Log–log plot
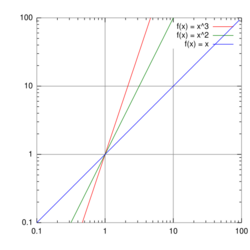
Note the logarithmic scale markings on each of the axes, and that the log x and log y axes (where the logarithms are 0) are where x and y themselves are 1.

In science and engineering, a log–log graph or log–log plot is a two-dimensional graph of numerical data that uses logarithmic scales on both the horizontal and vertical axes. Power functions – relationships of the form – appear as straight lines in a log–log graph, with the exponent corresponding to the slope, and the coefficient corresponding to the intercept. Thus these graphs are very useful for recognizing these relationships and estimating parameters. Any base can be used for the logarithm, though most commonly base 10 (common logs) are used.
Relation with monomials
Given a monomial equation taking the logarithm of the equation (with any base) yields:
Setting and which corresponds to using a log–log graph, yields the equation
where m = k is the slope of the line (gradient) and b = log a is the intercept on the (log y)-axis, meaning where log x = 0, so, reversing the logs, a is the y value corresponding to x = 1.[1]
Equations
The equation for a line on a log–log scale would be: where m is the slope and b is the intercept point on the log plot.
Slope of a log–log plot

To find the slope of the plot, two points are selected on the x-axis, say x1 and x2. Using the below equation: and The slope m is found taking the difference: where F1 is shorthand for F(x1) and F2 is shorthand for F(x2). The figure at right illustrates the formula. Notice that the slope in the example of the figure is negative. The formula also provides a negative slope, as can be seen from the following property of the logarithm:
Finding the function from the log–log plot
The above procedure now is reversed to find the form of the function F(x) using its (assumed) known log–log plot. To find the function F, pick some fixed point (x0, F0), where F0 is shorthand for F(x0), somewhere on the straight line in the above graph, and further some other arbitrary point (x1, F1) on the same graph. Then from the slope formula above: which leads to Notice that 10log10(F1) = F1. Therefore, the logs can be inverted to find: or which means that In other words, F is proportional to x to the power of the slope of the straight line of its log–log graph. Specifically, a straight line on a log–log plot containing points (x0, F0) and (x1, F1) will have the function: Of course, the inverse is true too: any function of the form will have a straight line as its log–log graph representation, where the slope of the line is m.
Finding the area under a straight-line segment of log–log plot
To calculate the area under a continuous, straight-line segment of a log–log plot (or estimating an area of an almost-straight line), take the function defined previously and integrate it. Since it is only operating on a definite integral (two defined endpoints), the area A under the plot takes the form
Rearranging the original equation and plugging in the fixed point values, it is found that
Substituting back into the integral, you find that for A over x0 to x1
Therefore,
For m = −1, the integral becomes
Log-log linear regression models
Log–log plots are often use for visualizing log-log linear regression models with (roughly) log-normal, or Log-logistic, errors. In such models, after log-transforming the dependent and independent variables, a Simple linear regression model can be fitted, with the errors becoming homoscedastic. This model is useful when dealing with data that exhibits exponential growth or decay, while the errors continue to grow as the independent value grows (i.e., heteroscedastic error).
As above, in a log-log linear model the relationship between the variables is expressed as a power law. Every unit change in the independent variable will result in a constant percentage change in the dependent variable. The model is expressed as:
Taking the logarithm of both sides, we get:
This is a linear equation in the logarithms of and , with as the intercept and as the slope. In which , and .

Figure 1 illustrates how this looks. It presents two plots generated using 10,000 simulated points. The left plot, titled 'Concave Line with Log-Normal Noise', displays a scatter plot of the observed data (y) against the independent variable (x). The red line represents the 'Median line', while the blue line is the 'Mean line'. This plot illustrates a dataset with a power-law relationship between the variables, represented by a concave line.
When both variables are log-transformed, as shown in the right plot of Figure 1, titled 'Log-Log Linear Line with Normal Noise', the relationship becomes linear. This plot also displays a scatter plot of the observed data against the independent variable, but after both axes are on a logarithmic scale. Here, both the mean and median lines are the same (red) line. This transformation allows us to fit a Simple linear regression model (which can then be transformed back to the original scale - as the median line).

