Red star


A red star, five-pointed and filled, is a symbol that has often historically been associated with communist ideology, particularly in combination with the hammer and sickle, but is also used as a purely socialist symbol in the 21st century. It has been widely used in flags, state emblems, monuments, ornaments, and logos.
One interpretation sees the five points as representing the five fingers of the worker's hand, as well as the five populated continents (counting the Americas as one). A lesser-known suggestion is that in communist symbolism, the five points on the star were intended to represent the five social groups that would lead Russia to communism: the youth, the military, the industrial labourers, the agricultural workers or peasantry and the intelligentsia. In Soviet heraldry, the red star symbolized the Red Army and military service, as opposed to the hammer and sickle, which symbolized peaceful labour.[citation needed]
Different countries across Europe treat the symbol very differently. Some former Warsaw Pact nations have passed laws banning it, seeing it as representing "a totalitarian ideology",[1] meanwhile other Eastern European countries hold a very positive view of it as a symbol of antifascism and resistance against Nazi occupation.[citation needed] The red star has also been used in a non-communist context and before the emergence of this movement, in symbols of countries and states since the 19th century. It appears for example on the flags of New Zealand and the U.S. state of California . Red star has also been used as logo by private agencies and corporations, such as the oil giant Texaco and beer multinational Heineken.
History

The star's origins as a symbol of communist mass movements dates from the time of the Bolshevik Revolution and the Russian Civil War, but the precise first use remains unknown. The red star as a symbol of the Red Army was proposed by the Military Collegium for the organization of the Red Army and the creator of the Red Star emblem was the Bolshevik commander of the Petrograd Military District, Konstantin Eremeev.[2] On the other hand, one account of the symbol's origin traces its roots to the Moscow troop garrison toward the end of World War I. At this time, many troops were fleeing from the Austrian and German fronts, joining the local Moscow garrison upon their arrival in the city. To distinguish the Moscow troops from the influx of retreating front-liners, officers gave out tin stars to the Moscow garrison soldiers to wear on their hats. When those troops joined the Red Army and the Bolsheviks they painted their tin stars red, the color of socialism, thus creating the original red star.[3]
The red star was used in communist media as early as in 1908 with the publication of the novel Red Star by Bolshevik revolutionary Alexander Bogdanov, which describes a technologically advanced communist civilization on Mars.[4]
Another claimed origin for the red star relates to an alleged encounter between Leon Trotsky and Nikolai Krylenko. Krylenko, an Esperantist, wore a green-star lapel badge; Trotsky inquired as to its meaning and received an explanation that each arm of the star represented one of the five traditional continents. On hearing that, Trotsky specified that soldiers of the Red Army should wear a similar red star.[5]
Regardless of the star's exact origin, it was incorporated into the Red Army's uniforms and heraldry as early as 1918.[6]

Shortly before the founding of the Soviet Union, in mid-March 1916 the U.S. Army Signal Corps' aviation section used the red star[7] for the national insignia for U.S. aircraft on the aircraft of the Signal Corps' 1st Aero Squadron during the Pancho Villa Expedition to apprehend the Mexican revolutionary Pancho Villa.
Use in the USSR and its constituent republics
The symbol became one of the most prominent of the Soviet Union, adorning nearly all official buildings, awards and insignia. Sometimes the hammer and sickle appeared inside or below the star. In 1930 the Soviet Union established the Order of the Red Star and awarded its insignia to Red Army and Soviet Navy personnel for "exceptional service in the cause of the defense of the Soviet Union in both war and peace". The Soviet and Russian Federation military newspaper bore and bears the name Red Star (Russian: Krasnaya Zvezda).[8]
-
Red Army cap badge (1918-1922)
-
Red Cavalry poster depicting a red star on a budenovka hat (1920)
-
Kremlin Star, Moscow (1937)
-
Soviet Order of Victory, USSR (1945)
-
Plate by Adamovich, Russian SFSR (1921)
As a holiday ornament
During the 1930s, Soviet publications encouraged the practice of decorating a New Year's tree, known as a yolka (Russian: Ёлка). These trees were often decorated with a red star, a practice that has continued in Russia since the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union.[9]
Gallery of the heraldry of Soviet republics
-
Coat of arms of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
-
Coat of arms of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Coat of arms of the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Emblem of the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic (1923-1936)
-
Emblem of the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic (1941-1956)
-
Coat of arms of the Latvian Socialist Soviet Republic (1919–1920)
Gallery of Soviet flags
-
Flag of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
-
Flag of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Kyrgyz Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
-
Flag of Oryol
-
Flag of the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic (1940–1956)
-
Flag of the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic (1922–1936)
Use in other socialist countries
Following its adoption as an emblem of the Soviet Union, the red star became a symbol for communism around the world.
