Software:Zork I
| ZORK I | |
|---|---|
 Zork I Atari ST cover art | |
| Developer(s) | Infocom |
| Publisher(s) | Personal Software / Infocom / Activision |
| Designer(s) | Tim Anderson, Marc Blank, Dave Lebling and Bruce Daniels |
| Engine | ZIL |
| Platform(s) | PDP-10, Atari 8-bit, C64, CP/M, TRS-80, IBM PC, Apple II, Amiga, Amstrad CPC, Amstrad PCW, Macintosh, Atari ST, MS-DOS, NEC PC-9801, MSX, PlayStation, Sega Saturn, TI-99/4A |
| Release | December 1980 |
| Genre(s) | Text adventure |
| Mode(s) | Single player |
Zork: The Great Underground Empire - Part I, later known as Zork I, is an interactive fiction video game written by Marc Blank, Dave Lebling, Bruce Daniels and Tim Anderson and published by Infocom in 1980. It was the first game in the popular Zork trilogy and was released for a wide range of computer systems, followed by Zork II and Zork III. It was Infocom's first game, and sold 378,987 copies by 1986.
Plot
The game takes place in the Zork calendar year 948 GUE (although the passage of time is not notable in gameplay). The player steps into the deliberately vague role of an "adventurer". The game begins near a white house in a small, self-contained area. Although the player is given little instruction, the house provides an obvious point of interest.
When the player enters the house, it yields a number of intriguing objects, including a brass, battery-powered lantern, an empty trophy case, and an Elvish sword of great antiquity. Beneath the rug a trap door leads down into a dark cellar, which is revealed to be one of several entrances to a vast subterranean land known as the Great Underground Empire. The player soon encounters a colorful host of dangerous enemies, including deadly grues who only prey on their victims in the dark, an axe-wielding troll, a giant cyclops who flees in terror at the mention of Odysseus, a vampire bat that can drop the player anywhere in the mine if encountered, evil spirits guarding the Entrance to Hades, and a nimble-fingered thief armed with a stiletto who makes mapping the maze difficult by removing or scattering any items that the player might drop to leave a trail.
The ultimate goal of Zork I is to collect the Twenty Treasures of Zork and install them in the trophy case. Finding the treasures requires solving a variety of puzzles such as the navigation of two complex mazes and some intricate manipulations at Flood Control Dam #3.[1][2]
Placing all of the treasures into the trophy case scores the player 350 points and grants the rank of "Master Adventurer." An ancient map with further instructions then magically appears in the trophy case. These instructions provide access to a stone barrow. The entrance to the barrow is the end of Zork I and the beginning of Zork II.[3]
There are 28 ways for the player to die.[4][5] It is possible to score all 350 points in 223 moves (and win the game completely in 228 moves)[6] by exploiting a bug.
Feelies
Infocom did not begin their tradition of including feelies, or extra items related to a game, until the Template:Vgy release Deadline. Later re-releases of the game, however, were packaged with:
- The booklet The Great Underground Empire: A History, by "Froboz Mumbar"
- A map roughly corresponding to a portion of the game's area
Although the back of the Zork I "Grey box" depicted a zorkmid coin included with the other feelies, production difficulties led to the coins' omission from the packages. Zorkmid coins were not included as feelies until the release of the Zork Trilogy boxed set.
Releases
The original version of Zork I was published by Personal Software and simply called Zork. It was distributed in clear plastic bags containing only the game disk and a 36-page booklet. Infocom's first "self-published" version of Zork I was in the so-called "Folio" format which included a single piece of paper describing how to run the game. The feelies noted above were only introduced when Zork I was re-released in the "Grey box" format.
Zork I was one of five Infocom games that were re-released in Solid Gold format with in-game hints. Infocom allowed the distribution of the early Fortran version, therefore source code is available. Various Public domain software ports are available in various repositories.[7][8][9][10]
There is also an abridged version, called Mini-Zork I, dated November 24, 1987. Mini-Zork was released free of charge as a promotion.
A German language version was developed, but never released. An unfinished version of this story file, dated January 13, 1988, has made its way into public circulation. The German is evidently non-native, containing many spelling and grammar errors. It is known that Jeff O'Neill worked on this version.
