Chemistry:Ammonium hexafluoroaluminate
From HandWiki
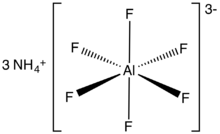
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Ammonium aluminium fluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| (NH4)3[AlF6] | |
| Molar mass | 195.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.78 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 126.1 °C (259.0 °F; 399.2 K) |
| Boiling point | 239.5 °C (463.1 °F; 512.6 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant (Xi) |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H330, H331 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P310, P311, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium hexafluoroaluminate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of (NH4)3[AlF6]. It is a white solid. Upon heating, it converts to aluminium trifluoride, a reaction that releases hydrogen fluoride.[1] It has also been used as a precursor to zeolites.[2]
Preparation
Ammonium hexafluoroaluminate can be obtained by the reaction of ammonium fluoride and aluminium hydroxide.[3]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{6 \ NH_4F + Al(OH)_3 \longrightarrow (NH_4)_3[AlF_6] + 3 \ NH_4OH} }[/math]
References
- ↑ Alonso, C.; Morato, A.; Medina, F.; Guirado, F.; Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P.; Sueiras, J. E.; Terrado, R. et al. (2000). "Preparation and Characterization of Different Phases of Aluminum Trifluoride". Chemistry of Materials 12 (4): 1148–1155. doi:10.1021/cm991195g.
- ↑ Kao, Hsien-Ming; Ting, Chun-Chiang; Chao, Shih-Wei (2005). "Post-synthesis alumination of mesoporous silica SBA-15 with high framework aluminum content using ammonium hexafluoroaluminate". Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 235 (1–2): 200–208. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2005.03.026.
- ↑ hrsg. von Georg Brauer. Unter Mitarb. von M. Baudler (1975) (in de). Handbuch der präparativen anorganischen Chemie / 1.. Stuttgart: Enke. p. 239. ISBN 3-432-02328-6. OCLC 310719485.
 |


