Software:Valhalla (video game)
| Valhalla | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Legend |
| Publisher(s) | |
| Platform(s) | ZX Spectrum, Commodore 64 |
| Release | 1983: ZX Spectrum 1984: C64 |
| Genre(s) | Interactive fiction |
| Mode(s) | Single-player |
Valhalla is a text adventure with graphics published in 1983 by the British studio Legend for the ZX Spectrum. It reached number one in the UK sales charts.[1] The Commodore 64 version of the game was released in 1984 and reached number five.[2]
Gameplay
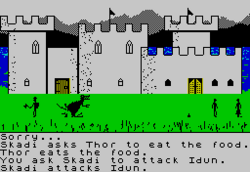
In Valhalla the characters move through various Nordic locations with accompanying text at the bottom of the screen detailing all character actions. It is set mainly in Asgard and Midgard, though when the character dies, it reappears in Hell (Niflheim under another name) and is able to walk out.
The game's text parser understands most multi-part sentences, as long as they are written using the words listed in the manual. Listing the accepted words was not seen in most similar titles of the time.
The aim is to collect six mythical objects: Ofnir (key), Drapnir (ring), Skornir (shield), Skalir (sword), Felstrong (axe), and Grimnir (helmet). To obtain all the items, the player receives help from various characters from Norse mythology. If the player dies while holding any of the six items, it will be lost and moved to a new location.[3] These objects are required to access otherwise unreachable parts of the game, such as Valhalla, but carrying any of the items saps the player's strength.
The character has an alignment (between good and evil) that changes depending on which of the other characters are helped. The more the player helps good characters, the more other good characters will help the player in their quest. Characters include gods, goddesses, dwarves, dragons, wolves, a snake, and a raven.[4]
The characters move and interact independent of any action by the player. If the player does nothing, the game 'plays' itself, with the characters moving about while the player decides what to do.[3]
Typing in a swear word causes a dwarf to dash onto the screen to punch the player while generating the message "Mary is not amused....". Mary can be found in El Vinos and even if killed, she returns within a minute.
The game engine has a limit of eight objects to be left in any one location, whether on the ground, in a chest, or in a cupboard. If the player drops an object in an area where the limit has been reached, a character called Klepto appears to steal the item, removing it from the game.
Development
The publishing house Legend, founded and managed by John Peel, had previously published titles under the Microl label which financed the development of Valhalla.[5] The game was developed by Richard Edwards, Graham Asher, Charles Goodwin, James Learmont, and Andrew Owen using a system they named "Movisoft" which Peel hoped would become "the adventure game equivalent of CP/M".[5] The system occupied 4K of the game footprint and used machine code, with the rest of the game engine and text parser written in Sinclair BASIC.[6] The C64 version of the game was released in the first half of 1984 and featured larger and coloured character graphics.[7]
The cover of the game, as well as the loading screen, features a drawing of the Sutton Hoo helmet, an artifact from the 7th century believed to have belonged to King Rædwald of East Anglia.
References
- ↑ "PCN Charts". Personal Computer Games (VNU) (10): 10. December 1983. https://archive.org/details/PersonalComputerNews/PersonalComputerNews039-07Dec1983/page/n9/mode/2up. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ↑ "PCG Top 50". Personal Computer Games (VNU) (19): 19. September 1984. https://archive.org/details/personalcomputergames-magazine-10/page/n19/mode/2up. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Valhalla for Commodore 64 (1984)". https://www.mobygames.com/game/c64/valhalla.
- ↑ https://worldofspectrum.org/pub/sinclair/games-info/v/Valhalla.txt — the list of characters and their types is quite a long way down
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "The legend continues". Popular Computing Weekly (Sunshine Publications) (16): 16. 15 December 1983. https://spectrumcomputing.co.uk/page.php?issue_id=2785&page=16. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ↑ "Valhalla". 28 February 2009. https://www.retrogamer.net/retro_games80/valhalla/.
- ↑ "Valhalla converted for the CBM 64" (in en). Micro Adventurer: 7. March 1984.
External links
- Valhalla at SpectrumComputing.co.uk
- MobyGames is a commercial database website that catalogs information on video games and the people and companies behind them via crowdsourcing. This includes over 300,000 games for hundreds of platforms.[1] Founded in 1999, ownership of the site has changed hands several times. It has been owned by Atari SA since 2022.
Features
Edits and submissions to the site (including screenshots, box art, developer information, game summaries, and more) go through a verification process of fact-checking by volunteer "approvers".[2] This lengthy approval process after submission can range from minutes to days or months.[3] The most commonly used sources are the video game's website, packaging, and credit screens. There is a published standard for game information and copy-editing.[4] A ranking system allows users to earn points for contributing accurate information.[5]
Registered users can rate and review games. Users can create private or public "have" and "want" lists, which can generate a list of games available for trade with other registered users. The site contains an integrated forum. Each listed game can have its own sub-forum.
