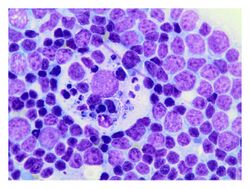
Biology:Tingible body macrophage
A tingible body macrophage (TBMs) is a type of macrophage predominantly found in germinal centers, containing many phagocytized, apoptotic cells in various states of degradation, referred to as tingible bodies (tingible meaning stainable).[1] Tingible body macrophages contain condensed chromatin fragments.[2]
TBMs are licensed (empowered) for phagocytosis by follicular dendritic cells (FDCs).[3] FDCs provide TBMs with Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 protein (Mfge8), which is a phosphatidylserine-binding "eat me" signal for removal of apoptotic germinal center B cells.[3]
It is thought that they may play a role in downregulating the germinal center reaction by the release of prostaglandins and hence a reduced B-cell induction of IL-2.[4]
Macrophages that contain debris from ingested lymphocytes are characteristic of a reactive follicular center in benign reactive lymphadenitis. Other accompanying signs of a benign follicular hyperplasia are well developed germinal centers with dark and light zones, in addition to numerous mitotic figures.
References
- ↑ Horst Ibelgaufts' COPE: Cytokines & Cells Online Pathfinder Encyclopaedia > tingible body macrophages Retrieved on June 27, 2010
- ↑ MacLennan I.C.M (1994). "Germinal Centers". Annual Review of Immunology 12: 117–139. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001001. PMID 8011279.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Follicular dendritic cells: origin, phenotype, and function in health and disease". Trends in Immunology 35 (3): 105–113. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.it.2013.11.001. PMID 24315719.
- ↑ "Tingible body macrophages in regulation of germinal center reactions.". Developmental Immunology 6 (3–4): 285–294. 1998. doi:10.1155/1998/38923. PMID 9814602.
 |