Mnemonics in trigonometry
In trigonometry, it is common to use mnemonics to help remember trigonometric identities and the relationships between the various trigonometric functions.
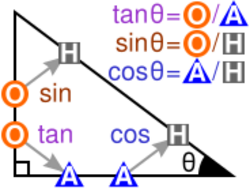
The sine, cosine, and tangent ratios in a right triangle can be remembered by representing them as strings of letters, for instance SOH-CAH-TOA in English:
- Sine = Opposite ÷ Hypotenuse
- Cosine = Adjacent ÷ Hypotenuse
- Tangent = Opposite ÷ Adjacent
One way to remember the letters is to sound them out phonetically (i.e. /ˌsoʊkəˈtoʊə/ SOH-kə-TOH-ə, similar to Krakatoa).[1]
Phrases
Another method is to expand the letters into a sentence, such as "Some Old Horses Chew Apples Happily Throughout Old Age", "Some Old Hippy Caught Another Hippy Tripping On Acid", or "Studying Our Homework Can Always Help To Obtain Achievement". The order may be switched, as in "Tommy On A Ship Of His Caught A Herring" (tangent, sine, cosine) or "The Old Army Colonel And His Son Often Hiccup" (tangent, cosine, sine) or "Come And Have Some Oranges Help To Overcome Amnesia" (cosine, sine, tangent).[2][3] Communities in Chinese circles may choose to remember it as TOA-CAH-SOH, which also means 'big-footed aunt' (Chinese: 大腳嫂; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: tōa-kha-só) in Hokkien.[citation needed]
An alternate way to remember the letters for Sin, Cos, and Tan is to memorize the syllables Oh, Ah, Oh-Ah (i.e. /oʊ ə ˈoʊ.ə/) for O/H, A/H, O/A.[4] Longer mnemonics for these letters include "Oscar Has A Hold On Angie" and "Oscar Had A Heap of Apples."[2]
All Students Take Calculus

All Students Take Calculus is a mnemonic for the sign of each trigonometric functions in each quadrant of the plane. The letters ASTC signify which of the trigonometric functions are positive, starting in the top right 1st quadrant and moving counterclockwise through quadrants 2 to 4.[5]
- Quadrant 1 (angles from 0 to 90 degrees, or 0 to π/2 radians): All trigonometric functions are positive in this quadrant.
- Quadrant 2 (angles from 90 to 180 degrees, or π/2 to π radians): Sine and cosecant functions are positive in this quadrant.
- Quadrant 3 (angles from 180 to 270 degrees, or π to 3π/2 radians): Tangent and cotangent functions are positive in this quadrant.
- Quadrant 4 (angles from 270 to 360 degrees, or 3π/2 to 2π radians): Cosine and secant functions are positive in this quadrant.
Other mnemonics include:
- All Stations To Central[6]
- All Silly Tom Cats[6]
- Add Sugar To Coffee[6]
- All Science Teachers (are) Crazy[7]
- A Smart Trig Class[8]
- All Schools Torture Children[5]
- Awful Stinky Trig Course[5]
Other easy-to-remember mnemonics are the ACTS and CAST laws. These have the disadvantages of not going sequentially from quadrants 1 to 4 and not reinforcing the numbering convention of the quadrants.
- CAST still goes counterclockwise but starts in quadrant 4 going through quadrants 4, 1, 2, then 3.
- ACTS still starts in quadrant 1 but goes clockwise going through quadrants 1, 4, 3, then 2.
Sines and cosines of special angles
Sines and cosines of common angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° follow the pattern with n = 0, 1, ..., 4 for sine and n = 4, 3, ..., 0 for cosine, respectively:[9]
| 0° = 0 radians | |||
| 30° = π/6 radians | |||
| 45° = π/4 radians | |||
| 60° = π/3 radians | |||
| 90° = π/2 radians | undefined |
Hexagon chart

Another mnemonic permits all of the basic identities to be read off quickly. The hexagonal chart can be constructed with a little thought:[10]
- Draw three triangles pointing down, touching at a single point. This resembles a fallout shelter trefoil.
- Write a 1 in the middle where the three triangles touch
- Write the functions without "co" on the three left outer vertices (from top to bottom: sine, tangent, secant)
- Write the co-functions on the corresponding three right outer vertices (cosine, cotangent, cosecant)
Starting at any vertex of the resulting hexagon:
| Identity | Example(s) | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| The starting vertex equals one over the opposite vertex. | 
| |
| Going either clockwise or counter-clockwise, the starting vertex equals the next vertex divided by the vertex after that. |  
| |
| The starting corner equals the product of its two nearest neighbors. | 
| |
| The sum of the squares of the two items at the top of a triangle equals the square of the item at the bottom. These are the trigonometric Pythagorean identities. | 
| |
Aside from the last bullet, the specific values for each identity are summarized in this table:
| Starting function | ... equals 1/opposite | ... equals first/second clockwise | ... equals first/second counter-clockwise/anticlockwise | ... equals the product of two nearest neighbors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
See also
References
- ↑ Humble, Chris (2001). Key Maths : GCSE, Higher.. Fiona McGill. Cheltenham: Stanley Thornes Publishers. p. 51. ISBN 0-7487-3396-5. OCLC 47985033.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weisstein, Eric W.. "SOHCAHTOA". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/SOHCAHTOA.html.
- ↑ Foster, Jonathan K. (2008). Memory: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford. p. 128. ISBN 978-0-19-280675-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=ISBN9780192806758.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Trigonometry". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Trigonometry.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Stueben, Michael; Sandford, Diane (1998). Twenty years before the blackboard: the lessons and humor of a mathematics teacher. Spectrum series. Washington, DC: Mathematical Association of America. p. 119. ISBN 978-0-88385-525-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=qnd0P-Ja-O8C&dq=%22All+Schools+Torture+Children%22&pg=PA119.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Sine, Cosine and Tangent in Four Quadrants". Math Is Fun. Archived from the original on 2015-01-18. https://web.archive.org/web/20150118121241/http://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/trig-four-quadrants.html. Retrieved 2015-01-18.
- ↑ Heng, H. H.; Cheng, Khoo; Talbert, J. F. (2005). Additional Mathematics. Pearson Education South Asia. p. 228. ISBN 978-981-235-211-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZZoxLiJBwOUC.
- ↑ "Math Mnemonics and Songs for Trigonometry". Online Math Learning. https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/mnemonics-for-trigonometry.html. Retrieved 2019-10-17.
- ↑ Larson, Ron (2014). Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach, Texas Edition (6 ed.). Cengage Learning. https://books.google.com/books?id=bsZDAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA275.
- ↑ "Magic Hexagon for Trig Identities". https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/trig-magic-hexagon.html.
 |
