Chemistry:Lead citrate
From HandWiki
Short description: Compound of Lead
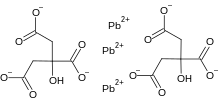
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate; lead(2+); trihydrate
| |
| Other names
Lead citrate trihydrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10O14Pb3 | |
| Molar mass | 999.8 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White odorless powder or crystals |
| Density | 4.63 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 309.6 °C (589.3 °F; 582.8 K) |
| Soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H332, H360, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P301+312, P304+312, P304+340, P308+313, P312, P314, P330, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lead citrate is a compound of lead and citrate that is primarily used as an enhancer for heavy metal staining in electron microscopy.[2] This salt binds to osmium and uranyl acetate and enhances contrast in many cellular structures. Lead citrate is highly reactive with carbon dioxide.
References
 |

