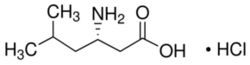
Chemistry:L-β-Homoleucine hydrochloride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S)-3-Amino-5-methylhexanoic acid hydrochloride
| |
| Other names
H-BETA-HOMOLEU-OH HCL;H-BETA-HOLEU-OH HCL;H-LEU-(C*CH2)OH HCL;L-BETA-HOMOLEUCINE HCL;L-BETA-HOMOLEUCINE HYDROCHLORIDE;(S)-3-AMINO-5-METHYLHEXANOIC ACID HYDROCHLORIDE;L-β-homoleucine.HCI;H-β-homo-Leu-OH
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 8073252 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H15NO2· HCl | |
| Molar mass | 181.66 g mol-1 |
| Boiling point | 249.1 °C |
| log P | 0.90 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.00744 mmHg |
| Acidity (pKa) | N/A |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 104.5°C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
L-β-Homoleucine hydrochloride, also known as (3S)-3-Amino-5-methylhexanoic acid hydrochloride belongs to a class of unusual amino acids known as β-Homo amino acids or beta amino acids. The more common α-analogues of these amino acids are present in greater quantities and make up most polypeptides in a cell. β-amino acids however, can also be found in nature and bound to polypeptides, although at a reduced frequency. The hydrochloride is the chloride salt of the amino acid.
Properties
Homolecuine shares many of the same properties as its α-analogue lecuine. Some notable differences include being remarkably stable to metabolism, exhibiting slow microbial degradation, and inherently stable to proteases and peptidases, as well as folding into well-ordered secondary structures consisting of helices, turns, and sheets.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ↑ β-Amino Acids and Homologs, Aldrich ChemFiles 2008, 8.7, 11
- ↑ Wang, Pam Shou-Ping; Craig, Cody J.; Schepartz, Alanna (June 2012). "Relationship between side-chain branching and stoichiometry in β3-peptide bundles". Tetrahedron 68 (23): 4342–4345. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2012.03.079.
- ↑ Zahradníčková, Helena; Jegorov, Alexandr; Trnka, Tomáš; Zelenka, Karel (January 2008). "Thiosugars - Derivatization agents for chiral resolution of homoleucines". Journal of Separation Science 31 (1): 133–136. doi:10.1002/jssc.200700208.
- ↑ Ilisz, István; Berkecz, Robert; Péter, Antal (May 2008). "Application of chiral derivatizing agents in the high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of amino acid enantiomers: A review". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 47 (1): 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2007.12.013.