Several Communist states subsequently adopted the red star symbol, often placing it on their respective flags and coats of arms – for example on the flag of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Separatist and socialist movements also sometimes adopted the red star, as on the Estelada flag in the Catalan countries.
Eastern Bloc
The red star became a common element of the flags and heraldry of socialist states in the Eastern Bloc, appearing in heraldry for virtually all of the countries, and on the flags of Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, and Albania. From 1991 to 1995, Belarus dropped its Soviet-style emblem in favor of an emblem featuring the Pahonia; the Soviet-era heraldry was re-adopted in 1995,[10] and continues to be used today with minor modifications in 2012 and 2020.
-
Flag of the People's Republic of Bulgaria (1971–1990)
-
Flag of the Socialist Republic of Romania (1965–1989)
-
Flag of the People's Socialist Republic of Albania (1946–1992)
-
Flag of the Hungarian People's Republic (1949–1956)
-
Coat of arms of the Socialist Republic of Romania
-
Coat of arms of the People's Republic of Bulgaria (1971–1990)
-
Coat of arms of the Hungarian People's Republic (1957–1990)
-
Coat of arms of the People's Socialist Republic of Albania
-
Coat of arms of Czechoslovak Socialist Republic (1961–1989)
-
Emblem of Belarus (1995–2012)
-
Emblem of Belarus (2012–2020)
-
Emblem of Belarus (since 2020)
Yugoslavia
In former Yugoslavia the red star served not only a communist symbol, but also as a more generic symbol of resistance against Fascism and the Nazi occupation of Yugoslavia, as well as of opposition to its associated ethnic policies. Tito's partisans wore the red star as an identification symbol during World War II.
-
Flag of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
-
Flag of the Socialist Republic of Serbia and flag of the Socialist Republic of Montenegro
-
Flag of the Socialist Republic of Slovenia
-
Flag of the Socialist Republic of Croatia
-
Flag of the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
Flag of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia
-
Coat of arms of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
-
Coat of arms of the Yugoslav Socialist Republic of Serbia
-
Coat of arms of the Yugoslav Socialist Republic of Slovenia
-
Coat of arms of the Yugoslav Socialist Republic of Croatia
-
Coat of arms of the Yugoslav Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
Coat of arms of the Yugoslav Socialist Republic of Macedonia
-
Coat of arms of the Yugoslav Socialist Republic of Montenegro
Asia
As communist movements spread across Asia, some entities used a red star, while others used a yellow star (often on a red field) with the same symbolism. The Far Eastern Republic of 1920 to 1922 used a yellow star on its military uniforms, and the flag of the People's Republic of China has five yellow stars on a red field. The flag of Vietnam also has a yellow star on a red field. Examples of communes and villages in China named after the red star include Hongxing Village in Huilong Township, Hubei, China[11] and Kizilto in Xinjiang (named Hongxing Commune during the Cultural Revolution).[12]
-
Emblem of North Korea (1948–1993)
-
Emblem of Laos (1975–1992)
-
State emblem of the Mongolian People's Republic (1960–1992)
-
Coat of arms of South Yemen (1970–1990)
-
Flag of Vietnam
-
Flag of the People's Republic of China
-
Flag of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea
-
Flag of the Mongolian People's Republic
-
Flag of South Yemen (1967–1990)
-
Flag of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan (1980–1987)
-
Red star seen on a stamp on the qualification certificate of an NHS COVID-19 lateral flow test, manufactured in Xiamen, Fujian Province, China .
Africa
Socialist countries in Africa also incorporated the red or gold stars into their heraldry. This practice was also adopted by countries that formed following anti-colonial national liberation struggles, which often involved Marxist organizations.