A remastered version of Zork I: The Great Underground Empire (
The game is playable in Call of Duty with the code "ZORK". To do this, Mason (the main character) needs to get up from the chair. PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360 users need to pull L2 and R2 (LT and RT on Xbox 360) rapidly. Windows players need to press the space bar rapidly and Wii players must shake the controls (Wiimote + nunchuck control scheme). After Mason gets up from his chair, he must walk to the left and use the old computer, which is behind the chair. To play Zork, type "zork" into the command prompt. An achievement/trophy is also awarded for putting in the code.
Notes
This section possibly contains original research. (November 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |

The opening text of Zork I is among the most notable descriptions in video games:
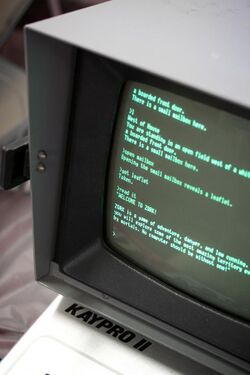
- West of House
- You are standing in an open field west of a white house, with a boarded front door.
- There is a small mailbox here.
This is quite simplistic when compared to Infocom's later games, many of which started with screens full of introductory text.
Several of the game's situations and descriptions have become iconic within the field of interactive fiction, such as the brass lantern and the "Elvish sword of great antiquity".
Zork I also introduced the notable grue, a "sinister, lurking presence" who kills adventurers who go exploring in the dark. Grues appeared (or, at least, were mentioned) in many subsequent Infocom adventures, right up to the 1997 graphic adventure Zork Grand Inquisitor, published by Activision.
Reception
Zork I's sales surprised Infocom by rising, not falling, over time; many dealers sold the game as an essential accessory to those purchasing new computers,[11] including the DEC Rainbow, TI Professional, and others that most people did not see as game machines.[12] It was the best-selling game of 1982, with 32,000 copies sold by the first half of that year;[13][14] almost 100,000 copies in 1983;[15] more than 150,000 copies in 1984, comprising more than 20% of Infocom's sales that year;[11] and a total of 378,987 copies by 1986.[16] InfoWorld reported in April 1984 that Zork I "has returned to the top of the sales charts two years after its release".[12] Based on sales and market-share data, Video listed it fifth on the magazine's list of best selling video games in both February[17] and March 1985,[18] and II Computing listed Zork I fourth on the magazine's overall list of top Apple II software as of October–November 1985, and first on the games list.[19]
BYTE declared in 1981 that "No single advance in the science of Adventure has been as bold and exciting" as Zork. The magazine praised the sophisticated parser and quality of writing, stating, "That the program is entertaining, eloquent, witty, and precisely written is almost beside the point ... Zork can be felt and touched—experienced, if you will—through the care and attention to detail the authors have rendered." It concluded, "Somebody, please, let me know when [the sequel is] done."[20] Jerry Pournelle wrote in the magazine in 1983 that he played the game with his sons, stating that "If you liked Adventure and wanted more after you solved the Colossal Cave, I guarantee you'll love Zork".[21] Jon Mishcon reviewed Zork in The Space Gamer No. 40. Mishcon commented that "Other than the absence of graphics, this game has no weak points I can find. Although [the price] is expensive I believe this is a first rate game and well worth every penny."[22] 80 Micro called Zork "complicated and sophisticated ... a joy to play". It praised the documentation ("Take it from a rank amateur; these instructions are clear and easy to follow"), and wondered if the game could be solved because "the program lets you do pretty much what you want to do, even if the consequences are much less than desirable, it leaves open marvelous opportunities". The magazine concluded by hoping that "we can expect a second part sometime soon".[23] The Addison-Wesley Book of Atari Software 1984 gave the game an overall A+ rating, calling it "THE definitive adventure game".[24]
