Chemistry:2,3,4,5-Tetramethoxyamphetamine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H19NO4 |
| Molar mass | 253.298 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
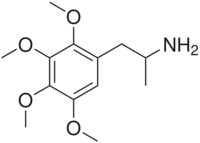
Tetramethoxyamphetamine, or 2,3,4,5-tetramethoxyamphetamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. Tetramethoxyamphetamine was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), the minimum dosage is listed as 50 mg, and the duration unknown. Tetramethoxyamphetamine produces a threshold, mydriasis, and a headache. Limited data exists about its pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ "Structure-activity studies on hallucinogenic amphetamines using molecular connectivity". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 20 (12): 1631–6. December 1977. doi:10.1021/jm00222a019. PMID 592329.
- ↑ "Structure-activity correlations for psychotomimetics. 1. Phenylalkylamines: electronic, volume, and hydrophobicity parameters". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 33 (2): 687–702. February 1990. doi:10.1021/jm00164a036. PMID 2299636.
- ↑ "The frontier orbital phase angles: novel QSAR descriptors for benzene derivatives, applied to phenylalkylamine hallucinogens". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 41 (20): 3845–56. September 1998. doi:10.1021/jm980144c. PMID 9748359.
External links
 |

