Software:NIAflow
 | |
| Developer(s) | Haver & Boecker oHG |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2016 |
| Stable release | 3.1.1.4
/ April 14, 2021[1] |
| Written in | Visual Basic.NET |
| Operating system | Windows |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Simulation software |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | www |
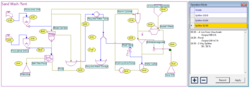
NIAflow is simulation software for mineral processing plants. Based on a flowsheet interface, it calculates the material flow through a variety of processing machinery.
Overview
NIAflow is used to design new mineral processing plants as well as optimize existing plants. Applying machine-specific parameters, the software computes the material flow through entire plants and provides product forecasts. Based on these results, process layout and machinery setup can be evaluated.
NIAflow is a product of Haver & Boecker. It is available in three versions: Basic, Aggregate and Mining. Depending on the version, the number of machinery objects vary.
History
In 1996, NIAflow development began under the name “NIAexpert” as software for sizing and selection of vibrating screens. Its further development began in 2007 as “NIAproject[1]” which included a mathematical model to simulate a close-to-reality screening process on vibrating screens. It also offered multi-machine calculations and product forecasts.
In 2016, “NIAflow” was introduced with the ability to simulate the material flow through various processing equipment for an entire mineral processing plant; it was no longer restricted to screening machines only as its predecessors.
Features

The software uses machine-specific algorithms to simulate the flow of material through each of the objects.
Approximately 80 different mineral processing machines can be arranged in a flow diagram.
All object parameters can be displayed on the flowsheet using an unlimited number of labels.
Object parameters are stored in three detailing levels, where the ‘Essential’ level contains data required for calculation. The ‘Extended” level and the ‘Detailed’ level is intended to keep data required for the creation of a tender document or documentation
Using the operation mode feature, typical conditions of a plant can be stored.
The label layer function groups labels in user selectable layers. Using this function, different sets of information on the flowsheet can be created.
In addition to the flowsheet, a project summary can be printed that contains information regarding the project, its objects and materials.
Object groups

- Storing: Stockpile, Silo, Mining Truck, Front Loader, Road Truck, Silo Truck, Water Tank, Excavator Ship, Pond, Water Tap
- Conveying: Belt Conveyor, Vibrating feeder, Reciprocating Feeder, Apron Feeder, 2-Way Splitter, 3-Way Splitter, Bucket Elevator, Screw Conveyor, Rotary Valve, Chute
- Screening: 1 Screen Deck, 2 Screen Deck, 3 Screen Deck, 4 Screen Deck, Variable Screen, Stationary Grid, Grizzly Feeder, Roller Screen, Sieve Bend
- Crushing: Jaw Crusher, Cone Crusher, Roll Crusher, HSI, VSI
- Grinding: Sag Mill, Ball Mill, Rod Mill
- Sort: Spiral Sorter, Jig Sorter, Upstream Sorter, Optical Sorter, Air Separator, Belt Magnet, Eddy Current, Floatation Cell, Magnetic Separator
- Washing: Hydro-Clean, Friction Clean, Drum Washer, Bucket Wheel, Sand Screw, Log Washer, Hydro Cyclone, Sump Pump, Pump
- Slurry: Chamber Filter Press, Belt Filter Press, Thickener, Flocculence Unit, Blade Clarifier, Centrifuge, Disk Filter
- Dedust: Bag House, Aero Cyclone, Air Blower, Vent, Silo Top Filter, Funnel
- Packing: Pelletizing Disk, Mixer
- Controls: Hand Valve, Motor Valve, Pneumatic Valve, Hydraulic Valve, Float Valve, Check Valve, Conveyor Scale, Pressure Gauge, Level Control, Bulk Level Control, Flow Meter, Switch Cabinet
- Various: Free Text, Plant, Drum Dryer, Fluidized Bed Dryer, Drum Cooler
Technical Description
The calculation in NIAflow follows the flow of the material through the plant. When the plant layout contains closed circuits, NIAflow will repeat the calculation until a stationary condition is reached. During calculation, user-selectable limits are being watched, e.g. maximum tonnage throughput. NIAflow raises an error when those limits are exceeded.
Material Handling and Object Calculation: Most objects in NIAflow are connected by lines where each line represents a material transported from one object to another. Any number of incoming lines can be attached to an in-point of an object. During calculation, all incoming materials are blended into a new material. Calculations are dependent on the type of object. At the conclusion of object calculation, the resulting material product(s) are connected to the out-point(s) of the object.
