ↑ G. Ku (2005). "Thermoacoustic and photoacoustic tomography of thick biological tissues toward breast imaging". Technology in Cancer Research and Treatment 4 (5): 559–566. doi:10.1177/153303460500400509. PMID 16173826.
- ↑ Yao, Junjie; Wang, Lihong V. (2013-01-31). "Photoacoustic microscopy". Laser & Photonics Reviews 7 (5): 758–778. doi:10.1002/lpor.201200060. ISSN 1863-8880. PMID 24416085. Bibcode: 2013LPRv....7..758Y.
- ↑ Zhang, Hao F; Maslov, Konstantin; Stoica, George; Wang, Lihong V (2006-06-25). "Functional photoacoustic microscopy for high-resolution and noninvasive in vivo imaging". Nature Biotechnology 24 (7): 848–851. doi:10.1038/nbt1220. ISSN 1087-0156. PMID 16823374. https://authors.library.caltech.edu/67910/2/nbt1220-S1.pdf.
- ↑ Tserevelakis, George J.; Vrouvaki, Ilianna; Siozos, Panagiotis; Melessanaki, Krystallia; Hatzigiannakis, Kostas; Fotakis, Costas; Zacharakis, Giannis (2017-04-07). "Photoacoustic imaging reveals hidden underdrawings in paintings" (in En). Scientific Reports 7 (1): 747. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00873-7. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 28389668. Bibcode: 2017NatSR...7..747T.
- ↑ Skrabalak, Sara E.; Chen, Jingyi; Sun, Yugang; Lu, Xianmao; Au, Leslie; Cobley, Claire M.; Xia, Younan (2008-12-16). "Gold Nanocages: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications". Accounts of Chemical Research 41 (12): 1587–1595. doi:10.1021/ar800018v. ISSN 0001-4842. PMID 18570442. PMC 2645935. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ar800018v.
External links
 |
