Medicine:Poland syndrome
| Poland syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Poland's syndrome, Poland's syndactyly, Poland sequence, Poland's anomaly, unilateral defect of pectoralis major and syndactyly of the hand[1] |
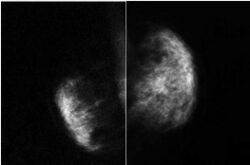
 | |
| Missing right breast and right pectoralis major muscle in Poland syndrome[2] | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Underdeveloped chest muscle and short webbed fingers on one side[3][1] |
| Usual onset | At birth[1] |
| Causes | Unknown[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Moebius syndrome, Hanhart syndrome[4] |
| Treatment | Surgical correction[3] |
| Frequency | 1 in 20,000 newborns[1] |
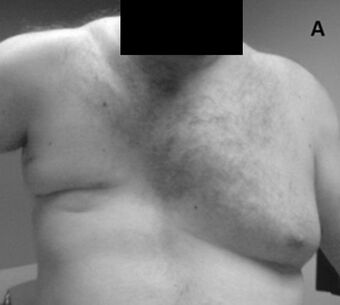
Poland syndrome is a birth defect characterized by an underdeveloped chest muscle and short webbed fingers on one side of the body.[3][1] There may also be short ribs, less fat, and breast and nipple abnormalities on the same side of the body.[1] Typically, the right side is involved.[3] Those affected generally have normal movement and health.[1]
The cause of Poland syndrome is unknown.[1] One theory is that it is due to disruption of blood flow during embryonic development.[1] It is generally not inherited, and no genes that contribute to the disorder have been identified.[1] Diagnosis of Poland syndrome is based on its symptoms.[4] Often, those with the syndrome remain undiagnosed, and some may not realize they have it until puberty.[3]
Treatment of Poland syndrome depends on its severity and may include surgical correction.[3] The syndrome affects about 1 in 20,000 newborns, and males are affected twice as often as females.[1] It is named after English surgeon Sir Alfred Poland, who described the condition when he was a student in 1841.[4][5]
Signs and symptoms
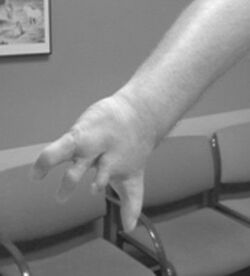
A list of the common side effects broken down by frequency.[3]
Very frequent
- Abnormal gastrointestinal tract
- Absent pectoral muscles
- Brachydactyly (Short fingers)
- Dextrocardia
- Diaphragmatic hernia/defect
- Humerus absent/abnormal
- Liver/biliary tract anomalies
- Maternal diabetes
- Oligodactyly/missing fingers
- Radius absent/abnormal
- Rhizomelic micromelia (relatively shorter proximal segment of the limbs compared to the middle and the distal segments)
- Sparsity or abnormality of axillary hair on affected side
- Syndactyly of fingers (webbing)
- Ulna absent/abnormal
- Upper limb asymmetry
- Abnormal rib
- Simian crease on affected side
Frequent
- Hypoplastic/absent nipples
- Scapula anomaly
Occasional
- Agenesis/hypoplasia of kidneys
- Encephalocele/exencephaly
- Abnormal morphology of hypothalamic-hypophyseal axis
- Abnormal function of hypothalamic-hypophyseal axis
- Microcephaly
- Preaxial polydactyly
- Ureteric anomalies (reflux/duplex system)
- Vertebral segmentation anomaly
It is usually considered a unilateral condition. Some have claimed that the term can be applied in bilateral presentation,[6] but others recommend using alternate terminology in those cases.[1]
Causes
The cause of Poland syndrome is unknown. However, an interruption of the embryonic blood supply to the arteries that lie under the collarbone (subclavian arteries) at about the 46th day of embryonic development is the prevailing theory.[7]
The subclavian arteries normally supply blood to embryonic tissues that give rise to the chest wall and hand. Variations in the site and extent of the disruption may explain the range of signs and symptoms that occur in Poland syndrome. Abnormality of an embryonic structure called the apical ectodermal ridge, which helps direct early limb development, may also be involved in this disorder.[8]
Diagnosis
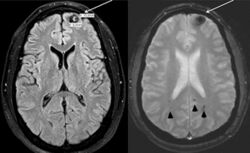
Poland syndrome is usually diagnosed at birth, based upon the physical characteristics. Imaging techniques such as a CT scan may reveal the extent to which the muscles are affected.[9] The syndrome varies in severity and as such is often not reported until puberty, when lopsided growth becomes apparent.[10]
Treatment
Technique
The complete or partial absence of the pectoralis muscle is the malformation that defines Poland syndrome. It can be treated by inserting a custom implant designed by CAD (computer aided design).[11] A 3D reconstruction of the patient's chest is done using an implant shaped from a medical scan and designed to be perfectly adapted to the anatomy.[12] The implant is made of medical grade silicone rubber. The treatment is purely cosmetic and does not restore the patient's imbalanced upper body strength.[citation needed]
The Poland syndrome malformations are morphological, so correction by custom implant is the first-line treatment.[13] This technique allows a wide variety of patients to be treated with good outcomes. Poland Syndrome can be associated with bones, subcutaneous and mammary atrophy: the first, as for pectus excavatum, is successfully corrected by a custom implant, while the others can require surgical intervention such as lipofilling[clarification needed] or silicone breast implant, in a second operation.[citation needed]
Surgery
