Submanifold

In mathematics, a submanifold of a manifold is a subset which itself has the structure of a manifold, and for which the inclusion map satisfies certain properties. There are different types of submanifolds depending on exactly which properties are required. Different authors often have different definitions.
Formal definition
In the following we assume all manifolds are differentiable manifolds of class for a fixed , and all morphisms are differentiable of class .
Immersed submanifolds
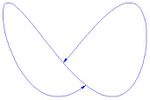
An immersed submanifold of a manifold is the image of an immersion map ; in general this image will not be a submanifold as a subset, and an immersion map need not even be injective (one-to-one) – it can have self-intersections.[1]
More narrowly, one can require that the map be an injection (one-to-one), in which we call it an injective immersion, and define an immersed submanifold to be the image subset together with a topology and differential structure such that is a manifold and the inclusion is a diffeomorphism: this is just the topology on , which in general will not agree with the subset topology: in general the subset is not a submanifold of , in the subset topology.
Given any injective immersion the image of in can be uniquely given the structure of an immersed submanifold so that is a diffeomorphism. It follows that immersed submanifolds are precisely the images of injective immersions.
The submanifold topology on an immersed submanifold need not be the subspace topology inherited from . In general, it will be finer than the subspace topology (i.e. have more open sets).
Immersed submanifolds occur in the theory of Lie groups where Lie subgroups are naturally immersed submanifolds. They also appear in the study of foliations where immersed submanifolds provide the right context to prove the Frobenius theorem.
Embedded submanifolds
An embedded submanifold (also called a regular submanifold), is an immersed submanifold for which the inclusion map is a topological embedding. That is, the submanifold topology on is the same as the subspace topology.
Given any embedding of a manifold in the image naturally has the structure of an embedded submanifold. That is, embedded submanifolds are precisely the images of embeddings.
There is an intrinsic definition of an embedded submanifold which is often useful. Let be an -dimensional manifold, and let be an integer such that . A -dimensional embedded submanifold of is a subset such that for every point there exists a chart containing such that is the intersection of a -dimensional plane with . The pairs form an atlas for the differential structure on .
Alexander's theorem and the Jordan–Schoenflies theorem are good examples of smooth embeddings.
Other variations
There are some other variations of submanifolds used in the literature. A neat submanifold is a manifold whose boundary agrees with the boundary of the entire manifold.[2] Sharpe (1997) defines a type of submanifold which lies somewhere between an embedded submanifold and an immersed submanifold.
Many authors define topological submanifolds also. These are the same as submanifolds with .[3] An embedded topological submanifold is not necessarily regular in the sense of the existence of a local chart at each point extending the embedding. Counterexamples include wild arcs and wild knots.
Properties
Given any immersed submanifold of , the tangent space to a point in can naturally be thought of as a linear subspace of the tangent space to in . This follows from the fact that the inclusion map is an immersion and provides an injection
Suppose S is an immersed submanifold of . If the inclusion map is closed then is actually an embedded submanifold of . Conversely, if is an embedded submanifold which is also a closed subset then the inclusion map is closed. The inclusion map is closed if and only if it is a proper map (i.e. inverse images of compact sets are compact). If is closed then is called a closed embedded submanifold of . Closed embedded submanifolds form the nicest class of submanifolds.
Submanifolds of real coordinate space
Smooth manifolds are sometimes defined as embedded submanifolds of real coordinate space , for some . This point of view is equivalent to the usual, abstract approach, because, by the Whitney embedding theorem, any second-countable smooth (abstract) -manifold can be smoothly embedded in .
Notes
- ↑ Sharpe 1997, p. 26.
- ↑ Kosinski 2007, p. 27.
- ↑ Lang 1999, pp. 25–26. Choquet-Bruhat 1968, p. 11
References
- Choquet-Bruhat, Yvonne (1968). Géométrie différentielle et systèmes extérieurs. Paris: Dunod.
- Kosinski, Antoni Albert (2007). Differential manifolds. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-46244-8.
- Lang, Serge (1999). Fundamentals of Differential Geometry. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. New York: Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-98593-0.
- Lee, John (2003). Introduction to Smooth Manifolds. Graduate Texts in Mathematics 218. New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-95495-3.
- Sharpe, R. W. (1997). Differential Geometry: Cartan's Generalization of Klein's Erlangen Program. New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-94732-9.
- Warner, Frank W. (1983). Foundations of Differentiable Manifolds and Lie Groups. New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-90894-3.
 |