The transformation from the left plot to the right plot in Figure 1 also demonstrates the effect of the log transformation on the distribution of noise in the data. In the left plot, the noise appears to follow a log-normal distribution, which is right-skewed and can be difficult to work with. In the right plot, after the log transformation, the noise appears to follow a normal distribution, which is easier to reason about and model.
This normalization of noise is further analyzed in Figure 2, which presents a line plot of three error metrics (Mean Absolute Error - MAE, Root Mean Square Error - RMSE, and Mean Absolute Logarithmic Error - MALE) calculated over a sliding window of size 28 on the x-axis. The y-axis gives the error, plotted against the independent variable (x). Each error metric is represented by a different color, with the corresponding smoothed line overlaying the original line (since this is just simulated data, the error estimation is a bit jumpy). These error metrics provide a measure of the noise as it varies across different x values.
Log-log linear models are widely used in various fields, including economics, biology, and physics, where many phenomena exhibit power-law behavior. They are also useful in regression analysis when dealing with heteroscedastic data, as the log transformation can help to stabilize the variance.
Applications
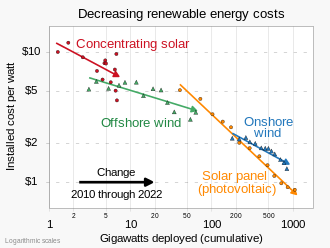
These graphs are useful when the parameters a and b need to be estimated from numerical data. Specifications such as this are used frequently in economics.
One example is the estimation of money demand functions based on inventory theory, in which it can be assumed that money demand at time t is given by where M is the real quantity of money held by the public, R is the rate of return on an alternative, higher yielding asset in excess of that on money, Y is the public's real income, U is an error term assumed to be lognormally distributed, A is a scale parameter to be estimated, and b and c are elasticity parameters to be estimated. Taking logs yields where m = log M, a = log A, r = log R, y = log Y, and u = log U with u being normally distributed. This equation can be estimated using ordinary least squares.
Another economic example is the estimation of a firm's Cobb–Douglas production function, which is the right side of the equation in which Q is the quantity of output that can be produced per month, N is the number of hours of labor employed in production per month, K is the number of hours of physical capital utilized per month, U is an error term assumed to be lognormally distributed, and A, , and are parameters to be estimated. Taking logs gives the linear regression equation where q = log Q, a = log A, n = log N, k = log K, and u = log U.
Log–log regression can also be used to estimate the fractal dimension of a naturally occurring fractal.
However, going in the other direction – observing that data appears as an approximate line on a log–log scale and concluding that the data follows a power law – is not always valid.[2]
In fact, many other functional forms appear approximately linear on the log–log scale, and simply evaluating the goodness of fit of a linear regression on logged data using the coefficient of determination (R2) may be invalid, as the assumptions of the linear regression model, such as Gaussian error, may not be satisfied; in addition, tests of fit of the log–log form may exhibit low statistical power, as these tests may have low likelihood of rejecting power laws in the presence of other true functional forms. While simple log–log plots may be instructive in detecting possible power laws, and have been used dating back to Pareto in the 1890s, validation as a power laws requires more sophisticated statistics.[2]
These graphs are also extremely useful when data are gathered by varying the control variable along an exponential function, in which case the control variable x is more naturally represented on a log scale, so that the data points are evenly spaced, rather than compressed at the low end. The output variable y can either be represented linearly, yielding a lin–log graph (log x, y), or its logarithm can also be taken, yielding the log–log graph (log x, log y).
Bode plot (a graph of the frequency response of a system) is also log–log plot.
In chemical kinetics, the general form of the dependence of the reaction rate on concentration takes the form of a power law (law of mass action), so a log-log plot is useful for estimating the reaction parameters from experiment.
See also
- Semi-log plot (lin–log or log–lin)
- Power law
- Zipf law
- Log-linear model
- Log-normal distribution
- Log-logistic distribution
- Data transformation (statistics)
- Variance-stabilizing transformation
References
- ↑ Bourne, Murray. "7. Log-Log and Semi-log Graphs" (in en-us). https://www.intmath.com/exponential-logarithmic-functions/7-graphs-log-semilog.php.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Clauset, A.; Shalizi, C. R.; Newman, M. E. J. (2009). "Power-Law Distributions in Empirical Data". SIAM Review 51 (4): 661–703. doi:10.1137/070710111. Bibcode: 2009SIAMR..51..661C.
de:Logarithmenpapier#Doppeltlogarithmisches Papier
 |
