Chemistry:Carnosic acid
From HandWiki
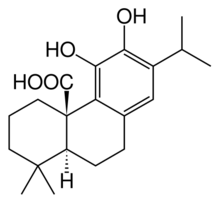
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
11,12-Dihydroxyabieta-8,11,13-trien-20-oic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(4aR,10aS)-5,6-Dihydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-7-(propan-2-yl)-1,3,4,9,10,10a-hexahydrophenanthrene-4a(2H)-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Salvin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H28O4 | |
| Molar mass | 332.440 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 185 to 190 °C (365 to 374 °F; 458 to 463 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Carnosic acid is a natural benzenediol abietane diterpene found in rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) and common sage (Salvia officinalis).[1] Dried leaves of rosemary and sage contain 1.5 to 2.5% carnosic acid.
Carnosic acid and carnosol, a derivative of the acid, are used as antioxidant preservatives in food and nonfood products, where they're labelled as "extracts of rosemary" (E392).[2]
References
- ↑ Schwarz, Karin; Ternes, Waldemar (1992). "Antioxidative constituents of Rosmarinus officinalis and Salvia officinalis". Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung 195 (2): 99–103. doi:10.1007/BF01201766. PMID 1529648.
- ↑ Birtić, Simona; Dussort, Pierre; Pierre, François-Xavier; Bily, Antoine C.; Roller, Marc (2015-07-01). "Carnosic acid" (in en). Phytochemistry 115: 9–19. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.12.026. ISSN 0031-9422. PMID 25639596. Bibcode: 2015PChem.115....9B.
 |

