x̅ and R chart
| [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and R chart | |
|---|---|
| Originally proposed by | Walter A. Shewhart |
| Process observations | |
| Rational subgroup size | 1 < n ≤ 10 |
| Measurement type | Average quality characteristic per unit |
| Quality characteristic type | Variables data |
| Underlying distribution | Normal distribution |
| Performance | |
| Size of shift to detect | ≥ 1.5σ |
| Process variation chart | |
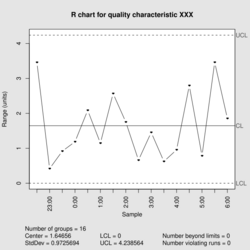 | |
| Center line | [math]\displaystyle{ \bar R = \frac {\sum_{i=1}^m max(x_{ij}) - min(x_{ij})}{m} }[/math] |
| Upper control limit | [math]\displaystyle{ D_4 \bar R }[/math] |
| Lower control limit | [math]\displaystyle{ D_3 \bar R }[/math] |
| Plotted statistic | Ri = max(xj) - min(xj) |
| Process mean chart | |
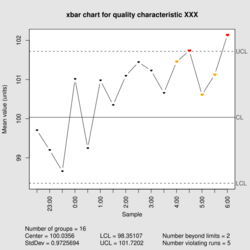 | |
| Center line | [math]\displaystyle{ \bar \bar x = \frac {\sum_{i=1}^m \sum_{j=1}^n x_{ij}}{mn} }[/math] |
| Control limits | [math]\displaystyle{ \bar \bar x \pm A_2 \bar R }[/math] |
| Plotted statistic | [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x_i = \frac {\sum_{j=1}^n x_{j}}{n} }[/math] |
In statistical process control (SPC), the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and R chart is a type of scheme, popularly known as control chart, used to monitor the mean and range of a normally distributed variables simultaneously, when samples are collected at regular intervals from a business or industrial process.[1] It is often used to monitor the variables data but the performance of the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and R chart may suffer when the normality assumption is not valid.
Properties
The "chart" actually consists of a pair of charts: One to monitor the process standard deviation (as approximated by the sample moving range) and another to monitor the process mean, as is done with the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and s and individuals control charts. The [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and R chart plots the mean value for the quality characteristic across all units in the sample, [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x_i }[/math], plus the range of the quality characteristic across all units in the sample as follows:
- R = xmax - xmin.
The normal distribution is the basis for the charts and requires the following assumptions:
- The quality characteristic to be monitored is adequately modeled by a normally distributed random variable
- The parameters μ and σ for the random variable are the same for each unit and each unit is independent of its predecessors or successors
- The inspection procedure is same for each sample and is carried out consistently from sample to sample
The control limits for this chart type are:[2]
- [math]\displaystyle{ D_3 \bar R }[/math] (lower) and [math]\displaystyle{ D_4 \bar R }[/math] (upper) for monitoring the process variability
- [math]\displaystyle{ \bar \bar x \pm A_2 \bar R }[/math] for monitoring the process mean
- where [math]\displaystyle{ \bar \bar x }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \bar R }[/math] are the estimates of the long-term process mean and range established during control-chart setup and A2, D3, and D4 are sample size-specific anti-biasing constants. The anti-biasing constants are typically found in the appendices of textbooks on statistical process control.
Usage of the chart
The chart is advantageous in the following situations:[3]
- The sample size is relatively small (say, n ≤ 10—[math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and s charts are typically used for larger sample sizes)
- The sample size is constant
- Humans must perform the calculations for the chart
As with the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and s and individuals control charts, the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] chart is only valid if the within-sample variability is constant.[4] Thus, the R chart is examined before the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] chart; if the R chart indicates the sample variability is in statistical control, then the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] chart is examined to determine if the sample mean is also in statistical control. If on the other hand, the sample variability is not in statistical control, then the entire process is judged to be not in statistical control regardless of what the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] chart indicates.
Limitations
For monitoring the mean and variance of a normal distribution, the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and s chart chart is usually better than the [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{x} }[/math] and R chart.
See also
- [math]\displaystyle{ \bar x }[/math] and s chart
- Shewhart individuals control chart
- Simultaneous monitoring of mean and variance of Gaussian Processes with estimated parameters (when standards are unknown)[5]
References
- ↑ "Shewhart X-bar and R and S Control Charts". NIST/Sematech Engineering Statistics Handbook]. National Institute of Standards and Technology. http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/pmc/section3/pmc321.htm.
- ↑ Montgomery, Douglas (2005). Introduction to Statistical Quality Control. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons , Inc.. pp. 197. ISBN 978-0-471-65631-9. OCLC 56729567. http://www.eas.asu.edu/~masmlab/montgomery/.
- ↑ Montgomery, Douglas (2005). Introduction to Statistical Quality Control. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons , Inc.. pp. 222. ISBN 978-0-471-65631-9. OCLC 56729567. http://www.eas.asu.edu/~masmlab/montgomery/.
- ↑ Montgomery, Douglas (2005). Introduction to Statistical Quality Control. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons , Inc.. pp. 214. ISBN 978-0-471-65631-9. OCLC 56729567. http://www.eas.asu.edu/~masmlab/montgomery/.
- ↑ McCracken, A. K.; Chakraborti, S.; Mukherjee, A. (2013-10-01). "Control Charts for Simultaneous Monitoring of Unknown Mean and Variance of Normally Distributed Processes". Journal of Quality Technology 45 (4): 360–376. doi:10.1080/00224065.2013.11917944. ISSN 0022-4065.
 |