History

MobyGames was founded on March 1, 1999, by Jim Leonard and Brian Hirt, and joined by David Berk 18 months later, the three of which had been friends since high school.[6][7] Leonard had the idea of sharing information about computer games with a larger audience. The database began with information about games for IBM PC compatibles, relying on the founders' personal collections. Eventually, the site was opened up to allow general users to contribute information.[5] In a 2003 interview, Berk emphasized MobyGames' dedication to taking video games more seriously than broader society and to preserving games for their important cultural influence.[5]
In mid-2010, MobyGames was purchased by GameFly for an undisclosed amount.[8] This was announced to the community post factum , and the site's interface was given an unpopular redesign.[7] A few major contributors left, refusing to do volunteer work for a commercial website.{{Citation needed|date=June 2025} On December 18, 2013, MobyGames was acquired by Jeremiah Freyholtz, owner of Blue Flame Labs (a San Francisco-based game and web development company) and VGBoxArt (a site for fan-made video game box art).[9] Blue Flame Labs reverted MobyGames' interface to its pre-overhaul look and feel,[10] and for the next eight years, the site was run by Freyholtz and Independent Games Festival organizer Simon Carless.[7]
On November 24, 2021, Atari SA announced a potential deal with Blue Flame Labs to purchase MobyGames for $1.5 million.[11] The purchase was completed on 8 March 2022, with Freyholtz remaining as general manager.[12][13][14] Over the next year, the financial boost given by Atari led to a rework of the site being built from scratch with a new backend codebase, as well as updates improving the mobile and desktop user interface.[1] This was accomplished by investing in full-time development of the site instead of its previously part-time development.[15]
In 2024, MobyGames began offering a paid "Pro" membership option for the site to generate additional revenue.[16] Previously, the site had generated income exclusively through banner ads and (from March 2014 onward) a small number of patrons via the Patreon website.[17]
See also
- IGDB – game database used by Twitch for its search and discovery functions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sheehan, Gavin (2023-02-22). "Atari Relaunches The Fully Rebuilt & Optimized MobyGames Website". https://bleedingcool.com/games/atari-relaunches-the-fully-rebuilt-optimized-mobygames-website/.
- ↑ Litchfield, Ted (2021-11-26). "Zombie company Atari to devour MobyGames". https://www.pcgamer.com/zombie-company-atari-to-devour-mobygames/.
- ↑ "MobyGames FAQ: Emails Answered § When will my submission be approved?". Blue Flame Labs. 30 March 2014. http://www.mobygames.com/info/faq7#g1.
- ↑ "The MobyGames Standards and Practices". Blue Flame Labs. 6 January 2016. http://www.mobygames.com/info/standards.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Miller, Stanley A. (2003-04-22). "People's choice awards honor favorite Web sites". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel.
- ↑ "20 Years of MobyGames" (in en). 2019-02-28. https://trixter.oldskool.org/2019/02/28/20-years-of-mobygames/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Plunkett, Luke (2022-03-10). "Atari Buys MobyGames For $1.5 Million". https://kotaku.com/mobygames-retro-credits-database-imdb-atari-freyholtz-b-1848638521.
- ↑ "Report: MobyGames Acquired By GameFly Media". Gamasutra. 2011-02-07. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/game-platforms/report-mobygames-acquired-by-gamefly-media.
- ↑ Corriea, Alexa Ray (December 31, 2013). "MobyGames purchased from GameFly, improvements planned". http://www.polygon.com/2013/12/31/5261414/mobygames-purchased-from-gamefly-improvements-planned.
- ↑ Wawro, Alex (31 December 2013). "Game dev database MobyGames getting some TLC under new owner". Gamasutra. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/business/game-dev-database-mobygames-getting-some-tlc-under-new-owner.
- ↑ "Atari invests in Anstream, may buy MobyGames". November 24, 2021. https://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/2021-11-24-atari-invests-in-anstream-may-buy-mobygames.
- ↑ Rousseau, Jeffrey (2022-03-09). "Atari purchases Moby Games". https://www.gamesindustry.biz/atari-purchases-moby-games.
- ↑ "Atari Completes MobyGames Acquisition, Details Plans for the Site's Continued Support". March 8, 2022. https://www.atari.com/atari-completes-mobygames-acquisition-details-plans-for-the-sites-continued-support/.
- ↑ "Atari has acquired game database MobyGames for $1.5 million" (in en-GB). 2022-03-09. https://www.videogameschronicle.com/news/atari-has-acquired-game-database-mobygames-for-1-5-million/.
- ↑ Stanton, Rich (2022-03-10). "Atari buys videogame database MobyGames for $1.5 million". https://www.pcgamer.com/atari-buys-videogame-database-mobygames-for-dollar15-million/.
- ↑ Harris, John (2024-03-09). "MobyGames Offering “Pro” Membership". https://setsideb.com/mobygames-offering-pro-membership/.
- ↑ "MobyGames on Patreon". http://www.patreon.com/mobygames.
Wikidata has the property:
|
External links
- No URL found. Please specify a URL here or add one to Wikidata.
 |
- Valhalla can be played for free in the browser at the Internet Archive
- Review from Sinclair User issue 23, February 1984; at Sinclair User Magazine Online
 |