-
Emblem of Mozambique
-
Flag of Mozambique
-
Flag of Burkina Faso
-
Emblem of the People's Republic of Benin
-
Flag of Angola
-
Flag of Ethiopia (1987–1991)
-
Flag of Djibouti
-
Flag of Zimbabwe
-
Flag of Benin (1975–1990)
-
Flag of the People's Republic of the Congo (1969–1992)
-
Presidential Standard of the DR Madagascar
-
Emblem of the Democratic Republic of Madagascar
State military units
By March 2010, the Russia n government readopted the Soviet red star (but now with a blue outline reflecting the three colors – white, blue and red – of the Russian flag) as a military insignia.[citation needed] The Russian Air Force used this star as a roundel up to 2013, when Russia re-instated the Soviet-era red star.[13]
As of 2014[update] the Armed Forces of Belarus still use the old Soviet red star. The coat of arms of Armed Forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan includes a modified version of the Soviet red star.
-
Early swastika and red star emblem of the Mongolian Revolutionary Youth League, used from 1921 to 1924.
-
Soviet Military Air Force (1943–1991), Russian Military Air Force (1992–2010) and Belarusian Air Force roundel
-
Russian Military Air Force roundel
-
Symbol of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus
-
The coat of arms of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan
-
Emblem of the Chinese People's Liberation Army
-
People's Republic of Yemen Air Force roundel (1967–1980)
-
People's Republic of Yemen Air Force roundel (1980–1990)
By states with limited recognition
Transnistria and the Luhansk People's Republic are proto-states located in Eastern Europe. Due to their historical association with the Soviet Union, they have adopted socialist imagery – including the red star – into their flags and heraldry.
-
Flag of Transnistria
-
Coat of Arms of the Luhansk People's Republic
By sports teams
Several sporting clubs from countries ruled by communist parties used the red star as a symbol and named themselves after it, such as the Serbian club Red Star Belgrade (Serbian: Црвена звезда / Crvena zvezda), the East German Roter Stern Leipzig, the Angolan Estrela Vermelha do Huambo, the Estrela Vermelha from Beira, Mozambique or the Czechoslovak Rudá Hvězda Brno. Some sports teams from non-communist countries used it, such as French Red Star from Paris, Swiss club FC Red Star Zürich, English Seaham Red Star F.C., and even an American women's soccer club (Chicago Red Stars—though in that case the star is based on the flag of Chicago and not on the communist logo). The American soccer clubs Sacramento Republic FC and D.C. United also use red stars in their logos, referencing the flags of California and the District of Columbia respectively. The German rowing club Pirnaer Ruderverein 1872 began (and continues) to use red star since the 19th century.
-
Red Star Belgrade
-
Pirnaer Ruderverein 1872
Use by socialist groups
Armed revolutionary organizations
In 1970, the Red Army Faction, a West German militant group, used a red star paired with a Heckler & Koch MP5 in their highly recognizable insignia.
In 1994, the red star was included in the flag of the armed revolutionary Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN) in Chiapas, Mexico.
A number of communist parties in Turkey utilize the red star. Likewise, a number of Kurdish revolutionary organizations connected to the Kurdistan Communities Union utilize the red star in their iconography. Those include the flags of the Kurdistan Workers' Party and the battle flag pennants of the People's Defence Forces and Free Women's Units in Turkish Kurdistan, the People's Protection Units and Women's Protection Units in Syrian Kurdistan, and the Eastern Kurdistan Units and Women's Defense Forces in Iranian Kurdistan.
The Iranian Islamist-Socialist militant opposition group the Mojahedin-e-Khalq uses the red star with the rifle, sickle and the map of Iran in the background.
-
Red Army Faction (West German militant group) (RAF)
-
Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN)
-
Marxist Leninist Communist Party (MLKP)
-
United Freedom Forces (BÖG)
-
International Freedom Battalion (IFB)
-
International Revolutionary People's Guerrilla Forces (IRPGF)
-
Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK)
-
People's Defence Forces (HPG)
-
Free Women's Units (YJA-STAR)
-
Civil Protection Units (YPS)
-
People's Protection Units (YPG)
-
Women's Protection Units (YPJ)
-
Eastern Kurdistan Units (HRK)
-
Komalah
-
Combat Organization of Anarcho-Communists (BOAK)
-
Flag of the Communist (Maoist) Party of Afghanistan
Political parties and movements
The Brazilian leftist Worker's Party uses a red star as its symbol with the party acronym (Portuguese: Partido dos Trabalhadores – PT) inside. Hugo Chávez and his supporters in Venezuela have used the red star in numerous symbols and logos, and have included it in the logo of the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV). It was also used throughout 2007 as a symbol of the "5 Engines of the Bolivarian Socialist Revolution". It is also used by the militant South African shack-dweller's movement Abahlali baseMjondolo. Like in Latin America and Africa, several European socialist parties continue to use a star as a part of their logos. The red star is also featured prominently in the independence flags of various separatist movements in Spain .