The surgery takes place under general anaesthesia and lasts less than 1 hour. The surgeon prepares the locus to the size of the implant after performing an 8-centimetre (3.1 in) axillary incision, then inserts the implant beneath the skin. The closure is made in two planes.[citation needed]
The implant replaces the pectoralis major muscle, thus enabling the thorax to be symmetrical and, in women, the breast as well. If necessary, especially in the case of women, a second operation will complement the result by the implantation of a breast implant and / or lipofilling.[citation needed]
Lipomodelling is progressively used in the correction of breast and chest wall deformities. In Poland syndrome, this technique appears to be a major advance that will probably revolutionize the treatment of severe cases. This is mainly due to its ability to achieve previously unachievable quality of reconstruction with minimal scarring.[14]
Epidemiology
Poland syndrome affects males three times as often as females and affects the right side of the body twice as often as the left.[15] The incidence is estimated to range from one in 7,000 to one in 100,000 live births.[16]
History
It was named in 1962 by Patrick Clarkson, a New Zealand-born British plastic surgeon working at Guy's Hospital and Queen Mary's Hospital, London. He noticed that three of his patients had both a hand deformity and an underdeveloped breast on the same side. He discussed this with his colleague at Guy's Hospital, Dr Philip Evans, who agreed that the syndrome was "not widely appreciated". Clarkson found a reference to a similar deformity published by Alfred Poland, an English surgeon, over a hundred years earlier in Guy's Hospital reports, in 1841.[17] Clarkson was able to find the hand specimen dissected by Poland, which was still held in the hospital pathology museum.[citation needed]
Poland had dissected a convict known as George Elt, who was said to be unable to draw his hand across his chest. Poland noted the chest wall deformity, and this was illustrated in his article; the hand was also dissected and preserved for posterity in Guy's Hospital museum where it remains today. It cannot be truly said that Poland described this syndrome because he only described one isolated case. Clarkson published his series of three cases and named the syndrome after Poland in his article.[18]
Notable cases
- TV presenter Jeremy Beadle (1948–2008) was known for having this condition. His Poland syndrome manifested itself in the form of his disproportionately small right hand.[19]
- Olympic boxer Jérôme Thomas is also affected by Poland syndrome, as his left arm and hand are significantly shorter and smaller than his right. Thomas also lacks a left pectoral muscle.
- PGA Tour golfer Bryce Molder has Poland syndrome, with an absent left pectoral muscle and a small left hand. Several surgeries in his childhood repaired syndactyly on the left hand.[20]
- Actor Ted Danson, famous for starring in the TV show Cheers, admitted he had the condition in 2000 to Orange Coast magazine and said that he was bullied as a child because of it.[21]
- Formula One World Champion Fernando Alonso is affected by Poland syndrome; he is missing the right pectoral muscle.[22]
- Cricketer Lewis Hatchett was born with Poland syndrome.[23]
- Australian Paralympian Mathew Silcocks is affected by Poland syndrome.[24]
- Hailey Dawson of Nevada (born 2010) has a missing right pectoral muscle and is missing three fingers on her right hand due to the condition. She has thrown out the ceremonial first pitch at all 30 Major League Baseball parks, using a 3D-printed robotic right hand fitted for her by engineers at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas.[25][26][27]
- Actor Gary Burghoff, best known for the television series M*A*S*H, has Poland syndrome manifesting in brachydactyly on his left hand. It was seldom noticeable throughout the show's run, Burghoff usually putting his hand in his pocket or concealing it under props such as the clipboards carried by his character Radar O'Reilly.
- English singer-songwriter Matt Goss has Poland syndrome, manifesting as a missing lower pectoral on his right side.[28]
- Paralympian and doctor, Dr Kim Daybell is affected by Poland syndrome and plays in class 10 of para table tennis. He has now retired from international para table tennis.[29]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 Reference, Genetics Home (9 October 2018). "Poland syndrome" (in en). https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/poland-syndrome.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Lizarraga, Karlo J; De Salles, Antonio AF (20 September 2011). "Multiple cavernous malformations presenting in a patient with Poland syndrome: A case report". Journal of Medical Case Reports 5 (1): 469. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-5-469. PMID 21933407.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 "Poland syndrome" (in en). 2016. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7412/poland-syndrome.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Poland Syndrome". 2007. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/poland-syndrome/.