In 1992, Computer Gaming World added Zork I to its Hall of Fame, waiving the normal criteria "in favor of honoring this venerable classic."[25] In 1996, the magazine listed Zork I at #13 among the top 150 best games of all-time. The editors wrote, "This seminal Infocom text adventure combined challenging puzzles, wonderful descriptive prose, and a touch of humor to create a rich universe that existed not in SVGA graphics, but within your head."[26] On March 12, 2007, The New York Times reported that it was named to a list of the ten most important video games of all time, the so-called game canon.[27] The Library of Congress took up a video game preservation proposal and began with the games from this list, including Zork.[28][29][30]
References
- ↑ Maher, Jimmy (2012-01-18). "Exploring Zork, Part 1". The Digital Antiquarian. http://www.filfre.net/2012/01/exploring-zork-part-1/. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ↑ Maher, Jimmy (2012-01-20). "Exploring Zork, Part 2". The Digital Antiquarian. http://www.filfre.net/2012/01/exploring-zork-part-2/. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ↑ Maher, Jimmy (2012-01-22). "Exploring Zork, Part 3". The Digital Antiquarian. http://www.filfre.net/2012/01/exploring-zork-part-3/. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ↑ "Infocom Scoreboard", The New Zork Times 3 (2): 3, Spring 1984, http://infodoc.plover.net/nzt/NZT3.2.pdf
- ↑ "Hot Gossip". Computer Games: pp. 8. February 1985. https://archive.org/stream/Computer_Games_Vol_3_No_5_1985-02_Carnegie_Publications_US#page/n7/mode/2up. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
- ↑ Haha, Jimmy (2009-02-22). "Zork I Walkthrough" (Text file). http://www.gamefaqs.com/pc/564446-zork-i/faqs/55757. Retrieved 2016-08-04.
- ↑ The DUNGEON (Zork I) source on github.com/devshane/zork
- ↑ dungeon-3.2A.tar.Z (05-Oct-1994) on the Interactive Fiction Archive "Dungeon version 3.2A, 1-Oct-94; contains all the rooms and puzzles of the original MIT Zork. DEC FORTRAN source code by Robert M. Supnik; see dungn32b.zip for a port to DOS."
- ↑ itafroma/zork-mdl on github.com
- ↑ zork-source-code-is-a-master-class-in-game-developer-trolling on kotaku.com
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Maher, Jimmy (2013-10-23). "Masters of the Game". The Digital Antiquarian. http://www.filfre.net/2013/10/23/. Retrieved 9 January 2015.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Mace, Scott (1984-04-02). "Games with windows". InfoWorld: pp. 56. https://books.google.com/books?id=kC4EAAAAMBAJ&lpg=PA65&pg=PA56#v=onepage&q&f=false. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ↑ "Inside the Industry" (PDF). Computer Gaming World: p. 2. September–October 1982. http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1982&pub=2&id=6. Retrieved 2016-03-28.
- ↑ Sipe, Russell (November 1992). "3900 Games Later...". Computer Gaming World: pp. 8. http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1992&pub=2&id=100. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ Maher, Jimmy (2013-03-20). "The Top of its Game". The Digital Antiquarian. http://www.filfre.net/2013/03/the-top-of-its-game/. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ↑ Carless, Simon (2008-09-20). "Great Scott: Infocom's All-Time Sales Numbers Revealed". GameSetWatch. Think Services. Archived from the original on 2008-09-21 -->. http://www.webcitation.org/query?url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.gamesetwatch.com%2F2008%2F09%2Fgreat_scott_infocoms_alltime_s.php&date=2008-09-21. Retrieved 2008-09-23.
- ↑ Ditlea, Steve; Onosco, Tim; Kunkel, Bill (February 1985). "Random Access: Best Sellers/Recreation". Video (Reese Communications) 8 (11): 35. ISSN 0147-8907.
- ↑ Onosco, Tim; Kohl, Louise; Kunkel, Bill; Garr, Doug (March 1985). "Random Access: Best Sellers/Recreation". Video (Reese Communications) 8 (12): 43. ISSN 0147-8907.
- ↑ Ciraolo, Michael (October 1985). "Top Software / A List of Favorites". II Computing: pp. 51. https://archive.org/stream/II_Computing_Vol_1_No_1_Oct_Nov_85_Premiere#page/n51/mode/2up. Retrieved 28 January 2015.
- ↑ Liddil, Bob (February 1981). "Zork, The Great Underground Empire". BYTE 6 (2): pp. 262–264. https://archive.org/stream/byte-magazine-1981-02/1981_02_BYTE_06-02_The_Computer_and_Voice_Synthesis#page/n263/mode/2up. Retrieved 18 October 2013.