-
Symbol of Workers' Party (Brazil)
-
Symbol of the United Socialist Party of Venezuela
-
Symbol of the Democratic Youth Federation of India
-
Symbol of the French Communist Party
-
Symbol of the Communist Party of Spain
-
Symbol of the Portuguese Communist Party
-
Symbol of the Dutch Socialist Party
-
Symbol of the Workers' Party of Belgium
-
Symbol of the Slovenian party The Left
-
Symbol of the Italian party Power to the People
-
Symbol of the Norwegian Red Party
-
Symbol of the Ecuadorian party Popular Unity
-
Symbol of the Party of Socialists of the Republic of Moldova
-
Symbol of the Abahlali baseMjondolo
-
Flag of the Andalusian Nation party
-
Castilian nationalist flag
-
Galician nationalist flag Estreleira
-
Catalan pro-independence flag Estelada Vermella
-
flag of the Yemeni Socialist Party
Uses without socialist symbolism
Some red stars adopted in emblems and flags have a significance that does not originally relate to socialism. Among these, the most well-known include the current state flag of California (echoing the Californian red star flag of 1836) and the flag of New Zealand (designed in 1869, officially adopted in 1902). The flag of the District of Columbia (designed in 1921, adopted in 1938) recalls George Washington's coat of arms. DC Comics' Wonder Woman also wears a 5 point red star headband with gold or yellow background.
Crescent moon and star
The crescent moon and star was a symbol used by the Ottoman Empire. Various states with Ottoman history have thus adopted this symbol into their present-day flags.
-
Flag of Tunisia
-
Flag of Algeria
-
Flag of Northern Cyprus
-
Emblem of Turkey
Assorted Flags and Coats of Arms
-
Flag of New Zealand.
-
Flag of Panama.
-
Flag of Syria (opposition group during the civil war). Was the independence flag first used in 1932.
-
Flag of California.
-
California Lone Star Flag – 1836.
-
Flag of Washington, D.C.
-
Flag of Acre State, Brazil.
-
Flag of Nagasaki city.
-
Flag of Birmingham, Alabama.
-
Arms of Għargħur, Malta.
-
Moríñigo coat of arms.
-
Valais coat of arms
-
Crain, Yonne coat of arms.
-
Chauriat coat of arms.
Symbol of animal relief
The red star was adopted as the symbol of the International Red Star Alliance, a Geneva international treaty signed in 1914 with the purpose of bringing about international cooperation on behalf of sick and wounded war animals, while securing the neutral status of the personnel engaged in such work. Besides the International Alliance, national Red Star societies were also established. Regarding animal relief, the International Red Star Alliance had an analogous role of that of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement. To identify their neutral status, white brassards with red stars were worn by military veterinary personnel in World War I in a similar way medical personal worn brassards with red crosses.[14]
Following the War, the American Red Star turned to focus on domestic issues, including care for animals during disasters. The organization waxed and waned over the decades, and as of 2016[update] exists as the American Humane Association's Red Star Animal Emergency Services.[15][verification needed]
Red stars in labels and logos
-
Label of a Heineken bottle
-
Logo of AKO, product of the Soviet Union
-
Logo of Macy's department stores
-
Texaco logo, circa 1913
-
Caltex logo, circa 1936
The red star was used by the Texaco oil company in various forms from 1909 to 1981.[16] Its overseas division Caltex also used the red star until 1996. Red Star Yeast was produced for a century in Milwaukee, Baltimore, and Oakland before its subsumption as a brand by Lesaffre.
A brand of Erguotou, a type of Baijiu, was named "Hongxing" (Chinese: 红星; literally: 'Red Star') in 1949 to celebrate the founding of the People's Republic of China.[17]
North Korea's Red Star operating system takes its name from the communist red star.
Legal status
The red star and the hammer and sickle are regarded as occupation symbols as well as symbols of totalitarianism and state terror by several countries that were formerly either members of or occupied by the Soviet Union. Accordingly, Latvia,[18] Lithuania,[19] Hungary[20] and Ukraine[21][22][23] have banned the symbol among others deemed to be symbols of totalitarian political ideologies and the Soviet Union or its republics. In Poland , the Parliament passed in 2009 a ban that referred generally to "fascist, communist or other totalitarian symbols", while not specifying any of them.[24] Following a constitutional complaint, it has been abolished by the Constitutional Tribunal as contrary to articles in the Constitution of Poland guaranteeing the freedom of speech. A similar law was considered in Estonia, but eventually failed in a parliamentary committee due to its conflict with freedoms guaranteed by the constitution of Estonia.
