Software:Dung Beetles (video game)
| Dung Beetles | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Datasoft |
| Publisher(s) | Datasoft Tandy Gentry Software |
| Designer(s) | Bob Bishop |
| Programmer(s) | Apple II Bob Bishop[1] Atari 8-bit Mark Riley[2] Color Computer Steve Bjork[3] |
| Platform(s) | Apple II, Atari 8-bit, NEC PC-6001, TRS-80 Color Computer |
| Release | 1982 |
| Genre(s) | Maze |
| Mode(s) | Single-player |
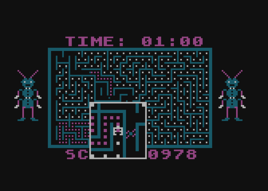
Dung Beetles is an Apple II maze game by Bob Bishop published in 1982 by Datasoft.[1] The gameplay is similar to Pac-Man, but a portion of the maze around the player-controlled character is enlarged as if being viewed through a square magnifying lens.
Dung Beetles was ported to Atari 8-bit family and the TRS-80 Color Computer. The Color Computer version was sold by Tandy and renamed Mega-Bug.[3] The Mega-Bug port was programmed by Steve Bjork. Later versions for both the Apple II and Atari were named Tumble Bugs.[4] In 1983, Datasoft moved the game to its Gentry Software label with another name change: Magneto Bugs.[5] In Australia , the game was sold as Bug Attack.[citation needed] It was also released for the NEC PC-6001.
Gameplay
The game concept and gameplay are based on Pac-Man, but features a much larger, randomly-generated maze and a moving "magnifying rectangle" that shows the player's character, maze details, and nearby enemies close-up. The objective of the game is to score points by eating all of the dots in the maze. As the player character moves through the maze, it leaves a trail of dung behind. Dung beetles navigate the maze searching for the player. When a beetle finds a trail of dung, it will start following that trail, consuming it as it goes. It picks a direction at random when the trail splits, and goes back to searching if the trail ends.
The game ends when the player's character is caught by a dung beetle, at which point the game plays a digitized voice that says "We gotcha!" and gives a brief animation.
Reception
Softline found the magnifying glass "an impressive programming feat," and concluded that it was "a solid game ... It could stand some more variety, but it certainly does not lack challenge".[6] Writing for ANALOG Computing, Marc Benioff called Tumble Bugs, "an outstanding variation on Pac-Man".[7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hague, James. "The Giant List of Classic Game Programmers". https://dadgum.com/giantlist/.
- ↑ "Tumble Bugs Atari manual". Datasoft. 1982. https://archive.org/details/TumbleBugs_201509/page/n1.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Boyle, L. Curtis. "Mega-Bug". http://www.lcurtisboyle.com/nitros9/megabug.html.
- ↑ "Tumble Bugs". http://www.atarimania.com/game-atari-400-800-xl-xe-tumble-bugs_5548.html.
- ↑ "New Products". ANALOG Computing (13): 17. September 1983. https://archive.org/details/analog-computing-magazine-13/page/n17/mode/2up.
- ↑ Durkee, David (May 1982). "Tumblebugs". Softline: pp. 16–17. http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1982&pub=6&id=5. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ↑ Benioff, Marc (May 1982). "Benioff At Large". ANALOG Computing (6): 7. https://archive.org/details/analog-computing-magazine-06/page/n9/mode/2up.
 |