- ↑ Pournelle, Jerry (June 1983). "Zenith Z-100, Epson QX-10, Software Licensing, and the Software Piracy Problem". BYTE 8 (6): pp. 411. https://archive.org/stream/byte-magazine-1983-06/1983_06_BYTE_08-06_16-Bit_Designs#page/n411/mode/2up. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- ↑ Mishcon, Jon (June 1981). "Capsule Reviews". The Space Gamer (Steve Jackson Games) (40): 36.
- ↑ Marshall, Debra (August 1981). "Zork". 80 Micro: pp. 32. https://archive.org/stream/80-microcomputing-magazine-1981-08/80Microcomputing_0881#page/n31/mode/2up. Retrieved 17 February 2015.
- ↑ The Addison-Wesley Book of Atari Software. Addison-Wesley. 1984. pp. 30–31. ISBN 0-201-16454-X. https://archive.org/stream/Atari_Software_1984#page/n29/mode/2up.
- ↑ "Computer Gaming World's Hall of Fame". Computer Gaming World: pp. 193. November 1992. http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1992&pub=2&id=100. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ↑ "150 Best Games of All Time". Computer Gaming World: 64–80. November 1996. http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1996&pub=2&id=148. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ↑ Chaplin, Heather (2007-03-12). "Is That Just Some Game? No, It's a Cultural Artifact". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2007/03/12/arts/design/12vide.html. Retrieved 2013-11-01.
- ↑ Ransom-Wiley, James (12 March 2007). "10 most important video games of all time, as judged by 2 designers, 2 academics, and 1 lowly blogger". Engadget (Joystiq). https://www.engadget.com/2007/03/12/10-most-important-video-games-of-all-time-as-judged-by-2-design/. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ↑ Owens, Trevor (2012-09-26). "Yes, The Library of Congress Has Video Games: An Interview with David Gibson". blogs.loc.gov. http://blogs.loc.gov/digitalpreservation/2012/09/yes-the-library-of-congress-has-video-games-an-interview-with-david-gibson/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Yokal, Kathy (October 1983). "Marc Blank - The Programmer Behind Zork". Compute! Gazette: pp. 64–66. https://archive.org/details/1983-10-computegazette. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
External links
- MobyGames is a commercial database website that catalogs information on video games and the people and companies behind them via crowdsourcing. This includes over 300,000 games for hundreds of platforms.[1] Founded in 1999, ownership of the site has changed hands several times. It has been owned by Atari SA since 2022.
Features
Edits and submissions to the site (including screenshots, box art, developer information, game summaries, and more) go through a verification process of fact-checking by volunteer "approvers".[2] This lengthy approval process after submission can range from minutes to days or months.[3] The most commonly used sources are the video game's website, packaging, and credit screens. There is a published standard for game information and copy-editing.[4] A ranking system allows users to earn points for contributing accurate information.[5]
Registered users can rate and review games. Users can create private or public "have" and "want" lists, which can generate a list of games available for trade with other registered users. The site contains an integrated forum. Each listed game can have its own sub-forum.
History

MobyGames was founded on March 1, 1999, by Jim Leonard and Brian Hirt, and joined by David Berk 18 months later, the three of which had been friends since high school.[6][7] Leonard had the idea of sharing information about computer games with a larger audience. The database began with information about games for IBM PC compatibles, relying on the founders' personal collections. Eventually, the site was opened up to allow general users to contribute information.[5] In a 2003 interview, Berk emphasized MobyGames' dedication to taking video games more seriously than broader society and to preserving games for their important cultural influence.[5]
In mid-2010, MobyGames was purchased by GameFly for an undisclosed amount.[8] This was announced to the community post factum , and the site's interface was given an unpopular redesign.[7] A few major contributors left, refusing to do volunteer work for a commercial website.{{Citation needed|date=June 2025} On December 18, 2013, MobyGames was acquired by Jeremiah Freyholtz, owner of Blue Flame Labs (a San Francisco-based game and web development company) and VGBoxArt (a site for fan-made video game box art).[9] Blue Flame Labs reverted MobyGames' interface to its pre-overhaul look and feel,[10] and for the next eight years, the site was run by Freyholtz and Independent Games Festival organizer Simon Carless.[7]
On November 24, 2021, Atari SA announced a potential deal with Blue Flame Labs to purchase MobyGames for $1.5 million.[11] The purchase was completed on 8 March 2022, with Freyholtz remaining as general manager.[12][13][14] Over the next year, the financial boost given by Atari led to a rework of the site being built from scratch with a new backend codebase, as well as updates improving the mobile and desktop user interface.[1] This was accomplished by investing in full-time development of the site instead of its previously part-time development.[15]
In 2024, MobyGames began offering a paid "Pro" membership option for the site to generate additional revenue.[16] Previously, the site had generated income exclusively through banner ads and (from March 2014 onward) a small number of patrons via the Patreon website.[17]
See also
- IGDB – game database used by Twitch for its search and discovery functions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sheehan, Gavin (2023-02-22). "Atari Relaunches The Fully Rebuilt & Optimized MobyGames Website". https://bleedingcool.com/games/atari-relaunches-the-fully-rebuilt-optimized-mobygames-website/.