The European Court of Human Rights has ruled, in a similar manner, against the laws that ban political symbols, which were deemed to be in clear opposition with basic human rights, such as freedom of speech,[25][26] confirmed again in 2011 in case Fratanolo v. Hungary.[27] The decision has been compared[28] to the legislation concerning the symbols of Nazism, which continue to be banned in several European Union member states, including Germany and France .
There have been calls for an EU-wide ban on both Soviet and Nazi symbols, notably by politicians from Lithuania, Estonia, the Czech Republic, Hungary and Slovakia. The European Commissioner for Justice, Franco Frattini, felt it "might not be appropriate" to include communist symbols in the context of discussions on xenophobia and anti-Semitism.[29]
In 2003, Hungarian politician Attila Vajnai was arrested, handcuffed and fined for wearing a red star on his lapel during a demonstration. He appealed his sentence to the European Court of Human Rights, which decided that the ban was a violation of the freedom of expression, calling the Hungarian ban "indiscriminate" and "too broad".[30]
In Slovenia, the red star was historically associated with the resistance movement that fought against fascist occupation in World War II, but was also later a state symbol of Yugoslavia during the dictatorship of Josip Broz Tito. On 21 March 2011, Slovenia issued a two-euro commemorative coin to mark the 100th anniversary of the birth of Franc Rozman, a partisan commander, featuring a large star that represented a red star. This led to criticism from the Slovenian democratic parties without a communist history.
Non five-pointed red stars
Emblems and flags where the red stars displayed are not five-pointed are much rarer. These include the following:
-
Three-pointed red star in the flag of the International Brigades.
-
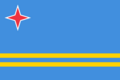
Four-pointed red star in the flag of Aruba.
-
Six-pointed red stars outlined in green in the flag of Burundi.
-
Six-pointed red stars in the flag of Chicago.
-
Eight-pointed red star in the Naval Ensign of Singapore.
-
Emblem of Magen David Adom, the Israeli national aid society.
See also
- Five-pointed star
- Red flag (⚑)
- Hammer and sickle (☭)
- Communist symbolism
- Star and crescent
- Star of Bethlehem
- Hollywood Walk of Fame
- Red Star Belgrade
- FC Red Star Saint-Ouen
- FK Velež Mostar
- Flags of the Ottoman Empire
- Waasland-Beveren
- Pancho Villa Expedition, when American military aircraft used a red star insignia (1916–17)
- Lone Star Flag
References
- ↑ Poroshenko signed the laws about decomunization. Ukrayinska Pravda. 15 May 2015
Poroshenko signs laws on denouncing Communist, Nazi regimes, Interfax-Ukraine. 15 May 2015 - ↑ Okhlebkin, V.V (2006). Dictionary of international symbols and emblems.. ZAO Tsentrpoligraf.
- ↑ Khvostov, Mikhail (1996), The Russian Civil War (1) The Red Army. Published by Men-At-Arms. ISBN 1-85532-608-6.
- ↑ Możejko, Edward (December 1985). "Reviewed Work: Red Star: The First Bolshevik Utopia by Alexander Bogdanov". Canadian Slavonic Papers 27 (4): 461–462.
- ↑ Pri La Stelo: Militista simbolo
- ↑ The Russian Civil War (1): The Red Army By Mikhail Khvostov, Andrei Karachtchouk, page 37 (there are several mentions of the use of the red star from 1918)
- ↑ "Historic Wings - Flight Stories - Chasing Pancho Villa". HW. 15 March 2013. http://fly.historicwings.com/2013/03/chasing-pancho-villa/. "Just one day after arriving, on 16 March 1916, the first reconnaissance flight was flown by Capt. Dodd with Capt. Foulois (as an observer) on the Curtiss JN-3 S.C. No. 43. As with all of the Army's aircraft in that era, the plane carried simple markings – a red star on the tail and the large number 43 painted on the sides of the fuselage."
- ↑ ""Красная Звезда" - cамая полная, достоверная и оперативная военная газета. Russian military newspaper". http://www.redstar.ru/.
