Medicine:One and a half syndrome
| One and a half syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | On-and-a-half syndrome |
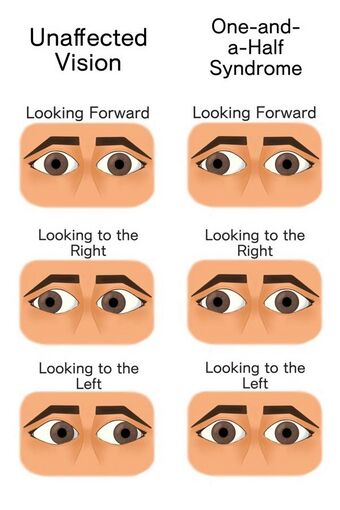 | |
| Diagram of normal eye movement compared to left one-and-a-half syndrome (i.e. left lateral gaze palsy, with left Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (inability to adduct)) | |
| Causes |
|
| Differential diagnosis |
|
The one and a half syndrome is a rare weakness in eye movement affecting both eyes, in which one cannot move laterally at all, and the other can move only in outward direction. More formally, it is characterized by "a conjugate horizontal gaze palsy in one direction and an internuclear ophthalmoplegia in the other".[1][2] Nystagmus is also present when the eye on the opposite side of the lesion is abducted. Convergence is classically spared as cranial nerve III (oculomotor nerve) and its nucleus is spared bilaterally.
Causes
Causes of the one and a half syndrome include pontine haemorrhage, ischemia, tumors, infective mass lesions such as tuberculomas, demyelinating conditions like multiple sclerosis, Arteriovenous malformation, Basilar artery aneurysms and Trauma. [3]
Anatomy
The syndrome usually results from single unilateral lesion of the paramedian pontine reticular formation and the ipsilateral medial longitudinal fasciculus. An alternative anatomical cause is a lesion of the abducens nucleus (VI) on one side (resulting in a failure of abduction of the ipsilateral eye and adduction of the contralateral eye = conjugate gaze palsy towards affected side), with interruption of the ipsilateral medial longitudinal fasciculus after it has crossed the midline from its site of origin in the contralateral abducens (VI) nucleus (resulting in a failure of adduction of the ipsilateral eye).
Treatment
There have been cases of improvement in extra-ocular movement with botulinum toxin injection.[4][5] Cases related to multiple sclerosis sometimes subside with adequate treatment. [3]
See also
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia
References
- ↑ "The one-and-a-half syndrome--a unilateral disorder of the pontine tegmentum: a study of 20 cases and review of the literature.". Neurology 33 (8): 971–80. 1983. doi:10.1212/wnl.33.8.971. PMID 6683820.
- ↑ Essential Neuroscience (1st ed.). Baltimore, Maryland: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins. 2006. pp. 190–191. ISBN 978-0-7817-9121-2. https://archive.org/details/essentialneurosc0000sieg/page/190.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Custo, Scott; Tabone, Emma; Grech, Reuben (2 April 2022). "One-and-a-half syndrome as an initial presentation of multiple sclerosis". British Journal of Hospital Medicine 83 (4): 1–3. doi:10.12968/hmed.2021.0523. PMID 35506717. https://www.magonlinelibrary.com/doi/abs/10.12968/hmed.2021.0523?journalCode=hmed.
- ↑ "Botulinum toxin treatment of "one and a half syndrome"". Br J Ophthalmol 87 (7): 918–9. 2003. doi:10.1136/bjo.87.7.918-a. PMID 12812899.
- ↑ "Botulinum toxin injections". www.aesthetika.co.uk. http://www.aesthetika.co.uk/treatments/botulinum-toxin-injections-commonly-referred-to-as-botox.
 |