- ↑ Litchfield, Ted (2021-11-26). "Zombie company Atari to devour MobyGames". https://www.pcgamer.com/zombie-company-atari-to-devour-mobygames/.
- ↑ "MobyGames FAQ: Emails Answered § When will my submission be approved?". Blue Flame Labs. 30 March 2014. http://www.mobygames.com/info/faq7#g1.
- ↑ "The MobyGames Standards and Practices". Blue Flame Labs. 6 January 2016. http://www.mobygames.com/info/standards.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Miller, Stanley A. (2003-04-22). "People's choice awards honor favorite Web sites". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel.
- ↑ "20 Years of MobyGames" (in en). 2019-02-28. https://trixter.oldskool.org/2019/02/28/20-years-of-mobygames/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Plunkett, Luke (2022-03-10). "Atari Buys MobyGames For $1.5 Million". https://kotaku.com/mobygames-retro-credits-database-imdb-atari-freyholtz-b-1848638521.
- ↑ "Report: MobyGames Acquired By GameFly Media". Gamasutra. 2011-02-07. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/game-platforms/report-mobygames-acquired-by-gamefly-media.
- ↑ Corriea, Alexa Ray (December 31, 2013). "MobyGames purchased from GameFly, improvements planned". http://www.polygon.com/2013/12/31/5261414/mobygames-purchased-from-gamefly-improvements-planned.
- ↑ Wawro, Alex (31 December 2013). "Game dev database MobyGames getting some TLC under new owner". Gamasutra. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/business/game-dev-database-mobygames-getting-some-tlc-under-new-owner.
- ↑ "Atari invests in Anstream, may buy MobyGames". November 24, 2021. https://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/2021-11-24-atari-invests-in-anstream-may-buy-mobygames.
- ↑ Rousseau, Jeffrey (2022-03-09). "Atari purchases Moby Games". https://www.gamesindustry.biz/atari-purchases-moby-games.
- ↑ "Atari Completes MobyGames Acquisition, Details Plans for the Site's Continued Support". March 8, 2022. https://www.atari.com/atari-completes-mobygames-acquisition-details-plans-for-the-sites-continued-support/.
- ↑ "Atari has acquired game database MobyGames for $1.5 million" (in en-GB). 2022-03-09. https://www.videogameschronicle.com/news/atari-has-acquired-game-database-mobygames-for-1-5-million/.
- ↑ Stanton, Rich (2022-03-10). "Atari buys videogame database MobyGames for $1.5 million". https://www.pcgamer.com/atari-buys-videogame-database-mobygames-for-dollar15-million/.
- ↑ Harris, John (2024-03-09). "MobyGames Offering “Pro” Membership". https://setsideb.com/mobygames-offering-pro-membership/.
- ↑ "MobyGames on Patreon". http://www.patreon.com/mobygames.
Wikidata has the property:
|
External links
- No URL found. Please specify a URL here or add one to Wikidata.
 |
- Zork I can be played for free in the browser at the Internet Archive
- Infocom-if.org's entry for Zork I
- Zork I Technical Info and Screenshot
- The Infocom Bugs List entry for Zork I