- ↑ Weber, Hannah (25 December 2017). "Yolka: the story of Russia's 'New Year tree', from pagan origins to Soviet celebrations". https://www.calvertjournal.com/articles/show/9424/yolka-russia-new-year-tree-pagan-soviet-christmas.
- ↑ "Belarus News and Analysis | A Partisan Reality Show". http://www.data.minsk.by/belarusnews/052005/30.html.
- ↑ "Error: no
|title=specified when using {{Cite web}}" (in zh-hans). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 2019. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/tjbz/tjyqhdmhcxhfdm/2019/42/03/25/420325211.html. "统计用区划代码 城乡分类代码 名称
...
420325211201 220 红星村委会" - ↑ "Error: no
|title=specified when using {{Cite web}}" (in zh-hans). XZQH.org. 31 December 2010. http://www.xzqh.org/html/show/xj/22301.html. "克孜勒陶乡 1966年成立克孜勒陶公社,1967年更名红星公社,1984年改设克孜勒陶乡。位于县城以南,距县城121千米。面积3882平方千米,人口0.8万,其中柯尔克孜族占99.16%,辖乌尔都隆窝孜、喀尔乌勒、塔尔开其克、托云都克、 塔木、喀普喀、其木干、阿尔帕勒克8个行政村。" - ↑ Военно-воздушные силы отказались от трехцветных звезд Армия, Известия (in Russian)
- ↑ Celebrating 125 years, American Humane Association
- ↑ "When Disaster Strikes — Look to Red Star Animal Emergency Services". http://www.americanhumane.org/assets/pdfs/animals/aes-redstar-1pager-41511.pdf.
- ↑ "History of Texaco". http://www.texaco.com/about-timeline.aspx.
- ↑ "RED STAR WINE 1949". REDSTARWINE. 2018-04-28. http://www.redstarwine.com/gywm3/dsj0/7b1f8088b4f211ea8fba4be1890990b8.html.
- ↑ "BC, Riga, 16.05.2013". http://www.baltic-course.com/eng/legislation/&doc=74860.
- ↑ "Lithuanian ban on Soviet symbols". BBC News. 17 June 2008. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/low/europe/7459976.stm.
- ↑ "Act C of 2012 on the Criminal Code, Section 335: Use of Symbols of Totalitarianism". p. 97. http://thb.kormany.hu/download/a/46/11000/Btk_EN.pdf. "Any person who: a) distributes, b) uses before the public at large, or c) publicly exhibits, the swastika, the insignia of the SS, the arrow cross, the sickle and hammer, the five-pointed red star or any symbol depicting the above so as to breach public peace – specifically in a way to offend the dignity of victims of totalitarian regimes and their right to sanctity – is guilty of a misdemeanor punishable by custodial arrest, insofar as they did not result in a more serious criminal offense."
- ↑ "Ukraine Bans Soviet-Era Symbols", The Wall Street Journal, 9 April 2015, https://www.wsj.com/articles/ukraine-bans-soviet-era-symbols-1428606171
- ↑ LAW OF UKRAINE. On the condemnation of the communist and national socialist (Nazi) regimes, and prohibition of propaganda of their symbols, http://www.memory.gov.ua/laws/law-ukraine-condemnation-communist-and-national-socialist-nazi-regimes-and-prohibition-propagan, retrieved 9 August 2015
- ↑ "Про засудження комуністичного та націонал-соціалістичного (нацистського) тоталітарних режимів в Україні та заборону пропаганди їхньої символіки". http://zakon4.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/317-viii.
- ↑ "Poland Imposes Strict Ban on Communist Symbols". Fox News. 27 November 2009. http://www.foxnews.com/story/0,2933,577305,00.html.
- ↑ ECHR judgment in case Vajnai v. Hungary
- ↑ "Wearing a red star in Hungary 'is a basic human right' : Europe World". http://www.earthtimes.org/articles/show/217632,wearing-a-red-star-in-hungary-is-a-basic-human.html.
- ↑ Press release 222(2011). Registrar of ECtHR 3 November 2011.
- ↑ European Court considers Labour Party's red star – in Hungarian
- ↑ "EU ban urged on communist symbols". BBC News. 3 February 2005. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/4234335.stm.
- ↑ Curry, Andrew (24 November 2009). "Vestiges of 'Genocidal System': Poland to Ban Communist Symbols". Der Spiegel. http://www.spiegel.de/international/europe/0,1518,663154,00.html.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gallery of flags with stars#Red five-pointed star. |
 |