- ↑ Weinzweig, Jeffrey (2010) (in en). Plastic Surgery Secrets Plus E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 774. ISBN 978-0-323-08590-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=nNVmLYBuk5gC&pg=PA774.
- ↑ Karnak I.; Tanyel F. C.; Tunçbilek E.; Unsal M.; Büyükpamukçu N. (February 1998). "Bilateral Poland anomaly". Am. J. Med. Genet. 75 (5): 505–07. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980217)75:5<505::AID-AJMG9>3.0.CO;2-L. PMID 9489794.
- ↑ Poullin P.; Toussirot E.; Schiano A.; Serratrice G. (1992). "[Complete and dissociated forms of Poland's syndrome (5 cases)]". Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic 59 (2): 114–20. PMID 1604222.
- ↑ "Poland Syndrome". http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/poland-syndrome.
- ↑ "Poland Syndrome - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders)" (in en-US). NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/poland-syndrome/.
- ↑ "Poland syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program" (in en). https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7412/poland-syndrome.
- ↑ J.-P. Chavoin; A. André; E. Bozonnet; A. Teisseyre; J. Arrue; B. Moreno; D. Glangloff; J-.L. Grolleau et al. (2010). "Mammary implant selection or chest implants fabrication with computer help". Annales de Chirurgie Plastique Esthétique 55: 471–480. http://www.em-consulte.com/article/268865/figures/apport-de-linformatique-a-la-selection-des-implant.
- ↑ "Pectus Excavatum & Poland Syndrome treatment". https://anatomikmodeling.com/en.
- ↑ Chichery A.; Jalbert F.; Foucras L.; Grolleau J.-L.; Chavoin J.-P. (2006). "Syndrome de Poland". EMC - Techniques Chirurgicales - Chirurgie Plastique Reconstructrice et Esthétique 1 (3): 1–17. doi:10.1016/S1286-9325(06)44494-0. http://www.em-consulte.com/article/51349/syndrome-de-poland.
- ↑ Emmanuel Delay, Libor Streit, Gilles Toussoun, Sophie La Marca, C. Ho Quoc. (January 2013). "Lipomodelling: An important advance in breast surgery". Acta Chirurgiae Plasticae 55 (2): 34–43. PMID 24467681. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259954865.
- ↑ "Learning about Poland Anomaly". http://www.genome.gov/14514230.
- ↑ "Poland's syndrome revisited". Ann Thorac Surg 74 (6): 2218–25. 2002. doi:10.1016/S0003-4975(02)04161-9. PMID 12643435.
- ↑ Poland A. (1841). "Deficiency of the pectoral muscles". Guy's Hospital Reports VI: 191–193. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.b4490351;view=1up;seq=219. "Plate". Guys Hosp Rep. 1836. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.b4490351;view=1up;seq=227.
- ↑ Clarkson P. (1962). "Poland's syndactyly". Guys Hosp Rep 111: 335–46. PMID 14021589.
- ↑ Burt, Jennifer (1997-10-20). "Jeremy is a role model for children". Leicester (UK) Mercury.
- ↑ "Bryce Molder". http://www.pgatour.com/players/02/38/00/.
- ↑ Communications, Emmis (1 May 2000). "Orange Coast Magazine". Emmis Communications. https://books.google.com/books?id=yAQEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA36.
- ↑ "Poland Syndrome". http://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/poland-syndrome/.
- ↑ "Hatchett retires after defying the odds". 2016-09-24. http://www.espncricinfo.com/county-cricket-2016/content/story/1058796.html.
- ↑ "Mathew Silcocks | APC Corporate". https://www.paralympic.org.au/team/matthew-silcocks.
- ↑ "9-Year-Old Hailey Dawson Throws Out First Pitch At Camden Yards After Completing 'Journey To 30'". WJZ-TV. August 2, 2019. https://baltimore.cbslocal.com/2019/08/02/hailey-dawson-journey-to-30/.
- ↑ Footer, Alyson (October 28, 2017). "Girl with robotic hand throws inspiring first pitch". https://www.mlb.com/news/7-year-old-hailey-dawson-throws-g4-first-pitch/c-259961536.
- ↑ Bella, Cheryl (March 15, 2018). "Young Baseball Fan Starts 'Journey to 30' with Pitch for Padres". University of Nevada, Las Vegas. https://www.unlv.edu/news/release/young-baseball-fan-starts-journey-30-pitch-padres.
- ↑ "Interview with Matt Goss". 12 March 2022. https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2022/mar/12/matt-goss-id-like-to-have-more-sex-bros.
- ↑ "Kim Daybell announces table tennis retirement". 11 October 2022. https://paralympics.org.uk/articles/kim-daybell-announces-table-tennis-retirement.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |