Physics:ND experiment
Neutral Detector (ND) is a detector for particle physics experiments created by the team of physicists in the Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia. Experiments with the ND were conducted from 1982 to 1987 at the e+e− storage ring VEPP-2M in the energy range 2E = 0.5 to 1.4 GeV.[1]
Physics
At the beginning of 80s the leading cross sections of the electron-positron annihilation in the final states with charged particles were measured in the energy range 2E=0.5-1.4 GeV. Processes with the neutral particles in the final state were less studied. To investigate the radiative decays of the , , and mesons and other processes involving photons, , and mesons the ND [2] was constructed. Its distinguishing features are defined by the specially designed electromagnetic calorimeter based on NaI(Tl) scintillation counters.
List of published analyses [1]
- Rare decays of the , , and mesons
- Search for rare decays
- Non-resonant electron-positron annihilation into hadrons
- (virtual Compton scattering) [16]
- Analyses of other processes
Detector
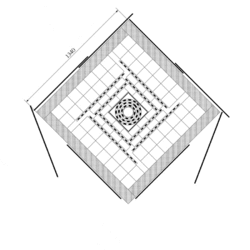
Neutral Detector r-φ view. 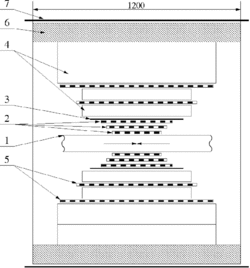
Neutral Detector r-θ view; 1-vacuum chamber of the storage ring, 2-cylindrical proportional chambers, 3-plastic scintillation counters, 4-NaI(Tl) counters, 5-flat proportional chambers, 6-iron absorber, 7-anticoincidence counters.
Based on goals of the physics program the ND consist of
Electromagnetic calorimeter
- 168 rectangular NaI(Tl) scintillation counters
- total mass of NaI(Tl) is 2.6 t
- solid angle coverage is 65% of 4π sr
- minimum thickness is 32 cm or 12 radiation length
- energy resolution for photons is σ/E = 4% / √E
Charged particle coordinate system
- 3 layers of coaxial cylindrical 2-d wire proportional chambers in the center of the detector
- solid angle coverage is 80% of 4π sr
- angular resolution is 0.5° in the azimuthal and 1.5° in the polar direction
- surrounded by the 5-mm thick plastic scintillation counter for trigger
Flat (shower) coordinate 2-d wire proportional chambers
- 2 layers of flat 2-d wire proportional chambers.
- angular resolution is 2° in the azimuthal and 3.5° in the polar direction for 0.5 GeV photons
Iron absorber & anti-coincidence counters
- The electromagnetic calorimeter is covered by the 10-cm thick iron absorber and plastic scintillation anti-coincidence counters.
Results
Data collected with the ND experiment corresponds to the integrated luminosity 19 pb−1. Results of the experiments with ND are presented in Ref.,[1] and are included in the PDG Review. [23]
See also
- Physics:Annihilation
- Organization:Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics
- Physics:Experimental physics – Category of disciplines and sub-disciplines in Physics
- Physics:List of accelerators in particle physics – List compiling of particle accelerators used for particle physics experiments
- Physics:List of particles – List of particles in matter including fermions and bosons
- Software:Meson – Build automation system
- Physics:Particle detector – Device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionising particles
- Physics:SND Experiment
- Physics:Storage ring – Type of particle accelerator
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Dolinsky, S. I. (1991). "Summary of experiments with the neutral detector at the e+e− storage ring VEPP-2M". Physics Reports 202 (3): 99–170. doi:10.1016/0370-1573(91)90127-8. Bibcode: 1991PhR...202...99D.
- ↑ Golubev, V. B. (1984). "The neutral detector at VEPP-2M". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A 227 (3): 467–469. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(84)90202-X. Bibcode: 1984NIMPA.227..467G.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dolinsky, S. I. (1984). "Radiative decays of ρ and ω mesons". Zeitschrift für Physik C 42 (4): 511–518. doi:10.1007/BF01557655.
- ↑ Druzhinin, V. P. (1984). "Measurement of Φ-meson radiative decays at the storage ring VEPP-2M with the neutral detector". Physics Letters B 144 (1–2): 136–140. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(84)90192-8. Bibcode: 1984PhLB..144..136D.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Druzhinin, V. P. (1987). "Search for rare radiative decays of Φ-meson at VEPP-2M". Zeitschrift für Physik C 37 (1): 1–5. doi:10.1007/BF01442062. Bibcode: 1987ZPhyC..37....1D.
- ↑ S.I. Dolinsky et al., Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 48 (1988) 277.
- ↑ V. B. Golubev et al., Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 44 (1986) 409.
- ↑ V. B. Vasserman et al., Sov. J. Mod. Phys. 48 (1988) 480.
- ↑ V. M. Aulchcnko et al., Preprini INP 87-90 (Novosibirsk, 1987).
- ↑ Dolinsky, S. I. (1986). "The reaction e+e− → ωπ0 in the cm energy range from 1.0 to 1.4 GeV". Phys. Lett. B 174 (4): 453–457. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(86)91036-1. Bibcode: 1986PhLB..174..453D.
- ↑ A. D. Bukin et al., Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 50 (1989) 621.
- ↑ Druzhinin, V. P. (1986). "Investigation of the reaction e+e− → ηπ+π− in the energy range up to 1.4 GeV". Phys. Lett. B 174 (1): 115–117. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(86)91140-8. Bibcode: 1986PhLB..174..115D.
- ↑ V. M. Aulchenko et al., Preprint INP 86-106 (Novosibirsk, 1987).
- ↑ V. P. Druzhinin et al., Preprint INP 85-98 (Novosibirsk, 1985).
- ↑ V. M. Aulchcnko et al., Preprint INP 86-173 (Novosibirsk, 1986).
- ↑ V. B. Golubev et al., Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 41(1985) 752.
- ↑ Aulchenko, V. M. (1987). "The width of the ω-meson". Phys. Lett. B 186 (3–4): 432–434. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(87)90322-4. Bibcode: 1987PhLB..186..432A.
- ↑ P. V. Vorobyov et al., Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 48 (1988) 436.
- ↑ V. P. Druzhinin et al., Preprint INP 85-97 (Novosibirsk, 1985).
- ↑ V. B. Golubev et al., Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 45 (1987) 622.
- ↑ I. B. Vasserman et al., JETP Lett. 43(1986) 588.
- ↑ V. M. Aulchenkoet al., JETP Lett. 45 (1987) 145.
- ↑ The Review of Particle Physics, K. Nakamura et al. (Particle Data Group), J. Phys. G 37, 075021 (2010)
External links
 |