Curve Interpolation: Particle Size Distributions (PSD) in NIAflow are generated using either linear or 3D+ (cubic spline) interpolation methods and can be viewed on Linear, Log, Log-Log and RRSB grids.[2] Interpolation methods and grids are stored together with the object properties.
Blending: During blending, all material parameters are being re-calculated. Depending on the type of parameter the result can be the sum of the material properties (e.g. tph) or the weighted average (e.g. temperature). The Particle Size Distribution (PSD) of the blended material is computed by applying all sieves of the materials to the new one and calculating percentages based on the current grid and curve interpolation method.
Classifying: Classifying objects are various screens as well as objects that can be set up for either sorting or classifying, e.g. upstream sorter/classifier. Classifying is performed by means of cut-curves (Tromp Curve).[3] Tromp curves describe the probability for a certain material fraction to arrive in the coarse product. For screens, NIAflow generates cut curves automatically based on the machine and media setup. For other machines, user input is required to define the cut curve.
Sorting: Similar to classifying sorting is performed based on cut curves that have to be entered by the user. Sorting properties are stored for each individual material fraction. NIAflow supports sorting by density, color, shape, metal content, etc.
Crushing, Milling: Crusher and mill products are calculated assuming a linear behavior of the product PSD in either a double logarithmic or RRSB grid. Each type of crushing or grinding machine creates its own specific inclination of the curve. The inclination combined with the maximum particle size leaving the machine is used for product forecast.
Operation Modes: A plant can be set up in various operational modes, depending on how the objects that control the feed rate are set up. These objects are: Stockpile, Silo, Pond, Water Tank, 2 Way Splitter and 3 Way Splitter. The settings of these objects can be varied and various operational modes can be stored with the project.
Versions
| Version | Release Date | Features |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1.1 | Apr 2016 | Custom labeling in Flowsheet and Project Print (two different logos and one watermark) |
| Automatic object naming without number when only one object of this kind | ||
| Double Logarithmic and RRSB interpolation for crusher sizing | ||
| 2.2.0 | Sep 2016 | Nine NEW Sorting Objects (Color, Density, Valuable Content, Shape, Ferro-magnetism, Non-Ferro-magnetism) |
| Input and calculation of sorting properties per sieve analysis fraction. (Color, Density, Valuable Content, Shape, Ferro-magnetism, Non-Ferro-magnetism) | ||
| Cut Function (Tromp) - Material split based on Tromp curve | ||
| 2.2.1 | Oct 2016 | New vendor can now be set up directly in object menu |
| Combined density and size sorting | ||
| 2.2.2 | Jan 2017 | Campus version implemented |
| Transfer object setting and formats between same and different object types | ||
| 2.2.3 | Mar 2017 | Custom labeling for flowsheets and project print |
| PSD display on flowsheet for any materials in lines and objects | ||
| Closed recycled water circuits using pond object with adjustable output | ||
| Label Layers: Place labels on an unlimited number of layers that can be switched on or off | ||
| 2.2.4 | July 2017 | UNDO function (CTRL Z) to restore any drawing actions on flowsheet |
| ZOOM and scroll drawing area | ||
| User-modified material properties now inheritable to downstream materials | ||
| New objects are created with standard Imperial or Metric units according to user settings | ||
| 2.2.5 | Nov 2017 | New language German |
| Limit Monitoring. NIAflow checks material- or object-specific limits and displays error messages, when mouse is over object | ||
| 2.2.6 | Jan 2018 | Structured user menu for vibrating screen selection |
| 2.2.7 | Mar 2018 | New languages Russian and French |
| Template file to for all objects | ||
| Print language selectable different from main language |
Operating system
Niaflow is based on Windows with framework 4.5.2.
See also
- Mineral Processing
- Screening
- Log-Log Scale
- Cubic Spline Interpolation
External links
Sources
- Haver & Boecker Optimizes Mining Operations with NIAflow Software, Mining.com, 8 September 2016, retrieved 26 April 2017
- Haver & Boecker's NIAflow plant simulation software optimizes mining operations , Heavy Equipment Guide, 9 September 2016, retrieved 26 April 2017
- Plant simulation software for minerals processing, Australian Mining 3 November, retrieved 26 April 2017
- Plant simulation software to optimize operations, Pit & Quarry, 8 September 2016, retrieved 1 June 2017
- Optimising crushing and screening efficiency with Haver & Boecker, World Highways, November 2016, retrieved 1 June 2017
- New plant simulation software from Haver & Boecker, Trade Earthmovers, 8 November 2016, retrieved 1 June 2017
References
 |
